Types of Sailboats: Essential Guide for Every Sailor
Sailboats have been an essential part of human history, contributing to exploration, trade, and leisure. With a myriad of designs and sizes, these versatile vessels cater to various purposes and preferences. The defining characteristics of sailboats come from their rigging, sails, and hull design.
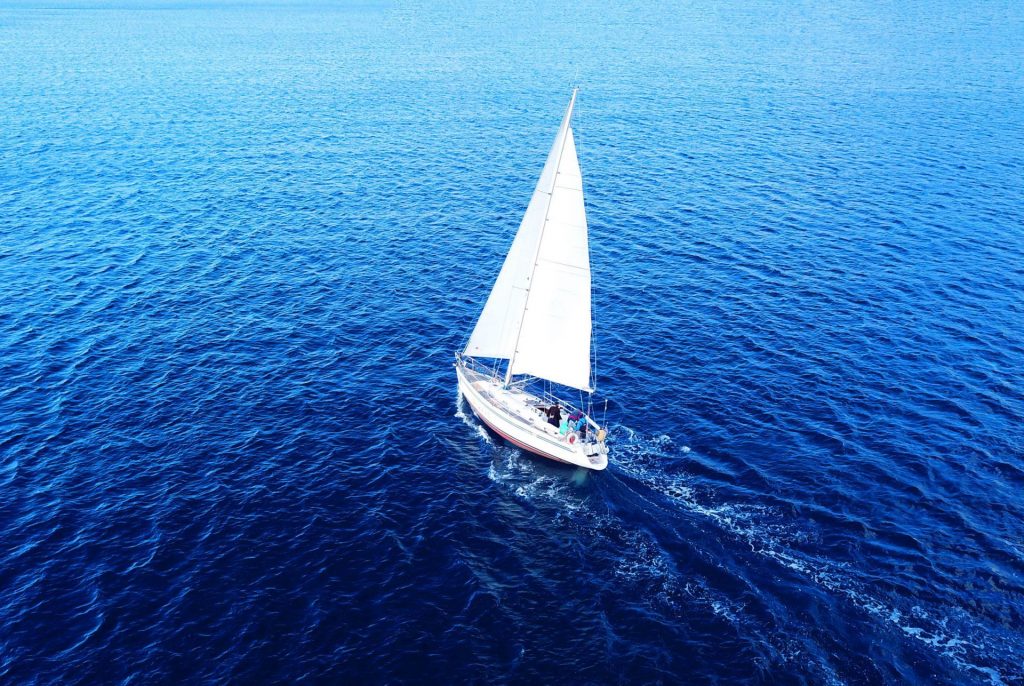

The basics of sailboat design play a significant role in the classification and function of these vessels. Hull shapes, keel types, and construction materials contribute to the speed, stability, and maneuverability of sailboats. Additionally, rigging and sails come in various shapes and sizes, which influence sailing performance and handling.

Key Takeaways
- Sailboats are classified by hull design, rigging, and sails that serve specific purposes.
- Designs and materials have a direct impact on the performance and handling of sailboats.
- A wide range of sailboat types exists, which cater to different needs and preferences.
Basics of Sailboat Design
Sailboats come in various shapes and sizes, designed for different purposes and sailing conditions. One can classify sailboats based on hull types, keel types, and mast configurations. This section will briefly discuss these basic components of sailboat design.
There are mainly two types of hulls: monohull and multihull.
- Monohull : This is the traditional and most common type of sailboat hull. It consists of a single hull, providing stability through the use of a keel or centerboard. Monohulls come in various shapes and sizes, suitable for various sailing conditions.
- Catamaran : Catamarans have two parallel hulls of equal size, offering increased stability and speed compared to monohulls. They are commonly used for cruising and racing.
- Trimaran : Trimarans have three hulls, with a larger central hull and two smaller outrigger hulls. This design offers even more stability and speed than catamarans.
The keel is an essential component in sailboat design, helping with stability and performance. There are various keel types, including:
- Full keel : This traditional design features a long and wide keel that extends along the boat's bottom. It offers good tracking and stability but sacrifices speed and maneuverability.
- Fin keel : Fin keels are shorter and deeper than full keels, providing a better combination of stability and maneuverability. These are common in modern monohull sailboats.
- Bulb keel : A bulb keel features a fin keel with a heavy bulb at the bottom, which concentrates the boat's weight, increasing stability and performance in rough conditions.
- Swing keel or centerboard : Swing keels and centerboards can be raised or lowered, allowing the boat to adapt to different water depths and sailing conditions. They are common in smaller boats and racing sailboats.
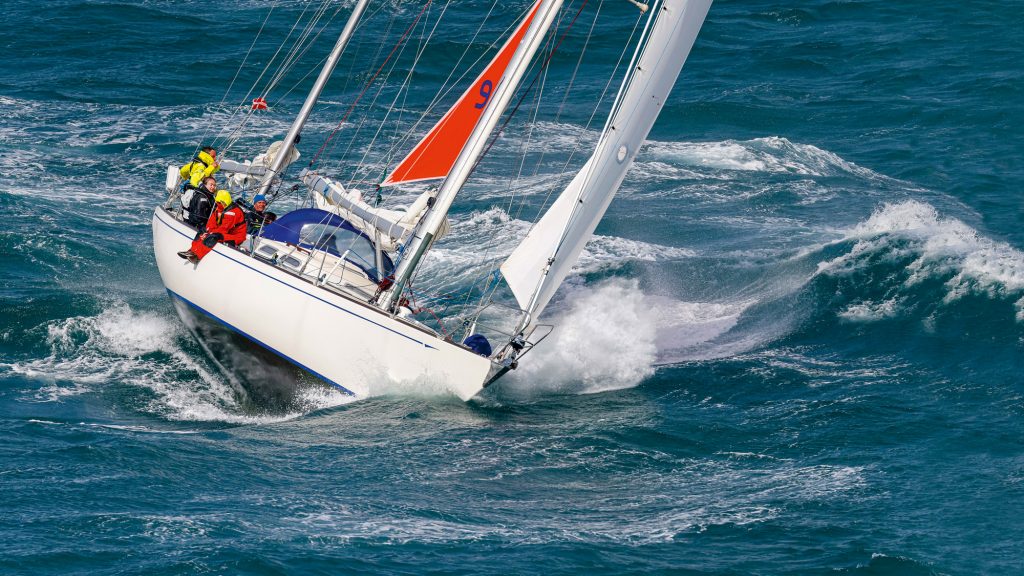

Mast Configuration
The mast configuration affects the sail plan and overall performance of a sailboat. Some common mast configurations include:
- Sloop : This is the most popular mast configuration and features a single mast with a mainsail and a headsail. The simple design makes it easy to handle and suitable for various sailing conditions.
- Cutter : Similar to the sloop, the cutter also has a single mast but carries two headsails, providing more sail area and better performance in heavy weather.
- Ketch : A ketch configuration has two masts: a taller main mast and a shorter mizzen mast. This design offers more flexibility in sail combinations and better balance in different sailing conditions.
- Yawl : Similar to a ketch, a yawl also features two masts but the mizzen is located further aft and is smaller. This design provides better balance and control, particularly in downwind sailing scenarios.
In conclusion, the basics of sailboat design involve selecting the appropriate hull type, keel type, and mast configuration for the desired sailing performance and conditions. Understanding these concepts can help sailors make informed decisions when choosing a sailboat or planning their sailing adventures.
Rigging and Sails
When it comes to sailboats, the rigging and sails play a crucial role in the boat's overall performance and capabilities. This section will briefly cover popular rig types and sail types seen on different sailboats.
There are several types of rigs commonly found on sailboats:
- Sloop : Sloops are the most common type of rig found on modern sailboats. They have a single mast with a mainsail and a single headsail, typically a genoa or jib.
- Ketch : Ketches have two masts, with the main mast taller than the mizzen mast situated aft. They carry a mainsail on the main mast and a mizzen sail on the mizzen mast. Ketches benefit from easier handling and reduced sail area under strong winds.
- Yawl : Similar to ketches, yawls have two masts, but the mizzen mast is smaller and sits further aft, behind the rudder post. Yawls are often chosen for their graceful appearance and improved balance.
- Schooner : Schooners have two or more masts, with the aft mast(s) typically taller than the forward mast(s). Schooners can handle more sails, offering increased sail area for better performance, especially downwind.
- Catboat : Catboats are single-masted sailboats with a single, large mainsail and no headsails. They have a wide beam, which provides stability and ample space for passengers.
- Cutter : Cutters are similar to sloops but carry two headsails, usually a jib and staysail. Cutters may have multiple headsails for increased versatility in various wind conditions.
In addition to the types of rigs, there are also several types of sails used on sailboats, including:
- Mainsail : The primary sail attached to the back of the main mast. It is typically raised on a track or luff groove and managed by a combination of halyard, sheet, and boom vang.
- Genoa : A large triangular sail that overlaps the mainsail, typically used in light winds to provide additional surface area for better performance.
- Jib : A smaller, non-overlapping triangular sail attached to the forestay. Jibs are easier to manage than genoas and are used in a variety of wind conditions.
- Spinnaker : A large, lightweight sail used primarily for downwind sailing . Spinnakers are often brightly colored and shaped like a parachute to catch wind efficiently.
- Staysail : A smaller sail typically used in cutter rigs, positioned between the main mast and the forestay. Staysails provide additional sail area and versatility in varied wind conditions.
Understanding the relationship between sail and rigging can help sailors optimize the performance of their sailboats. With various options for rig types and sail types, each sailboat can be configured to meet the unique needs of its skipper and crew.
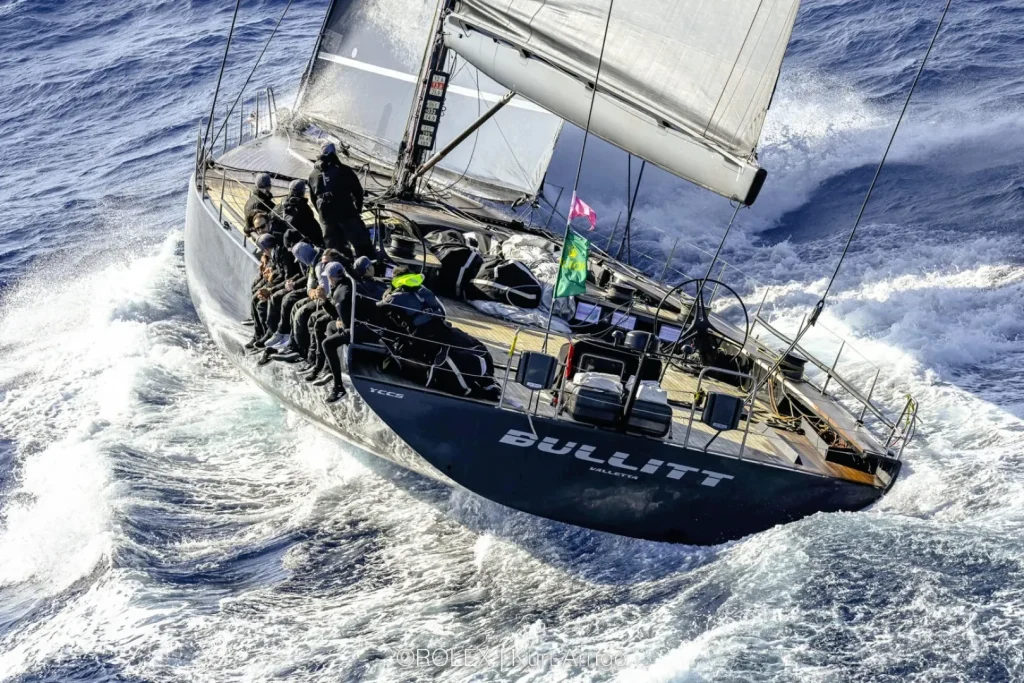

Classes and Types of Sailboats
Monohulls are the most common type of sailboats, consisting of a single hull that provides stability and balance. They come in various sizes and designs, depending on their intended use. Some popular monohull sailboats include the Optimist , Finn, and Sunfish, which are frequently used for racing and recreational sailing. Monohulls tend to have a deeper draft, requiring more water depth than their multi-hull counterparts.
Multihulls, also known as multi-hull sailboats, are a more modern innovation in sailing. They feature two or more hulls connected by a frame or bridgedeck. This design offers increased stability and speed over monohulls. Some common types of multihulls are catamarans (with two hulls) and trimarans (with three hulls). Due to their wider beam and shallower draft, multihulls are particularly suitable for cruising in shallow waters and provide more living space on board.
One-Design Sailboats
One-Design sailboats are a specific class of racing sailboats in which all boats are built to the same design specifications, ensuring that the competition focuses on the skill of the sailor rather than the design of the boat. These boats must adhere to strict rules and standards, with minimal variations allowed in terms of hull shape, sail area, and rigging. Some popular one-design sailboats include the Enterprise and the aforementioned Optimist and Finn sailboats.
Dinghies and Skiffs
Dinghies and skiffs are small, lightweight sailboats that are often used for sailing classes, short-distance racing, or as tenders to larger boats. Dinghies usually have a single mast with a mainsail and sometimes a small jib. Some popular types of sailing dinghies include the Optimist, which is specifically designed for children, and the versatile Sunfish sailboat. Skiffs, on the other hand, are high-performance sailboats primarily used for racing. They have a larger sail area relative to their size and typically include features such as trapezes and planing hulls, which allow for faster speeds and greater maneuverability.
In conclusion, there are various classes and types of sailboats, each with its own unique features and characteristics. From the simplicity of monohulls to the stability and speed of multihulls, and from the fair competition of one-design sailboats to the excitement of dinghies and skiffs, there is a sailboat to satisfy every sailor's preferences.
Sailboat Size and Use
When exploring the world of sailboats, it's important to understand their different sizes and purposes. Sailboats can be categorized into three main types, each with unique characteristics and uses: Day Sailers , Racing Sailboats, and Cruising Sailboats .
Day Sailers
Day Sailers are small sailboats typically ranging from 10 to 24 feet in length. These boats are perfect for short sailing trips and are easy to maneuver for beginners. They have limited accommodations on board, providing just enough seats for a small group of people. Some popular day sailer models include the Laser, Sunfish, and Flying Scot. Lightweight and agile, Day Sailers are often used for:
- Recreation: casual sailing or exploring nearby waters with family and friends
- Training: beginner sailing lessons or practicing sailing techniques
- Competition: local club races or interclub regattas
Racing Sailboats
Racing Sailboats are designed to provide maximum speed, maneuverability, and efficiency on the water. Sizes may vary greatly, from small dinghies to large yachts. Key features of racing sailboats include a sleek hull shape, high-performance sails, and minimalistic interiors to reduce weight.
Career racers and sailing enthusiasts alike participate in various types of racing events , such as:
- One-design racing: all boats have identical specifications, emphasizing crew skill
- Handicap racing: boats of different sizes and designs compete with time adjustments
- Offshore racing: long-distance racing from one point to another, often around islands or across oceans
Cruising Sailboats
Cruising Sailboats are designed for longer journeys and extended stays on the water. They typically range from 25 to 70 feet in length and provide comfortable accommodations such as sleeping cabins, a galley, and storage spaces for supplies and equipment. Sailing cruisers prioritize stability, comfort, and durability for their voyage.
Here are some common types of cruising sailboats:
- Cruiser-racers: These boats combine the speed of a racing sailboat with the comfort and amenities of a cruising sailboat. They are ideal for families or sailors who enjoy participating in racing events while still having the option for leisurely cruises.
- Bluewater cruisers: Designed for handling the world's most demanding ocean conditions, bluewater cruisers are built with a focus on sturdy, self-reliant sailboats that can withstand long-distance voyages and challenging weather conditions.
- Multihulls: Catamarans and trimarans are gaining popularity in the cruising world for their typically more spacious interiors and level sailing characteristics. With two or three hulls, multihulls offer high levels of stability and speed for a comfortable cruising experience.
Understanding the differences between various sailboat types will help potential sailors select the perfect vessel for their sailing goals, skills, and preferences. Day Sailers, Racing Sailboats, and Cruising Sailboats each have their unique features, catering to distinct uses and sailing experiences.
Advanced Sailboat Features
Sailboats have evolved over time, and many advanced features have been developed to enhance performance and safety. In this section, we will discuss some of the key advanced features in modern sailboats, focusing on performance enhancements and safety/navigation.
Performance Enhancements
One critical component that impacts a sailboat's performance is the type of keel it has, which affects stability, resistance, and maneuverability . There are several kinds of keels such as fin keel , wing keel , and bulb keel . Fin keels offer low drag and high efficiency, making them suitable for racing sailboats. On the other hand, wing keels provide better stability at low speeds, while bulb keels provide a lower center of gravity to enhance overall stability and comfort during long voyages.
Another feature that contributes to a sailboat's performance is its sails and rigging. The jib is a triangular sail at the front of the boat, which helps improve its upwind performance. More advanced sailboats use a combination of shrouds , which are the supporting cables running along the sides of the boat, and stays , the cables that help hold the mast in place, to create a stable and efficient rigging system.
A sailboat's performance can also be influenced by the presence of a centerboard or daggerboard , which can be adjusted to optimize stability, maneuverability, and speed. When racing or navigating in shallow waters, retractable centerboards and daggerboards are particularly useful as they provide better performance and versatility.
Safety and Navigation
Safety and navigation onboard a sailboat relies on a combination of advanced gear and equipment. A modern sailboat is usually equipped with:
- GPS and chartplotters to assist with navigation and planning routes
- VHF radios for communication with other vessels and authorities
- Radar to detect obstacles, weather systems, and other vessels
- AIS (Automatic Identification System) which helps monitor nearby vessel traffic
The design of a sailboat's hull, rigging, sails, and hardware also contribute to its safety. The boom , the horizontal pole that extends the sail, should be properly secured and designed to avoid accidents while sailing. The keel , whether it's a fin, wing, or bulb keel, plays a vital role in the overall stability and safety of the sailboat. The choice of keel should be based on the intended use of the sailboat and the prevailing sailing conditions.
In summary, advanced sailboat features significantly improve the performance, safety, and navigation capabilities of modern sailboats. Innovations in keel design, rigging systems, and onboard navigational equipment have undoubtedly contributed to the overall enjoyment and safety of sailing.
Sailboat Ownership
Buying Considerations
When considering buying a sailboat , it is important to understand the different types of sailboats available and the purpose each serves. Sailboats can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Racing sailboats: Designed for speed and performance, with minimalistic interiors and advanced sail systems.
- Cruising sailboats: Built for comfort and longer trips, featuring more spacious interiors and amenities.
- Daysailers: Smaller, easy-to-handle boats that are often used for short trips and recreational sailing.
Prospective boat owners should consider factors such as boat size, type, budget, and intended use (solo vs. family sailing, charter operations, etc.). It's also essential to evaluate the availability of necessary gear and the level of experience required to handle the chosen sailboat.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Sailboat ownership involves maintenance and upkeep to ensure the boat remains functional, safe, and holds its value. Some common maintenance tasks include:
- Hull cleaning and inspection: Regularly inspect the hull for damages and clean off any growth to maintain performance and fuel efficiency.
- Antifouling paint: Apply antifouling paint to prevent marine organisms from attaching to the hull, which can negatively impact the boat's performance.
- Engine maintenance: Check and replace engine oil, inspect cooling and fuel systems, and clean or replace air filters.
In addition to regular maintenance, sailboat owners should also be prepared to replace or repair critical systems and components, such as:
- Sails: Monitor the condition of your sails and replace them as needed to maintain performance and safety.
- Rigging: Regularly inspect and maintain the standing and running rigging, and replace worn or compromised parts.
- Electronics and instruments: Ensure navigation systems, radios, and other electronic equipment are functioning properly.
Taking proper care of a sailboat can be time-consuming, and some owners may choose to charter their boats when not in use as a way to offset ownership costs. Others may opt for hiring professionals to manage routine maintenance, particularly when sailing solo or with limited sailing experience.
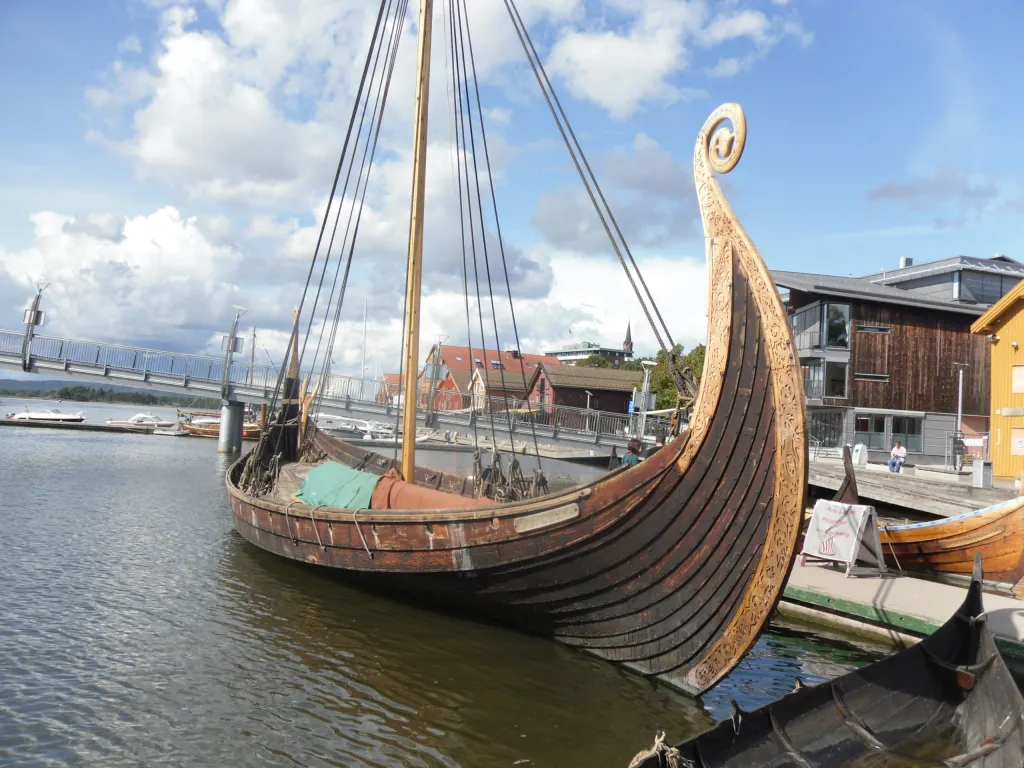

Historical and Special Sailboats
Tall ships and gaffers.
Tall Ships are large, traditionally rigged sailing vessels with multiple masts, typically square-rigged on at least one of their masts. Some examples of these ships include the clipper, brig, and square-rigged vessels. The clipper is a fast sailing ship known for its sleek hull and large sail area, while the brig features two square-rigged masts. Square-rigged ships were known for their impressive sail area and could cover large distances quickly.
Gaffers are a subset of historical sailing vessels with a gaff mainsail as their primary sail type. This gaff-rig is characterized by a spar (pole) that extends the top edge of the mainsail, giving it a quadrilateral shape to optimize wind coverage. Gaff mainsails were commonly used in England and influenced the development of other sailing vessels.
Classic and Antique Sailboats
Classic and antique sailboats refer to older, traditionally designed sailing vessels that have been preserved or restored. They often feature wooden construction and showcase a variety of rigging types, including gaff rigs and square rigs. These historical sailboats have unique designs, materials, and techniques that have since evolved or become rare.
Here are some examples of antique and classic sailboats:
- Sloop : A single-masted sailboat with a Bermuda rig and foresail
- Cutter : A single-masted vessel with a similar rig to the sloop, but with additional headsails for increased maneuverability
- Ketch : A two-masted sailboat with a smaller mizzen mast aft of the main mast
In summary, historical and special sailboats encompass a wide range of vessel types, from large, multi-masted tall ships to smaller, single-masted gaffers and classic sailboats. These vessels reflect the rich maritime history and the evolution of sailing techniques and designs over time.
Sailboat Culture and Lifestyle
Sailboat culture and lifestyle encompass a variety of aspects including racing events, leisurely cruising, and exploring new destinations. The main types of sailboats include racing yachts, cruising sailboats, and motorsailers, each offering a unique experience for sailors.
Regattas and Racing Circuits
A popular aspect of sailboat culture involves participating in regattas and racing circuits . These events create a competitive atmosphere and develop camaraderie among sailors. Racing sailboats are specifically designed for speed and agility , and sailors often team up to compete in prestigious races such as the Rolex Sydney Hobart Yacht Race or the America's Cup. Yacht clubs play an essential role in cultivating this competitive sailing environment.
Sailboat Charter and Tourism
Another facet of sailing culture is the sailboat charter and tourism industry, which allows people to experience the cruising lifestyle without owning a sailboat. Charters are offered for various types of sailboats, from family-sized cruising vessels to luxurious superyachts . Yacht sailing provides tourists with a unique travel experience, as they can explore diverse destinations, immerse themselves in local cultures, or simply relax on the open water.
Cruising sailboats are designed to provide comfortable living spaces and amenities, making them perfect for longer journeys or exploring remote destinations. Motorsailers, on the other hand, are equipped with both sails and engines, offering versatility and convenience for sailors.
Some popular sailing destinations include the Caribbean, Mediterranean Sea, and the South Pacific. These regions offer beautiful scenery, rich cultural experiences, and ideal sailing conditions.
The sailboat culture and lifestyle attract individuals who enjoy adventure, exploration, and camaraderie. From competitive racing events to leisurely cruising vacations, sailing offers diverse experiences that cater to a wide range of interests.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the distinguishing features of different sailboat classes?
There are various sailboat classes, each with its own distinguishing features. Monohulls, for example, are the most common type of sailboat and have a single hull. Multihulls, such as catamarans and trimarans, have two or three hulls, respectively. These differences in hull design often affect the boat's stability, speed, and maneuverability.
Which sailboat types are best for novice sailors?
Novice sailors often benefit from starting with smaller, more manageable boats. Sailing dinghies and daysailers are popular choices due to their simple rigging and ease of handling. These boats typically have a single mast and a limited number of sails, making them ideal for beginners to learn sailing basics.
What are common types of small sailboats ideal for day sailing?
For day sailing, small sailboats such as sailing dinghies, day sailers, and pocket cruisers are ideal options. These boats usually range between 12 and 25 feet in length and offer simplicity, ease of handling, and portability. Examples of common day sailing boats include the Sunfish, Laser, and O'Day Mariner.
How do the purposes of various sailboat types vary?
Sailboats serve different purposes based on their design, size, and features. Daysailers and dinghies are ideal for short trips, sailing lessons, and casual outings. Racing sailboats, with their lighter weight and streamlined design, are built for speed and competition. Cruising sailboats, on the other hand, are designed for longer voyages and often include living quarters and additional amenities for comfortable onboard living.
What is considered the most popular class of sailboat for recreational use?
The most popular class of sailboat for recreational use often varies depending on individual preferences and local conditions. However, monohulls are commonly preferred due to their widespread availability, versatility, and affordability. Within the monohull class, boats like the Sunfish, Laser, and Catalina 22 are popular choices for their ease of use and adaptability to various sailing conditions.
Could you describe a sailing dinghy designed for two people?
A two-person sailing dinghy typically has a simple rig with a single mast and one or more sails, making it easy to handle for both experienced and novice sailors. The RS Venture , for example, is a popular choice for two-person sailing. It features a spacious cockpit, durable construction, and simplicity in its rigging and control systems. These characteristics make it an excellent option for recreational sailing, training, and even racing.
Related Articles

Fishing Boats for Sale: Expert Guide to Top Choices

Hanover Yachts, All Models, Spec, Pricing: The 2024 Ultimate Buying Guide

Top 5 Places to Boat to in Sarasota: Salty Adventures for the Restless Soul

Jon Boat: Essentials, Maintenance, and Tips for Every Boat Owner

Boat Captain Essentials: Mastering Skills for Successful Voyages

Is Your Boat Ready for 2024's Extreme Hurricane Season? Solidify Your Plan and Meet Insurer Expectations

Fort Lauderdale Boat Show 2024: Comprehensive Guide and Highlights

Tom Brady Yacht: Exploring the Luxurious Vessel of a Football Legend

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Sailboat Types: Full-Guide
For generations, sailing has been a mode of essential transportation, a rewarding hobby, an active and competitive sport, and a lifestyle. Sailing appeals to all, and there are dozens and dozens of types of sailboats.
Small sailboats are perfect for kids to sail on, and massive sailboats are used to cross oceans in style. In between, there are daysailers, racers, and cruisers.
Table of Contents
- What Does a Sailboat Look Like?
Small Sailboats
Cruising boats, cruising catamarans, cruising trimarans, full keel boats, fin keel boats, centerboard keel.
- Hydrofoil Sailboats
A Purpose for Every Type of Sailboat
Faqs (frequently asked questions).

What Are Sailboat Types?
Sailboats are boats that are propelled by the wind. Sailboats use wind power instead of a motor or oars to move the boat. It should be noted, though, that nearly all modern sailboats have a motor as well. It comes in handy when docking in tight marinas and if the wind dies!
A sailboat has one, two, or three hulls. It has at least one mast, or tall vertical spar, that holds up one or more sails. The sails harness the power of the wind to move the boat forward.
To get started, here are some sailing boat types and terms to give you an idea of the sorts of boats that are out there.
- Dinghies — a small open boat, usually for only one or two people
- Daysailors — boats designed to go out for a day trip
- Cruising Sailboats — boats designed to travel long distances that have accommodations for their crew to live aboard a long term
- Sloop — the most common type of sailboat, with one mast and two sails (a jib and a mainsail)
- Ketch, yawl, or schooner — types of sailboats with two or more masts
- Monohull — a boat with only one hull
- Catamaran — a boat with two equal-sized hulls in the water that are connected together by a bridge deck
- Trimaran — a boat with three hulls in the water, the center of which is much larger than the outer two
What Does a Sailboat Look Like?
There are many different types of sailboats, so they look a little different from each other. The basics, however, are the same.
Each sailboat has at least one hull that sits in the water. Part of the hull is visible above the waterline. Part of the sailboat hull sits below the waterline.
The part beneath the waterline might be relatively small, or it can be quite large. The rudder, the mechanism used to steer the boat, is also underwater.
The cockpit is where the helmsperson sits and steers the boat. On small boats, the cockpit takes up the entire boat. Cruising boats have interior accommodations as well as a safe cockpit.
Sailboats have at least one mast and at least one mainsail. As you get to know the different types of sailboats, you’ll see many different hull and sail configurations.

Different Types of Sail Boats
Sailboats come in all types of sailboat shapes and sailboat sizes . Sailboats can be classified by their hull shape, size, or sail plan. The sail plan is how many sails they carry on how many masts.
Hull shapes include monohulls, catamarans, trimarans, and sailing hydrofoils. A monohull has just one hull, a catamaran has two hulls, a trimaran has three hulls, and a hydrofoil lifts out of the water.
Sizes range from eight-foot sailboats to megayachts that are hundreds of feet long. Some sailboats are so small they are only suitable for one child who wants to go skimming across the lake. The largest pure sailing yacht in the world is the Black Pearl at 350 feet long (106.7 meters) long. Visit our Yacht vs Sailboat guide for a more definitive difference between the two and their sizes.
Sailboats also have different sail configurations or sail plans. For example, a sailboat with just one big sail on a forward-mounted mast is called a catboat. A boat with dozens of different sails on three masts is called a three-mast schooner.
Small sailboats are extremely popular and offer a lot of fun to the young and old. Most of the time, these boats are just used for daytime use in pleasant weather conditions. Kids often learn to sail in small monohull sailboats. Families might go for a picnic in a Hobie catamaran.
Yacht club members might race their 16-foot daysailors, while adventurous souls might take their 19-ft weekender and anchor in a calm cove for the weekend.

What is a Small Sailboat Called?
Small sailboats have different names, depending on the type of sailboat and the number of sail boat hulls. For example, the boat might be a monohull dinghy, small catboat, small catamaran, or daysailor.
Additionally, like every car on the road, every boat on the water is identified by its make and model. In small boats that are commonly raced, a certain make and model may set up a class of racing boats. Class racing means that all of the boats are identical, so the race is based solely on the skills of the skippers.
Sailing Dinghies
Kids and adults often learn to sail on sailing dinghies. Sailing dinghies can be as small as eight feet long. This small size makes it easy for kids to handle.
Some common sailing dinghies are Optis, Lasers, and Sunfish.
This size sailboat is also functional. They can be used to ferry sailors from their larger anchored boats to shore. The small size also helps sailors easily store their dinghy on larger boats. The word dinghy is often used to refer to any small boat used as a tender for a larger vessel, even if the tender is a motorboat.
Cat Rig Boats
A cat rig boat, or cat boat, is a type of sailboat that usually just has one large mainsail and a forward-mounted mast. Many smaller dinghies and training boats are catboats. A catboat has a free-standing mast with no standing rigging.
Small Catamarans
A catamaran is a boat with two hulls. The Hobie brand is synonymous with small catamarans, which are popular with families looking for a fun hobby. Hobie Cats are seen on the sand at beach resorts all over the world—they’re safe, fun, and fast.
Catamarans are faster than monohulls, and these boats are fun to race. Small catamarans are often used by families that live on the waterfront. Their lightweight makes them easy to drag to the waterfront and launch.
Small catamarans are also popular on beaches. Many beach resorts offer Hobie cats for rent. Small catamarans are between 12-20 feet in length. The hulls are joined only with spars and netting, so these fast and light open boats are not set up to carry a lot of people or supplies.
Daysailors are the ultimate fun boat. As the name implies, this type of sailing boat is used for day sailing. These boats are usually between 12 to 20 feet long. Some use these smaller boats for racing or overnight camping, but most sailors use daysailors for a leisurely sail.
Small Sailboats with Cabins
While most small sailboats just have a large open cockpit, several small yacht types have cabins. These cabins offer a chance for sailors to use a porta-potty or get out of the sun. Some small sailboats even have sleeping accommodations for overnight stays.
An excellent example of this is the Cape Dory Typhoon Weekender. This small sailboat is known as “America’s Littlest Yacht.” Down below, there are two small bunks for sleeping and enough space to have a small stove and a porta-potty. Most owners don’t stay aboard long-term, but the cabin is a useful place to stow items while sailing or to hide during a rainstorm.
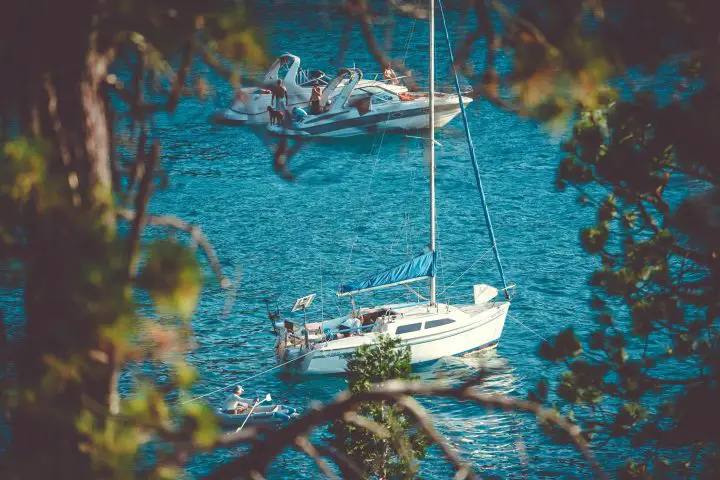

Cruising boats are boats that are capable of traveling long distances. Cruising boats have sleeping accommodations, cooking facilities, and bathroom facilities. These boats are like RVs for the waterway.
Cruising boats offer sailors the chance to live on their boats while sailing. Like RVs, cruising sailboats travel to different ports of call. Cruising sailboats are one of the more popular types of sailing boat. They offer adventurous sailors the chance to enjoy sailing as a sport while seeing new things.
Cruising boats are usually 30 to 50 feet long. Most cruising couples prefer a boat that is around 40 feet long since this provides enough space to live comfortably and enough storage space for all of their gear.
Monohulls are very popular cruising boats. These boats offer good storage, are safe, and are easy for a couple to handle together. Monohulls have different types of sail configurations.
Cruising Bermuda Rigged Sloops
Most monohulls are Bermuda rig sloops. This sail plan features one mast with a mainsail and a headsail. Bermuda rig sloops are easy to single-hand and very versatile. How many sails does a sloop have? A Bermuda sloop flies two sails at a time, which are the mainsail and a headsail.
However, the boat might have other sails onboard. For example, the captain might take down the jib in light winds and use a bigger genoa to capture more wind power. During a downwind sail with light winds, the captain might rig a large spinnaker, which looks like a huge kite, to keep sailing even in little wind.
Even within the sloop category, there are many variations in the design. A masthead sloop is one whose forestay (headsail) goes all the way to the top of the mast. In contrast, a fractional sloop’s forestay connects at some point lower. So a 3/4 fractional rig has a headsail that only goes up three-quarters of the way to the top.
Riggers and boat designers have a lot of tools in their toolbox from which they can make a boat faster or more user-friendly. The type of rigging and sail plan a boat is equipped with offers it performance improvements as well as functionality.
Cruising Cutter
A cutter is a sailboat with one mast, one mainsail, and two sails forward of the mast. The sail at the front of the boat is the jib, genoa, or yankee depending on its size and cut. The next sail in, the inner headsail, is called the staysail. Island Packets are popular boats with this sail plan.
Cutters are popular choices as cruising and bluewater cruiser boats because the staysail provides the skipper with many different sail options. They could fly all three sails fully, or they could fly a small partial mainsail and just the staysail for heavy winds.
Cruising Ketch With Mizzen Sail
Some cruising monohulls are ketches. A ketch can be easily identified by its two masts. The forward mast is the main mast with a mainsail. The aft mizzen mast is shorter and has a mizzen sail. This sail plan can make it easier to carry a big sail area and configure the sails for various sailing conditions.
A boat with more than one mast is called a split rig because the rig is split between two shorter masts instead of all mounted on one tall one. The advantage of a split rig is that there are more sails, each of which is smaller. That makes them easier to handle, and important consideration when you are sailing alone or with only one other person.
Cruising Yawl
A yawl is similar to a ketch and has two masts. However, the mizzen mast on a yawl is aft of the rudder post, whereas it is forward of the rudder post on a ketch. This mizzen mast location is even further back than a ketch’s. Yawls are one of the less popular types of sailboats. However, like the ketch, they offer diverse sail options and can keep sailing in many different types of weather.
On both ketches and yawls, the mizzen mast is shorter than the main mast. If the two masts are of equal height, or the forward mast is shorter, then you are looking at a schooner.

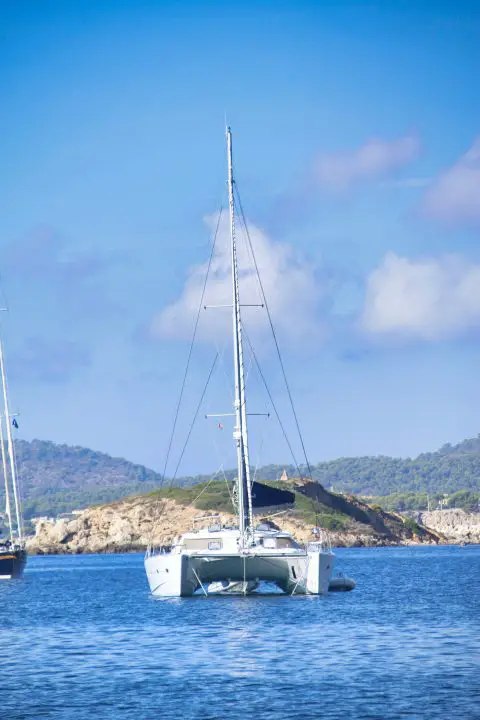
Cruising catamarans are one of the most popular classes of sailboats right now. This type of sailing boat has two hulls and offers sailors speed, space, and comfort. A cruising catamaran is usually between 40 and 60 feet long and 20 to 30 feet wide. The additional width offers cruise sailors huge amounts of space.
Cruising catamarans have excellent storage space and ample living accommodations if you intend to living on a boat . These boats are popular with couples and families and are often used to sail around the world on circumnavigations.
Cruising catamarans are usually fractional sloop rigs. They have one mast, a large mainsail, and a jib or genoa. In general, these boats are designed to be easy to sail and minimize complications.

Trimarans are a type of sailboat with three hulls. Trimarans are known to be fast and are popular with racing sailors. However, they are also gaining popularity as cruising boats. These boats usually have fewer accommodations than cruising monohulls and catamarans. However, more modern trimarans like the Neel Trimaran have luxurious living spaces.
Types of Keel
Another way to classify the different types of sailing boats is by looking at the boat’s keel type. You can easily get an idea of different keel designs by walking around a boatyard. When a sailboat is in the water, it is hard to tell the shape of its keel.
The keel is the bottom part of the hull and is underwater. The keel is structurally essential. The keel’s weight helps the boat sail evenly and uprightly. The force created by the water moving over the keel counteracts the effects of the wind on the sails.
So a keel does two jobs for a sailboat. First, it provides a force that allows a sailboat to sail into the wind. Second, it provides stability. If storm-force weather conditions cause a monohull boat to roll, the weight in the keel will help the boat right itself.
Many older cruising boats had full keels. The keel shape runs the entire length of the boat. A full-keel boat is strong and easy to manufacture. Full-keel boats often have deeper drafts. The boat’s draft refers to the amount of water it needs to float. Full-keel boats can’t go into the shallow anchorages that catamarans or swing-keel boats can access.
Captains often report that full-keel boats are harder to maneuver in tight places such as marinas. Full-keel boats lack quick maneuverability. They have a reputation for being slower than more modern designs, but they make up for this by providing a very comfortable and safe ride in rough weather.
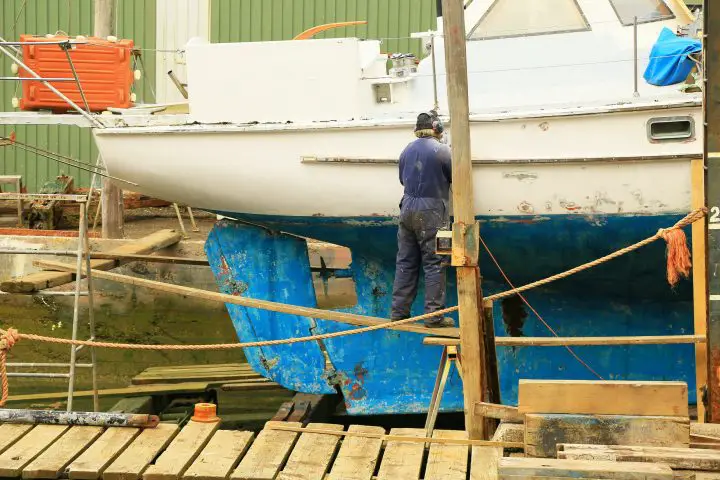

A boat with a fin keel has a smaller underwater profile than a boat with a full keel. This smaller keel resembles a fish fin. Captains find fin keel boats easier to maneuver. Fin keels use their shape to create very effective forces underwater. That makes them very good at countering the forces on the sails, meaning that fin keels sail upwind very well.
A boat with a bulb keel has a torpedo-shaped bulb on the bottom of a fin keel. Bulb keels offer improved stability. Bulb keels have shallower keels than a fin keel boat. The bulb also lowers the center of gravity in the boat, making it more stable overall.
A wing keel features a keel with a small wing on either side of the keel. Viewed from above, the keel looks like it has a set of small airplane wings.
Similar to a bulb keel, wing keel boats often have a shallower draft than fin-keel boats. However, the additional shape causes drag and can reduce sailing performance in some circumstances.
A centerboard is common on small daysailors that are launched and retrieved from trailers. Deep keels make getting those boats in and out of the water difficult. By chopping off the keel, you can make a sailboat as easy to launch as a powerboat.
Related: Best Trailerable Sailboats
But of course, a sailboat needs to have a keel. A centerboard is a simple swinging fin keel that can be raised or lowered. This provides some excellent benefits if the sailor on board likes to explore areas with shallow water.
Many bigger boats have centerboards, too. A boat with a centerboard can be seen as the best of both worlds. A centerboard boat has a fixed shallow draft keel. However, the captain can deploy the centerboard when sailing in deeper waters. The centerboard adds depth to the keel and offers increased stability and performance.
A modification of the centerboard is the swing keel — a ballasted keel that can be retracted like a centerboard . These are rare. They’re used on large cruising boats where the crews want the option of accessing shallow waters. In England, this type of boat is used and can be dried out when the tide goes out.
Racing Sailboats
Yacht racing is a popular sailing sport. It’s a great way to get out on the water while competing. In fact, racing is a great way for sailors to hone their sailing skills. Sailors have to pay close attention to weather conditions and manage their sails effectively to maximize their speed.
Sailors can race any boat with sails. Kids race sailing dinghies against each other. Club racers sail daysailors or catboats. Catamarans and trimarans are also popular race boats. Several classes of boat races in the Summer Olympics.
Hydrofoil Sailboats
A hydrofoil is a unique and modern type of racing sailboat. A hydrofoil can be a monohull, catamaran, or trimaran. A hydrofoil has wing-like foils on the hull’s underside.
As the sailboat speeds up, the hydrofoils lift the hull out of the water, and the hydrofoil sailboat almost appears to be flying above the water.
Because the hull is now out of the water, drag, and resistance are minimal, and the sailboat can sail even faster. For example, a dinghy that usually goes four knots can accelerate to 12 knots when fitted with a hydrofoil.
Most hydrofoil sailboats are catamarans and trimarans. The added width of these multihull sailboats gives the hydrofoil sailboat more stability.
Traditional Sailboats
Traditional sailboats are the type of sailboats used to transport people and goods before modern transportation options were available. Before the railway, cars, and airplanes, a tall ship sailboat was used to ship cargo and people across oceans and from port to port.

A gaff rig refers to the gaff, which is the upper spar on a square-shaped sail. Gaff rigs can be used with any mast configuration, but this feature is usually seen on traditional boats like a catboat, tall ship, or schooner.
A schooner has at least two masts. They are different from other mast configuration designs with two spars in that both masts are equal in height, or the forward mast is shorter. Schooners are faster than most traditional boats and were often used to transport perishable goods such as fruit.
Schooners were also popular race boats in the early 20th century. For example, first America’s Cup races were won by schooners.
Today, schooners are usually used as charters for vacations or youth sail training programs. But there are a few cruising boats out there that feature schooner rigs.
Any way you divvy it up, there are tons of different types of sailboats out there. With a little research and a little looking, you’re sure to find one that suits your style and boating plans.
What are the classes of sailboats?
Sailboat styles can be classified by hull type, use, or sail plan. The types of sailboat hulls include monohulls, catamarans, and trimarans. You can also categorize the kinds of sailboats by their use. For example, sailors use their boats for daysailing, cruising, and racing. Finally, different kinds of sailboats have different sail plans. A sailboat might be a sloop, ketch, yawl, catboat, or schooner. The term “classes” has a particular meaning in sailing, however. Class racing is the competitive racing between boats of the same make and model—boats of the same “class” or of “one design.” There are hundreds of different classes of sailboats out there. Some of the most popular classes include the Laser and Sunfish classes.
What is a small 2 person sailboat called?
A small two-person sailboat is a dinghy. These small boats are fun to sail on protected waters. Many kids learn to sail in a sailing dinghy. There are dozens of makes and models of sailing dinghies available, some are used in Olympic sailing racing while others are just rowboats with sail rigs attached.
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Paddle Board

A Complete Guide to Sailboats: All You Need to Know!
While motorboats are the preferred choice for watersports , they are loud, noisy, and don’t offer you the best experience for a clam boating experience. However, the sailboat provides a serene sailing experience that’s quiet, relaxing, offering you plenty of fun on the water.
Sailboats come in a wide variety of configurations, lengths, and features, giving you passenger capacities from one person to 15-people or more, depending on the size of the model. Learning to sail is a skill all watermen should have in their repertoire; it’s the original form of boating and a highly sought-after skill.
This brief guide to sailboats gives you everything you need to know about choosing the right sailboat for your aquatic adventures.

What is a Sailboat?
A sailboat is a broad term defining many different boats. There are several categories of sailboats with plenty of sail options. The types of sails define your boat, and here are the most popular choices for these watercraft.
- The modern sloop, featuring a single mast and two sails.
- The macaroni or Bermuda rig offers tall triangular-shaped sails.
- A racing sloop for higher speeds and competitive sailing.
- The masthead sloop, with the jib reaching to the end of the masthead.
- The fractional sloop rig features a proportionately larger mainsail and smaller jib.
- The single-sail cat rig.
- The ketch rig features a smaller mast aft, also known as a mizzenmast.
- The yawl is similar in design to a ketch rig.
- The schooner featuring two to four masts positioned further forward in the boat.
While these are the most common sail types, several others are less common with modern sailing techniques. The topsail featuring multi-flying jibs are better suited to long journeys, and many recreational sailors aren’t going to be out on the water for months at a time.
The rule of thumb is that the larger the sail and the more sails you have, the bigger the crew required to operate the boat. However, if you’re looking for a solo rig, there are plenty of smaller options available.
The Laser is an excellent example of a popular single-person sailboat designed for recreational and competitive use. These boats make the ideal starter vessel for someone who’s learning the ropes of sailing.

Different Types of Sailboats
Sailboats rely on the wind to power the vessel through the water. However, there are those days on the lake or ocean where the wind is flat. As a result, most sailboats come with small outboard or trolling motors to power them through the water on windless days.
You have several options for sailboat design, with the most popular options being the following.
The catamaran uses two hulls to power the boat through the water, offering less drag and faster sailing speeds. They are often the choice for professional racing boats, allowing the vessel to cut through rough seas.
These boats also come in luxury models allowing for spending days or weeks out on the water. The most advanced models will also feature hydrofoils that lift the hull out of the water at high speeds, providing more stability, less drag, and higher cruising speeds.
The beach catamaran operates with a sail, while the cruising model relies on an outboard motor for a backup to the sail on calm days.

Cruising Sailboat
The cruising sailboat features a design for covering long distances on the ocean. The cruiser will offer you the benefits of long-term liveaboard conditions, featuring luxury accommodations and amenities like full kitchens, heads, and bedrooms.
As the name implies, the daysailer is suitable for day trips out on the ocean or the lake. These models feature a multi-hull or monohull design, and some come with sleeping accommodations.
Due to the smaller size of these vessels, they are often trailerable, providing easy transport between launch locations. The motorsailer gives you the advantages of the daysailer, with an additional engine for powering the boat on windless days out on the water.
The daysailer will also feature amenities like a kitchen and head, and they often come with sleeping accommodation.
Racing Sailboat
The racing sailboat or yacht offers you a competitive vessel focusing on speed and maneuverability. Many models come with lightweight carbon fiber designs for higher speeds and hull stability when cutting through the water.
Most models also feature hydrofoils that lift the hull from the water, providing stable cruising speeds and fast sailing.
These boats are not suitable for beginners, and they require a competent, experienced team. You get full amenities, but they are more bare-bones, and don’t expect any luxury features because they need to save on weight with the design.
Sailing Dinghy
The sailing dinghy is a small sailboat suitable for one or two people. They are not ideal for open-ocean use as they present a sinking risk in rough water conditions.
However, they are great for learning how to sail, and many models come with a single-person operation for easy sailing. It’s a great boat for building your sailing skills in preparation for a larger model.
Kiteboards and Windsurfers
Kiteboards and windsurfers aren’t technically boats, but they rely on wind power for operation. They are a great choice for a sporty time out on the water and suitable for freshwater and ocean use.

The Fastest Sailing Boats
While they don’t have motors, and can’t reach the same speeds as powerboats, sailing yachts can reach high speeds in favorable wind conditions. If you have the need for speed with your sailing, then try one of the following models for a thrilling experience on the water.
The fastest sailboats include the following models.
- Specialized high-performance boats (up to 65-knots)
- Kiteboards and Windsurfers (50-knots)
- Hydrofoil monohulls (50-knots)
- Hydrofoil multi-hulls (44-knots)
- High-performance multi-hull boats (20-knots)
- Offshore racer monohulls (less than 20-knots)
The hydrofoil technology found in more expensive models lifts the hull from the water as the boat engages its top-end speed. The foil adds a smooth sailing experience that’s unlike any other hull type when engaged.
How Much Does a Sailboat Cost?
Sailboats come in various models, from small single-person models to boats requiring a full crew to operate. The cost of the vessel depends on the design materials (carbon fiber models are the most expensive), the length of the boat, the sail design, accessories and amenities, and the manufacturing brand.
Small to mid-sized boast can cost anything from $10,000 to $80,000, with sports models costing up to $150,000. Luxury models with longer lengths and sports cats can cost you anywhere up to $500,000 or more, depending on the features.

Benefits of Sailboats
The sailboat has plenty of advantages out on the water. Here are some of the top benefits of sailboats.
Quiet Sailing
Sailboats rely on the sail to power the vessel. As a result, you get no motor noise, and you can enjoy the sound of the ocean as you sail along. Some models come with motors to propel the boat if it’s a calm day with low winds.
Live Aboard
Most larger models come with V-berths and living accommodations for spending several days out on the water. The type of accommodations varies from basic in racing models to pure luxury in cruisers. However, the luxury models will add dollars to the price tag, depending on your customizations.

Trailerable
The smaller models of sailing boats are easy to trailer. The Laser is a good example, with easy trailering suitable for a single person to navigate.
Multiple Sizing Options
Sailboats come in designs and lengths to suit any activity out on the water. Whether you want a boat to cruise the lakes by yourself or tackle the oceans with a crew, there is a model to suit your needs.
Disadvantages of Sailboats
The sailboat offers you a fantastic cruising experience out on the water. However, these boats do come with a few drawbacks.
Smaller Motors
Since the boat relies on the sail to do the work, most models don’t come with large backup motors. You can expect low-power outboards or trolling motors to power the vessel when the wind is low.
Large Models Don’t Suit Trailers
The large sailboats over 30-feet don’t suit trailers. The larger keels and foils on these boats mean that they can’t reach shallow waters. As a result, you need a professional towing service to take the boat from the marina to the shipyard for repairs or alterations.

Not Suitable for Watersports
While some sailboats might be okay for diving, they are not suitable for watersports like skiing, tubing, and wakeboarding.
Expensive Customizations
Some of the high-end luxury models come with so many customizations your head will spin. It’s important to set your budget when looking at sailboats, or you could end up spending more than you expect on the customizations and accessories for these boats.
Sail Repairs
If your sail is up in stormy conditions, you run the risk of tearing the material. Sails can be costly to replace or repair, and it may take weeks to find the right sailor to make the repair, keeping your boat out of the water.
Top Sailboat Brands & Models
There are dozens of sailboat brands and hundreds of models available. We chose the following sailboats as the best option for your first boat.
Bavaria C57
The Bavaria C57 is the company’s flagship model, offering you a sleek, streamlined version of the cruiser-line model.

This boat features a design from Maurizio Cossutti. It comes with a smooth hull featuring nanotechnology to help the boat glide through the water effortlessly. The vinyl ester resin construction is durable and lightweight, adding speed to the boat in good wind conditions.
You get twin helms and dual rudders, along with a huge drop-down transom. This model comes with some surprising accessories, including a grill and refrigerator in the boat’s aft for fun on the water.
You have three lounges on the deck, with a large cockpit for the crew and captain.
X-Yachts X4.6
The X-Yachts X4.6 model is a performance cruiser offering you a vacuum-sealed epoxy hull for lightweight strength and durability. The boat comes with the signature galvanized steel grid found on X-Yacht models adding strength and rigidity to the frame for use in rough water conditions.

The boat features a self-tacking jib for easy coming about and total control of the vessel in turns. You get twin helms and an open cockpit design for racing or cruising. This model also includes a dedicated locker for a life raft under the cockpit bench on the vessel’s starboard side.
Beneteau Oceanis 30.1
The Beneteau Oceanis 30.1 is easy to sail, with a setup that suits any sailing style. This boat is a classic, offering purists a fantastic option for their sailboat. You get twin rudders with a fixed spirit, a plumb bow for fine entry, and a backstay-free rig accommodating a square-top design for easy sailing.

This model is a great choice for overnight sailing trips, offering you two full-size cabins kitted with luxury finishes. There are saloon benches that double as a berth, and you get an astounding 6’6″ of headroom below deck in the berth.
You also have the choice of a tiller or steering wheel for a truly authentic sailing experience purists will appreciate. You also have options for a swing keel version allowing for easy sailing along rivers and canals without the threat of hitting submerged rocks or logs or running the vessel aground.
This sailboat is the best choice for beginners. You get an easy-to-manage sail configuration that teaches you the basics of sailing and enough space on the boat for two people.
This model is a great choice for an affordable entry-level sailboat with a fiberglass design for lightweight movement and speed and the option of sailing the boat along with its user-friendly rigging system.
Wrapping Up
Whether you’re a purist, modern sailor, or competitor, you’ll find that there’s a sailboat model to suit your needs and sailing style. These boats offer you the most authentic experience when out on the water, and you don’t have to worry about filling up the gas tank to get home.

John is an experienced journalist and veteran boater. He heads up the content team at BoatingBeast and aims to share his many years experience of the marine world with our readers.
A Complete Guide to Micro Skiffs: All You Need to Know!
A complete guide to narrow boats: all you need to know, a guide to aluminum fishing boats.
Comments are closed.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Sail Rigs And Types - The Only Guide You Need

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
A well-designed sailboat is a thing of pure beauty. Whether you're a proud owner of one, a guest on one, or a shore-side admirer, you'll fall in love with the gliding sails, the excitement of a race, and the eco-friendly nature of these sophisticated yet magnificent vessels. With good sails, great design, and regular maintenance, sails and rigs are an important part of a sailboat.
If you’re thinking about going sailing, one of the first things you have to understand is the variety of modern sail plans. Unlike old sailboats, modern sailboats don't need huge, overlapping headsails and multiple masts just to get moving. In the past, when sailboats were heavy, keels were long, the only way to get the boat moving was with a massive relative sail area. You needed as much square footage as you could just to get your sailboat moving. But with the invention of fiberglass hulls, aluminum or composite masts, high-tensile but low diameter lines and stats, and more efficient sails, sailboats no longer need to plan for such large sail plans.. Still, there are various rig styles, from the common sloop, to the comfortable cat-rig, to the dual masted ketch and schooner, there are various sail types and rigs to choose from. The most important thing is to know the different types of sails and rigs and how they can make your sailing even more enjoyable.
There are different types of sails and rigs. Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The mainsail is generally fore-and-aft rigged and is triangular shaped. Various conditions and courses require adjustments to the sails on the boats, and, other than the mainsail, most boats can switch out their secondary sail depending on various conditions.. Do you want to sail upwind or go downwind? You cannot hoist just any sail and use it. It's, therefore, of great importance to understand how and when to use each sail type.
In this in-depth article, we'll look at various sail types and rigs, and how to use them to make your sailing more enjoyable.
Table of contents
Different Sail Types
It is perhaps worth noting that a sailboat is only as good as its sails. The very heart of sailing comes in capturing the wind using artfully trimmed sails and turning that into motion. . Ask any good sailor and he'll tell you that knowing how and when to trim the sails efficiently will not only improve the overall performance of your boat but will elevate your sailing experience. In short, sails are the driving force of sailboats.
As such, it's only natural that you should know the different types of sails and how they work. Let's first highlight different sail types before going into the details.
- Jib - triangular staysail
- Spinnaker - huge balloon-shaped downwind sail for light airs
- Genoa - huge jib that overlaps the mainsail
- Gennaker - a combination of a spinnaker and genoa
- Code zero - reaching genoa for light air
- Windseeker - tall, narrow, high-clewed, and lightweight jib
- Drifter - versatile light air genoa made from particularly lightweight cloth
- Storm jib - a smaller jib meant for stormy conditions
- Trysail - This is a smaller front-and-aft sail for heavy weather
The mainsail is the principal sail on a boat. It's generally set aft of the mainmast. Working together with the jib, the mainsail is designed to create the lift that drives the sailboat windward. That being said, the mainsail is a very powerful component that must always be kept under control.
As the largest sail, and the geometric center of effort on the boat, the mainsail is tasked with capturing the bulk of the wind that's required to propel the sailboat. The foot, the term for the bottom of any sail, secures to the boom, which allows you to trim the sail to your heading. The luff, the leading edge of the sail, is attached to the mast. An idealized mainsail would be able to swing through trim range of 180°, the full semi-circle aft of the mast, though in reality, most larger boats don’t support this full range of motion, as a fully eased sail can occasionally be unstable in heavy breeze.
. As fully controlling the shape of the mainsail is crucial to sailing performance, there are many different basic mainsail configurations. For instance, you can get a full-batten mainsail, a regular mainsail with short battens, or a two-plus-two mainsail with two full-length battens. Hyper-high performance boats have even begun experimenting with winged sails which are essentially trimmable airplane wings! Moreover, there are numerous sail controls that change the shape by pulling at different points on the sail, boom, or mast. Reefing, for instance, allows you to shorten the sail vertically, reducing the amount of sail area when the boat is overpowered.
Features of a Mainsail
Several features will affect how a particular sail works and performs. Some features will, of course, affect the cost of the sail while others may affect its longevity. All in all, it's essential to decide the type of mainsail that's right for you and your sailing application.
Sail Battens, the Roach, and the Leech
The most difficult part of the sail to control, but also the most important, are the areas we refer to as the leech and the roach. The roach is the part of the sail that extends backwards past the shortest line between the clew, at the end of the boom, and the top of the mast. It makes up roughly the back third of the sail. The leech is the trailing edge of the sail, the backmost curve of the roach. Together, these two components control the flow of the air off the back of the sail, which greatly affects the overall sail performance. If the air stalls off the backside of the sail, you will find a great loss in performance. Many sail controls, including the boom vang, backstay, main halyard, and even the cunningham, to name a few, focus on keeping this curve perfect.
As for parts of the sail itself, battens control the overall horizontal shape of the sail. Battens are typically made from fiberglass or wood and are built into batten pockets. They're meant to offer support and tension to maintain the sail shape Depending on the sail technology you want to use, you may find that full battens, which extend from luff to leech, or short battens, just on the trailing edge, are the way to go. Fully battened sails tend to be more expensive, but also higher performance.
Fully Battened Mainsails
They're generally popular on racing multihulls as they give you a nice solid sail shape which is crucial at high speeds. In cruising sailboats , fully battened mainsails have a few benefits such as:
- They prevent the mainsail from ragging. This extends the life of the sail, and makes maneuvers and trimming easier for the crew.
- It provides shape and lift in light-air conditions where short-battened mainsails would collapse.
On the other hand, fully-battened mainsails are often heavier, made out of thicker material, and can chafe against the standing rigging with more force when sailing off the wind.
Short Battens
On the other hand, you can choose a mainsail design that relies mostly on short battens, towards the leech of the sail. This tends to work for lighter cloth sails, as the breeze, the headsail, and the rigging help to shape the sail simply by the tension of the rig and the flow of the wind. The battens on the leech help to preserve the shape of the sail in the crucial area where the air is flowing off the back of the sail, keeping you from stalling out the entire rig.
The only potential downside is that these short battens deal with a little bit of chafe and tension in their pockets, and the sail cloth around these areas ought to be reinforced. If your sails do not have sufficient reinforcement here, or you run into any issues related to batten chafe, a good sail maker should be able to help you extend the life of your sails for much less than the price of a new set.
How to Hoist the Mainsail
Here's how to hoist the mainsail, assuming that it relies on a slab reefing system and lazy jacks and doesn't have an in-mast or in-boom furling system.
- Maintain enough speed for steeragewhile heading up into the wind
- Slacken the mainsheet, boom vang, and cunningham
- Make sure that the lazy jacks do not catch the ends on the battens by pulling the lazy jacks forward.
- Ensure that the reefing runs are free to run and the proper reefs are set if necessary.
- Raise the halyard as far as you can depending on pre-set reefs.
- Tension the halyard to a point where a crease begins to form along the front edge
- Re-set the lazy jacks
- Trim the mainsail properly while heading off to your desired course
So what's Right for You?
Your mainsail will depend on how you like sailing your boat and what you expect in terms of convenience and performance. That being said, first consult the options that the boatbuilder or sailmakers suggest for your rig. When choosing among the various options, consider what you want from the sail, how you like to sail, and how much you're willing to spend on the mainsail.
The headsail is principally the front sail in a fore-and-aft rig. They're commonly triangular and are attached to or serve as the boat’s forestay. They include a jib and a genoa.
A jib is a triangular sail that is set ahead of the foremost sail. For large boats, the roto-furling jib has become a common and convenient way to rig and store the jib. Often working in shifts with spinnakers, jibs are the main type of headsails on modern sailboats. Jibs take advantage of Bournoulli’s Principle to break the incoming breeze for the mainsail, greatly increasing the speed and point of any boat. By breaking the incoming wind and channeling it through what we call the ‘slot,’ the horizontal gap between the leech of the jib and the luff of the mainsail, the jib drastically increases the efficiency of your mainsail. It additionally balances the helm on your rudder by pulling the bow down, as the mainsail tends to pull the stern down. .
The main aim of the jib is to increase the sail area for a given mast size. It improves the aerodynamics of the mainsails so that your sailboat can catch more wind and thereby sail faster, especially in light air
Using Jibs on Modern Sailboats
In the modern contexts, jib’s mainly serve increase the performance and overall stability of the mainsail. The jib can also reduce the turbulence of the mainsail on the leeward side.
On Traditional Vessels
Traditional vessels such as schooners have about three jibs. The topmast carried a jib topsail, the main foresail is called the jib, while the innermost jib is known as the staysail. The first two were employed almost exclusively by clipper ships.
How to Rig the Jibs
There are three basic ways to rig the jib.
Track Sheets - A relatively modern approach to the self-tacking jib, this entails placing all the trimming hardware on a sliding track forward of the mast. This means that on each tack, the hardware slides from one side of the boat to the other. This alleviates the need to switch sheets and preserves the trim angle on both sides, though it can be finnicky and introduce friction.
Sheet up the Mast - This is a very popular approach and for a good reason. Hoist the jib sheet up the mast high enough to ensure that there's the right tension through the tack. Whether internally or externally, the sheet returnsto the deck and then back to the cockpit just like the rest of the mast baselines. The fact the hardware doesn't move through the tacks is essential in reducing friction.
Sheet Forward - This method revolves around ensuring that the jib sheet stays under constant pressure so that it does not move through the blocks in the tacks. This is possible if the through-deck block is extremely close to the jib tack. Your only challenge will only be to return the sheet to the cockpit. This is, however, quite challenging and can cause significant friction.
Dual Sheeting - The traditional method, especially on smaller dinghies, though it is not self-tacking. This requires a two ended or two separate sheet system, where one sheet runs to a block on starboard, and the other to port. Whenever you tack or gybe, this means you have to switch which sheet is active and which is slack, which is ok for well crewed boats, but a potential issue on under-crewed boats.
Another important headsail, a genoa is essentially a large jib that usually overlaps the mainsail or extends past the mast, especially when viewed from the other side. In the past, a genoa was known as the overlapping jib and is technically used on twin-mast boats and single-mast sloops such as ketches and yawls. A genoa has a large surface area, which is integral in increasing the speed of the vessel both in moderate and light winds.
Genoas are generally characterized by the percentage they cover. In most cases, sail racing classes stipulate the limit of a genoa size. In other words, genoas are usually classified by coverage.
Top-quality genoa trim is of great importance, especially if the wind is forward of the beam. This is because the wind will first pass over the genoa before the mainsail. As such, a wrongly sheeted genoa can erroneously direct the wind over the mainsail,spelling doom to your sailing escapades. While you can perfectly adjust the shape of a genoa using the mast rake, halyard tension, sheet tension, genoa car positioning, and backstay tension, furling and unfurling a genoa can be very challenging, especially in higher winds.
That being said, here are the crucial steps to always keep in mind.
- Unload and ease the loaded genoa sheet by going to a broad reach
- Do not use the winch; just pull on the furling line
- Keep a very small amount of pressure or tension on the loaded genoa sheet
- Secure the furling line and tighten the genoa sheets
- Get on the proper point of sail
- Have the crew help you and release the lazy genoa sheets
- Maintain a small tension while easing out the furling line
- Pull-on a loaded genoa sheet
- Close or cleat off the rope clutch when the genoa is unfurled
- Trim the genoa
To this end, it's important to note that genoas are popular in some racing classes. This is because they only categorize genoas based on the fore-triangle area covered, which essentially allows a genoa to significantly increase the actual sail area. On the contrary, keep in mind that tacking a genoa is quite a bit harder than a jib, as the overlapping area can get tangled with the mast and shrouds. It's, therefore, important to make sure that the genoa is carefully tended, particularly when tacking.
Downwind Sails
Modern sailboats are a lot easier to maneuver thanks to the fore-and-aft rig. Unfortunately, when sailing downwind they catch less wind, and downwind sails are a great way of reducing this problem. They include the spinnaker and the gennaker.
A spinnaker will, without a doubt, increase your sailing enjoyment. But why are they often buried in the cabin of cruising boats? Well, the first few attempts to rig and set a spinnaker can be difficult without enough help and guidance. Provided a solid background, however, spinnakers are quite straightforward and easy to use and handle with teamwork and enough practice. More importantly, spinnakers can bring a light wind passage to life and can save your engine.
Spinnakers are purposely designed for sailing off the wind; they fill with wind and balloon out in front of your sailboat. Structured with a lightweight fabric such as nylon, the spinnaker is also known as a kite or chute, as they look like parachutes both in structure and appearance.
A perfectly designed spinnaker should have taut leading edges when filled. This mitigates the risk of lifting and collapsing. A spinnaker should have a smooth curve when filled and devoid of depressions and bubbles that might be caused by the inconsistent stretching of the fabric. The idea here is that anything other than a smooth curve may reduce the lift and thereby reduce performance.
Types of Spinnakers
There are two main types of spinnakers: symmetric spinnakers and asymmetric spinnakers.
Asymmetric Spinnakers
Flown from a spinnaker pole or bowsprit fitted to the bow of the boat, asymmetric spinnakers resemble large jibs and have been around since the 19th century. The concept of asymmetric spinnaker revolves around attaching the tack of the spinnaker at the bow and pulling it around during a gybe.
Asymmetric spinnakers have two sheets just like a jib., These sheets are attached at the clew and never interact directly with the spinnaker pole. This is because the other corner of the spinnaker is fixed to the bowsprit. The asymmetric spinnaker works when you pull in one sheet while releasing the other. This makes it a lot easier to gybe but is less suited to sailing directly downwind. There is the loophole of having the asymmetric spinnaker gybed to the side opposite of the boom, so that the boat is sailing ‘wing-on-wing,’ though this is a more advanced maneuver, generally reserved for certain conditions and tactical racing situations.
On the contrary, the asymmetric spinnaker is perfect for fast planing dinghies. This is because such vessels have speeds that generate apparent wind forward. Because asymmetrics, by nature, prefer to sail shallower downwind angles, this apparent wind at high speeds makes the boat think that it is sailing higher than it really is, allowing you to drive a little lower off the breeze than normal. . In essence, the asymmetric spinnaker is vital if you're looking for easy handling.
Symmetric Spinnakers
Symmetric spinnakers are a classic sail type that has been used for centuries for controlling boats by lines known as a guy and a sheet. The guy, which is a windward line, is attached to the tack of the sail and stabilized by a spinnaker pole. The sheet, which is the leeward line, is attached to the clew of the spinnaker and is essential in controlling the shape of the spinnaker sail.
When set correctly, the leading edges of the symmetric spinnaker should be almost parallel to the wind. This is to ensure that the airflow over the leading edge remains attached. Generally, the spinnaker pole should be at the right angles to the apparent wind and requires a lot of care when packing.
The main disadvantage of this rig is the need to gybe the spinnaker pole whenever you gybe the boat. This is a complicated maneuver, and is one of the most common places for spinnakers to rip or get twisted. If, however, you can master this maneuver, you can sail at almost any angle downwind!
How to Use Spinnaker Effectively
If you decide to include the spinnakers to your sailboat, the sailmaker will want to know the type of boat you have, what kind of sailing you do, and where you sail. As such, the spinnaker that you end up with should be an excellent and all-round sail and should perform effectively off the breeze
The type of boat and where you'll be sailing will hugely influence the weight of your spinnaker cloth. In most cases, cruising spinnakers should be very light, so if you've decided to buy a spinnaker, make sure that it's designed per the type of your sailboat and where you will be sailing. Again, you can choose to go for something lighter and easier to set if you'll be sailing alone or with kids who are too young to help.
Setting up Spinnakers
One of the main reasons why sailors distrust spinnakers is because they don't know how to set them up. That being said, a perfectly working spinnaker starts with how you set it up and this revolves around how you carefully pack it and properly hook it up. You can do this by running the luff tapes and ensuring that the sails are not twisted when packed into the bag. If you are using large spinnakers, the best thing to do is make sure that they're set in stops to prevent the spinnakers from filling up with air before you even hoist them fully.
But even with that, you cannot fully set the spinnaker while sailing upwind. Make sure to bear away and have your pole ready to go as you turn downwind. You should then bear away to a reach before hoisting. Just don't hoist the spinnakers from the bow as this can move the weight of the crew and equipment forward.
Used when sailing downwind, a gennaker is asymmetric sail somewhere between a genoa and a spinnaker. It sets itself apart because it gennaker is a free-flying asymmetric spinnaker but it is tacked to the bowsprit like the jib.
Let's put it into perspective. Even though the genoa is a great sail for racing and cruising, sailors realized that it was too small to be used in a race or for downwind sail and this is the main reason why the spinnaker was invented. While the spinnakers are large sails that can be used for downwind sail, they are quite difficult to handle especially if you're sailing shorthanded. As such, this is how a gennaker came to be: it gives you the best of both worlds.
Gennakers are stable and easy to fly and will add to your enjoyment and downwind performance.
The Shape of a Gennaker
As we've just noted, the gennaker is asymmetrical. It doesn't attach to the forestay like the genoa but has a permanent fitting from the mast to bow. It is rigged exactly like a spinnaker but its tack is fastened to the bowsprit. This is fundamentally an essential sail if you're looking for something to bridge the gap between a genoa and a spinnaker.
Setting a Gennaker
When cruising, the gennaker is set with the tack line from the bow, a halyard, and a sheet that's led to the aft quarter. Attach the tack to a furling unit and attach it to a fitting on the hull near the very front of the sailboat. You can then attach the halyard that will help in pulling it up to the top of the mast before attaching it to the clew. The halyard can then run back to the winches to make the controlling of the sail shape easier, just like when using the genoa sail.
In essence, a gennaker is a superb sail that will give you the maximum versatility of achieving the best of both a genoa and a spinnaker, especially when sailing downwind. This is particularly of great importance if you're cruising by autopilot or at night.
Light Air Sails
Even though downwind sails can be used as light air sails, not all light air sails can be used for downwind sailing. In other words, there's a level of difference between downwind sails and light air sails. Light air sails include code zero, windseeker, and drifter reacher.
A cross between an asymmetrical spinnaker and a genoa, a code zero is a highly modern sail type that's generally used when sailing close to the wind in light air. Although the initial idea of code zero was to make a larger genoa, it settled on a narrow and flat spinnaker while upholding the shape of a genoa.
Modern boats come with code zero sails that can be used as soon as the sailboat bears off close-hauled even a little bit. It has a nearly straight luff and is designed to be very flat for close reaching. This sail is designed to give your boat extra performance in light winds, especially in boats that do not have overlapping genoas. It also mitigates the problem of loss of power when you are reaching with a non-overlapping headsail. Really, it is closer to a light air jib that sacrifices a little angle for speed.
In many conditions, a code zero sail can go as high as a sailboat with just a jib. By hoisting a code zero, you'll initially have to foot off about 15 degrees to fill it and get the power that you require to heel and move the boat. The boat will not only speed up but will also allow you to put the bow up while also doing the same course as before you set the zero. In essence, code zero can be an efficient way of giving your boat about 30% more speed and this is exactly why it's a vital inventory item in racing sailboats.
When it comes to furling code zero, the best way to do it is through a top-down furling system as this will ensure that you never get a twist in the system.
Generally used when a full size and heavier sail doesn't stay stable or pressurized, a windseeker is a very light sail that's designed for drifting conditions. This is exactly why they're designed with a forgiving cloth to allow them to handle these challenging conditions.
The windseeker should be tacked at the headstay with two sheets on the clew. To help this sail fill in the doldrums, you can heel the boat to whatever the apparent leeward side is and let gravity help you maintain a good sail shape while reaching.The ideal angle of a windseeker should be about 60 degrees.
Though only used in very specific conditions, the windseeker is so good at this one job that it is worth the investment if you plan on a long cruise. Still, you can substitute most off the breeze sails for this in a pinch, with slightly less performance gain, likely with more sacrifices in angle to the breeze.

Drifter Reacher
Many cruising sailors often get intimidated by the idea of setting and trimming a drifter if it's attached to the rig at only three corners or if it's free-flying. But whether or not a drifter is appropriate for your boat will hugely depend on your boat's rig, as well as other specific details such as your crew's ability to furl and unfurl the drifter and, of course, your intended cruising grounds.
But even with that, the drifter remains a time-honored sail that's handy and very versatile. Unlike other light air sails, the drifter perfectly carries on all points of sails as it allows the boat to sail close-hauled and to tack. It is also very easy to control when it's set and struck. In simpler terms, a drifter is principally a genoa that's built of lightweight fabric such as nylon. Regardless of the material, the drifter is a superb sail if you want to sail off a lee shore without using the genoa.
Generally stronger than other regular sails, stormsails are designed to handle winds of over 45 knots and are great when sailing in stormy conditions. They include a storm jib and a trysail.
If you sail long and far enough, chances are you have or will soon be caught in stormy conditions. Under such conditions, storm jibs can be your insurance and you'll be better off if you have a storm jib that has the following features:
- Robustly constructed using heavyweight sailcloth
- Sized suitably for the boat
- Highly visible even in grey and white seas
That's not all; you should never go out there without a storm jib as this, together with the trysail, is the only sails that will be capable of weathering some of nature's most testing situations.
Storm jibs typically have high clews to give you the flexibility of sheet location. You can raise the sail with a spare halyard until its lead position is closed-hauled in the right position. In essence, storm jib is your insurance policy when out there sailing: you should always have it but always hope that you never have to use it.
Also known as a spencer, a trysail is a small, bright orange, veritably bullet-proof, and triangular sail that's designed to save the boat's mainsail from winds over 45 knots and works in the same way as a storm jib. It is designed to enable you to make progress to windward even in strong and stormy winds.
Trysails generally use the same mast track as the mainsail but you have to introduce the slides into the gate from the head of the trysail.
There are two main types of rigs: the fore-and-aft rig and the square rigg.
Fore-and-aft Rig
This is a sailing rig that chiefly has the sails set along the lines of the keel and not perpendicular to it. It can be divided into three categories: Bermuda rig, Gaff rig, and Lateen rig.
Bermuda Rig - Also known as a Marconi rig, this is the typical configuration of most modern sailboats. It has been used since the 17th century and remains one of the most efficient types of rigs. The rig revolves around setting a triangular sail aft of the mast with the head raised to the top of the mast. The luff should run down the mast and be attached to the entire length.
Gaff Rig - This is the most popular fore-and-aft rig on vessels such as the schooner and barquentine. It revolves around having the sail four-cornered and controlled at its peak. In other words, the head of the mainsail is guided by a gaff.
Lateen Rig - This is a triangular fore-and-aft rig whereby a triangular sail is configured on a long yard that's mounted at a given angle of the mast while running in a fore-and-aft direction. Lateen rig is commonly used in the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean.
Square Rigged
This is a rig whereby the mainsails are arranged in a horizontal spar so that they're square or vertical to the mast and the keel of the boat. The square rig is highly efficient when sailing downwind and was once very popular with ocean-going sailboats.
Unquestionably, sailing is always pleasurable. Imagine turning off the engine of your boat, hoisting the sails, and filling them with air! This is, without a doubt, a priceless moment that will make your boat keel and jump forward!
But being propelled by the noiseless motion of the wind and against the mighty currents and pounding waves of the seas require that you know various sail types and how to use them not just in propelling your boat but also in ensuring that you enjoy sailing and stay safe. Sails are a gorgeous way of getting forward. They remain the main fascination of sailboats and sea cruising. If anything, sails and boats are inseparable and are your true friends when out there on the water. As such, getting to know different types of sails and how to use them properly is of great importance.
All in all, let's wish you calm seas, fine winds, and a sturdy mast!
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Sailboat Parts
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Sailing Totem
- Sailor & Galley
- Living Aboard
- Destinations
- Gear & Electronics
- Charter Resources
- Ultimate Boat Giveaway
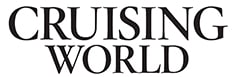
Learning How to Sail 101
- By John Rousmaniere
- Updated: May 4, 2020
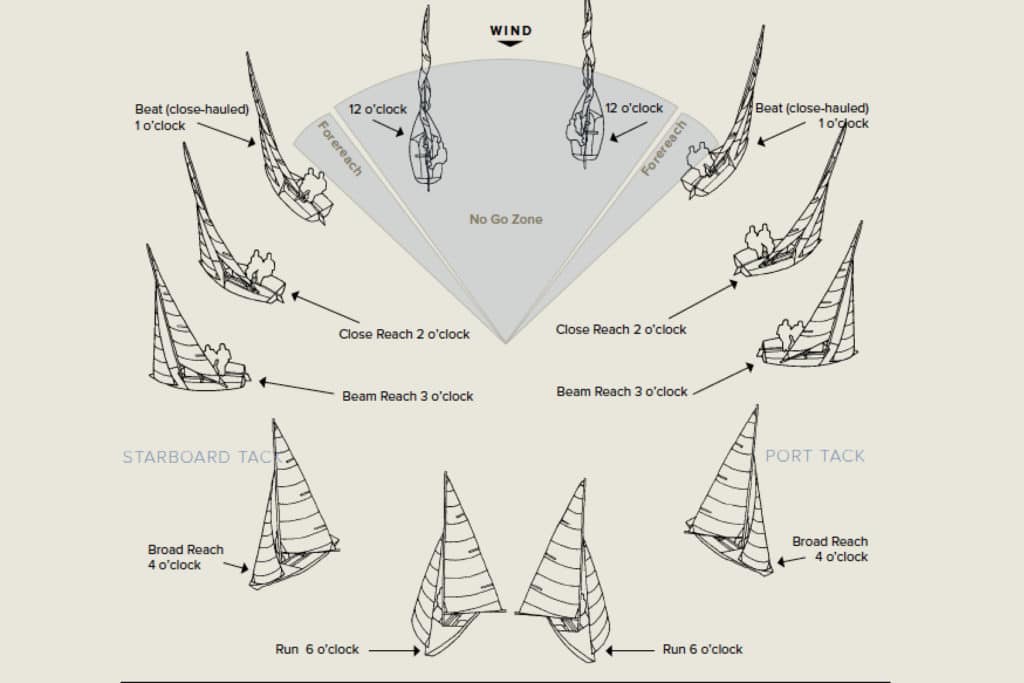
Points of Sail
“The idea of sailing a boat upon the sea can seduce even the happiest farmer or mountain climber. There is something about boat and water that sends romance churning in our hearts, and simply the sight of a boat can inspire a reverie.”
I wrote those words in the first edition of my sailing manual, The Annapolis Book of Seamanship , in 1983. They’re still there today in the updated fourth edition, published in 2014. And yet, as deeply as I feel about boats, I’m certain that when you’re afloat, romantic and magical thinking is no substitute for basic skills and fundamental knowledge.
To quote some other words I wrote back then: “Limitless in her poetry, a sailboat is still restricted by the realities of wind and sea.” Here I’ll describe some important basic skills when learning to sail for dealing with a few of those realities, including some tips and tricks of the seaman’s trade that I have learned and that should make you a more able, safe and confident skipper or crew.
How to Start Sailing
The very first step when you go sailing is to properly prepare yourself for the sometimes demanding and harsh elements you will encounter on the water. Take a wide-brim hat, a waterproof jacket, nonskid sneakers and, of course, a life jacket that fits you securely. Wipe on a gob or two of high-SPF sun lotion, and take the tube with you so you can continue to apply it lavishly. Those who suffer from motion sickness should consider taking a medication, preferably one that you’ve tested for side effects. Before heading out, write up a float plan including your itinerary and important contacts and share it with your friends and family, or your sailing club.
The most unsettling moment of a new sailor’s first day learning to sail often comes when you climb on board and feel the boat move under you. There’s plenty of reserve buoyancy, but if the boat’s small and skittish, you should step into the center of the cockpit. A bigger boat can be boarded via the side deck, but even it may sway and settle a little. Forget about looking graceful. Take advantage of any handhold you can grab.
Once everyone is on board, the skipper must assert command. To quote a wise captain and safety instructor, Karen Prioleau: “When leadership is obscure, tight situations get even tighter.” Assignments are made, gear is stowed, the bilge is pumped, an inspection is conducted to see that all is in order, sails are prepared to hoist, and plans are made to get underway. If the boat has a motor, it can be used to get away from the mooring or dock into open water before setting sail. But for now, let’s concentrate on getting underway on an engineless boat. Start by setting the mainsail, the big sail. The line to the boom (called the mainsheet) must be well eased so the sail, once set, spills wind (luffs) and doesn’t fill prematurely. The boom will flop around, so keep your head low and consider controlling it with a line called a preventer.
Trimming and Tacking a Sailboat
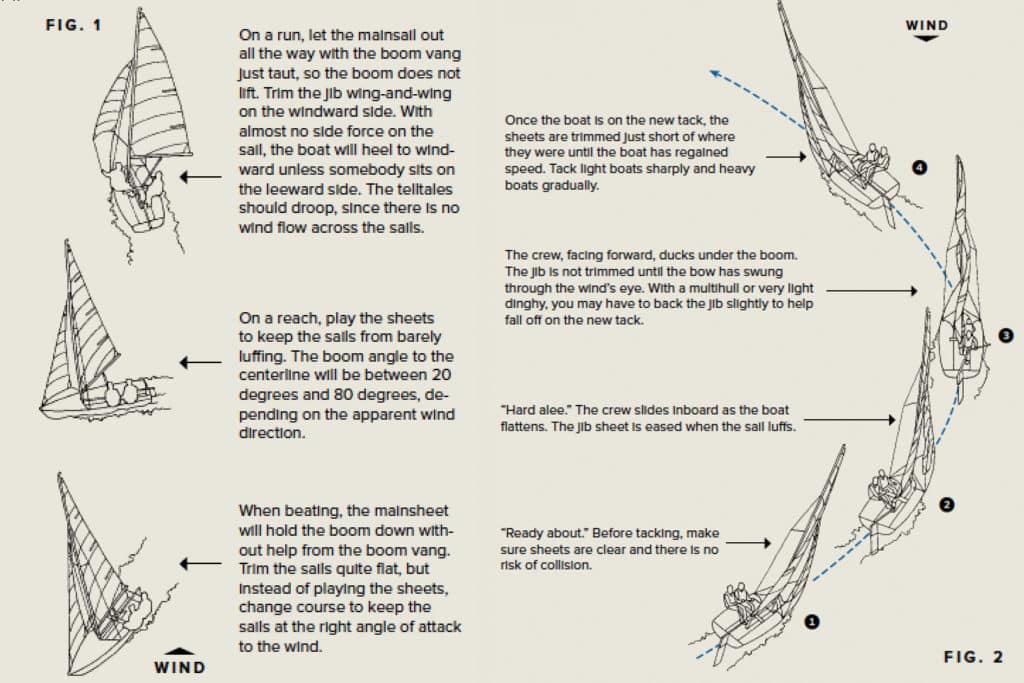
When the skipper says to cast off, up goes the jib, the smaller sail on the bow, also with a loose sheet. Casting off under sail is a little complicated because the boat isn’t moving, which means the rudder has little to no effect. That’s why the boat must be steered with the sails until there’s enough speed (or “steerageway”) for rudder steering. When learning to sail, start with the boat hanging off the mooring or pier; the sails will luff because the wind is blowing from directly ahead. If you’re looking at the bow, you’ll feel the wind on both ears. That angle is sometimes called the “wind’s eye.” Trim the jib—using the winch to bring the sail in, not let it out—to the side opposite the one where you want to sail. If you want to head off to the port side, you “back the jib,” or trim it to the “wrong” side. As the backed jib pulls the bow off, cast off the mooring. Once the wind is on that side, trim the jib to the correct side while also trimming the mainsail as the boat accelerates. In this way, the sails help steer the boat.
An entertaining and educational exercise is to sail a boat toward a buoy or other target on a reach, with the wind coming from the side (or beam) of the boat, and do a series of slow weaves as the sheets are eased and trimmed. When the skipper at the helm and the sail trimmers are in sync, everything goes well (see Figure 1). If you get nervous, slow down by easing the sails until they are just half-filled with wind.
Practice changing tacks. If you start off with the wind coming over the starboard side, you’re on the starboard tack. If the wind is on the port side, you’re on the port tack (see Figure 2). One of the two ways to change tacks is called “coming about,” or “tacking.” The helmsman starts the process by saying, “Ready about,” and after the crew answers that they’re ready, “Hard alee.” With a strong, fluid shove of the tiller or turn of the steering wheel, the bow passes through the eye of the wind and comes off onto the new tack (see Figure 3).
The other way to change tacks is to jibe, pulling the tiller or wheel in the other direction, easing the sheets out, and swinging the stern through the wind’s eye until the boom swings across (see Figure 4). The steerer’s commands are “stand by to jibe” and, after the crew acknowledges, “jibe-ho.” The boom will come across suddenly and rapidly, so all crewmembers must be careful to duck their head as they trim the mainsail and jib to the new sides.
Since we are talking about steering, this may be the place to encourage you to steer from the windward side of the tiller or wheel. The windward side (closer to the wind direction) is higher than the leeward side (farther from the wind) when the boat is heeling, so you will have greater visibility to see “puffs” of wind (the dark shadows moving across the water) as they approach.
Using Telltales
One phenomenon of sailing is that as the boat speeds up or slows down, the wind seems to change direction and force. That’s because there are two types of wind. One, called “true wind,” is the breeze you feel when standing still. The true wind’s velocity and direction are the same for all nearly stationary objects. But if one of those objects moves (like a boat does), its motion affects the true wind to create “apparent wind,” which is felt by people on the moving object.
Sails are trimmed to the apparent wind. You can gauge the apparent-wind direction and force by feeling it on your skin, reading it on an electronic instrument, or seeing it on a telltale, which is a short length of yarn tied to one of the boat’s side stays (shrouds) that support the mast. While all those devices indicate the wind direction, none of them tells you if your sails are trimmed correctly for that direction.
Sails are airfoils, with a deep curve that redirects the apparent wind to produce a force that pulls the boat forward (somewhat like a wing lifting an airplane off a runway). Side force is absorbed and redirected to forward force by the airfoil-shaped fins under the boat, the centerboard and keel. As airfoils, sails should be trimmed to suit the wind, and the boat should sail the most effective angle to that wind.
A simple, effective indicator of that sailing angle is a set of short lengths of special telltales—yarn or ribbons—that are sewn or glued to sails. Some telltales are placed on the jib, near its leading edge (the luff), on both sides of the sail. Ideally, there should be three pairs of jib telltales at equal intervals up and down the sail’s luff. But one pair about halfway up the sail should do the job. Other telltales are secured, one at a time, on the trailing edge of the mainsail (the leech), or at least at or near the second batten from the top. The jib telltales on both sides of the sail should stream aft most of the time, with the windward ones lifting slightly from time to time. The mainsail leech telltale should stream aft about half the time. If your telltales behave differently, try steering closer to or farther off the wind, and experiment with sail trim. An inch or two of sail trim or ease can get them flowing again and make the boat sail faster.
Sailing Rules of the Road
Once you’re sailing, you may be near other boats and worried about who is under an obligation to alter course to avoid a collision. The basic rule is that more maneuverable boats must give way (change course) to avoid boats that are less maneuverable and that, therefore, may continue on their course, giving them right of way. (These are sometimes called “stand-on vessels.”) Usually powerboats must give way to sailboats, but all smaller boats, sail and power, must give way to big ships in a narrow channel and other vessels requiring room to maneuver.
There are a few other basic rules. When one boat is overtaking another, no matter what type, the overtaking boat must give way. When boats under power meet each other bow to bow, they each should turn to starboard so they pass port side to port side. And when sailboats are sailing near each other, without engines turned on, the one on the port tack (with the wind coming over the port side) is obliged to give way to the one on starboard tack. But even if the rules give you the right of way, proceed just as sensibly and defensively as you would when you face the realities of wind and sea at other times in open waters.
Once you’ve mastered these basics, get out on the water as often as possible to hone your skills in all conditions. One of the great things about sailing is that no matter how many miles you cover, there’s something new and different to experience every time you set sail. Congratulations on taking the first step toward what, for so many of us sailors, has become an enjoyable, lifelong pursuit.
Renowned sailing writer John Rousmaniere has logged over 40,000 nautical miles of bluewater sailing, including nine Newport-Bermuda races. This article is based on material from the fourth edition of his comprehensive sailing manual, The Annapolis Book of Seamanship (Simon & Schuster, 2014).
- More: How To , learn to sail , sailing 101 , seamanship
- More How To

Rigging Redo: A Switch to Synthetic

Top Tools for Sailboat Cruising: Must-Have Gear for 2024

Made for Shade: Cockpit Cover Options

Blackwater Wisdom for Holding Tanks

North Sails Parent Company Buys Doyle, Quantum
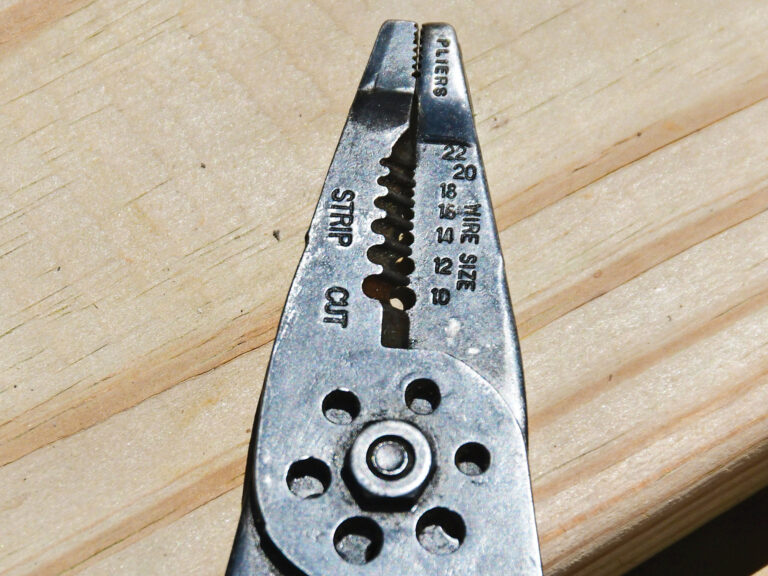

For Sale: 1984 Camper & Nicholsons 58

Sailing Avocet : A New Adventure Begins
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
How To Learn To Sail: Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide
Getting into sailing can seem daunting. When I first got interested, I was completely overwhelmed by all the skills, conflicting information, - and man oh man - all those insider terms. If you don't know where to start, it can be very confusing.
How to learn to sail? When first starting out, you want to gain some experience on the water, learn basic sail trim and navigation, and learn the basic safety rules. You can learn this by taking online courses, and by taking sailing lessons. With the right approach, you could get up to speed in a couple of months and for as little as $500.
Learning from my own experience, I wanted to create a very easy-to-understand guide which walks you through everything you'll need to know and learn when first starting out. In this guide, I'll walk you through all the different aspects of sailing: what to expect (ie. costs), what skills you'll need and how to learn those, and what knowledge you'll need and where to find it.
Spoiler : it's cheaper and easier to learn than you would expect.
Over the last few years, I have written on a lot of different aspects of getting into sailing. Throughout this guide, I will regularly refer to specific articles where you can learn more on a specific topic. This guide is a jumping-off point you can use to quickly get up to speed, and dive in deeper on a particular topic whenever you feel like it.
As a result, it is a long article with lots of information; it may be too much to read all in one sitting. The upside is: it's all here. I recommend bookmarking this article and coming back to it every now and then and pick up where you've left. Let's get started.

On this page:
How to get into sailing, myths that could be holding you back, how to get started, skills you need to learn to sail, things you'll need, in conclusion.

Sailing is both a practical and theoretical skill. You really should gain real-life experience, but you can also learn a lot of essential skills by reading up on them. Let me quickly walk you through my recommendation of how to getting into sailing.
7 easy steps to get into sailing:
- Focus on learning the theory first, focus on practice second
- The essential sailing skills are sail trim, navigation, and boat safety
- Start out using (free) online resources or Sailaway simulator
- After that, gain experience by taking at least a couple of sailing lessons
- To cut cost, you could also crew for an experienced captain instead
- Get your boater's license if necessary
- Hire a boat at first to cut cost and figure out what you like
By first focusing on the theory, which you can mostly do using free resources (and this website), you save on those valuable sailing lessons.
I'll break down all of these steps later. But now, we first have to talk about some common misconceptions about sailing, what it costs, and how long it takes before you sail your first boat by yourself. It's sooner than you might think.

Sailing is known to be an elite sport that costs way too much money. It's hard to learn, expensive to do, and you need all kinds of special knowledge - right? Well, all of those things can absolutely be true, if you want them to be. But sailing has always been one of the cheapest ways of transportation and can be quite easy to learn. I had a ton of those common misconceptions myself, and they were keeping me back. Maybe some of those are holding you back too?
Let me tell you some secrets that will probably change the way you think about the timeline of your sailing dream.
Sailing can be an affordable hobby
- A realistic budget for beginner sailors is $100 - $300 per month
- If you want to, you can get a decent education for as little as $500
- A decent beginner sailboat can cost between $200 - $2,000
In order to sail, you need some things that potentially cost a lot of money:
- a sailboat (preferably a 52' superyacht, right?)
- sailing lessons (and probably tons of them, right?)
- speciality gear like navigation equipment (you can't use regular water bottles, right?)
I say potentially because it really doesn't have to be that way. Sailing can be a normal hobby for regular people that have normal budgets.

Sure, you can spend tons of money on gear and lessons, as with any hobby. You can get yourself special sailing water bottles that provide more optimal water disposal flow in marine environments. You can buy a world-cruising yacht. But let's be fair: you don't own a plane (if you do, call me), yet you are able to fly to nearly every place on Earth if you want to. If you prioritize, you actually don't need all that much gear ór lessons.
In most states and countries, you actually don't even need an official education in order to sail smaller boats. I do recommend getting some training in advance. But you can really get a super decent training and tons of experience on just a $500 budget .
Want to get into sailing on a budget? I've written a detailed guide on how to learn the most important sailing skills on less than $500 . There are tips in there that cost absolutely nothing and are very good first steps.

9 Ways to Learn to Sail for (Practically) Free
A realistic starting budget is $100 - $300.
I've done research on the costs of all different aspects of sailing and I was surprised by the results. You could sail on any budget really, depending on how creative you want to get. $0 is possible but it takes work, patience, and luck. For most people, a realistic budget to get started is between $100 - $300 per month. That will allow you to hire a boat a couple of days per month, get some training, buy some gear, and eventually buy your first sailboat.

There are affordable beginner sailboats out there
Buying a boat will always cost money, but there are so many second-hand sailboats you can always find a decent deal, or even a free learning boat, as long as you don't immediately want to go out and get yourself a yacht.
In fact, you probably want to consider buying a very small beginner laser to start out. The smaller the boat, the faster you'll learn. Small, light sailboats give you faster and more precise feedback on what you do. And small lasers are pretty inexpensive. You can get good second-hand deals for just a couple of hundred bucks. This also means you can put them on a trailer and store them at home. Saves additional cost. Larger sailboats (22ft and up) get very expensive very quickly, though.

The Average Cost of Buying & Owning a Sailboat I have compared thousands of sailboat prices, and the cost of ownership. In this guide, we'll go over every dollar it will cost to own a boat . If you are unsure what it costs to buy and own a boat (and what's possible on your budget), this is a great resource for you.
But there's more cash-saving good news: you don't necessarily need to own a boat to get started.
You don't need to own a boat to get started
Hiring a boat is pretty straightforward nowadays, and more and more private owners are renting out there boat for fair prices on platforms like Boatsetter (Airbnb for boats). So when first starting out, I recommend renting a sailboat for a couple of weekends first, which should get you a good feel for the whole thing.
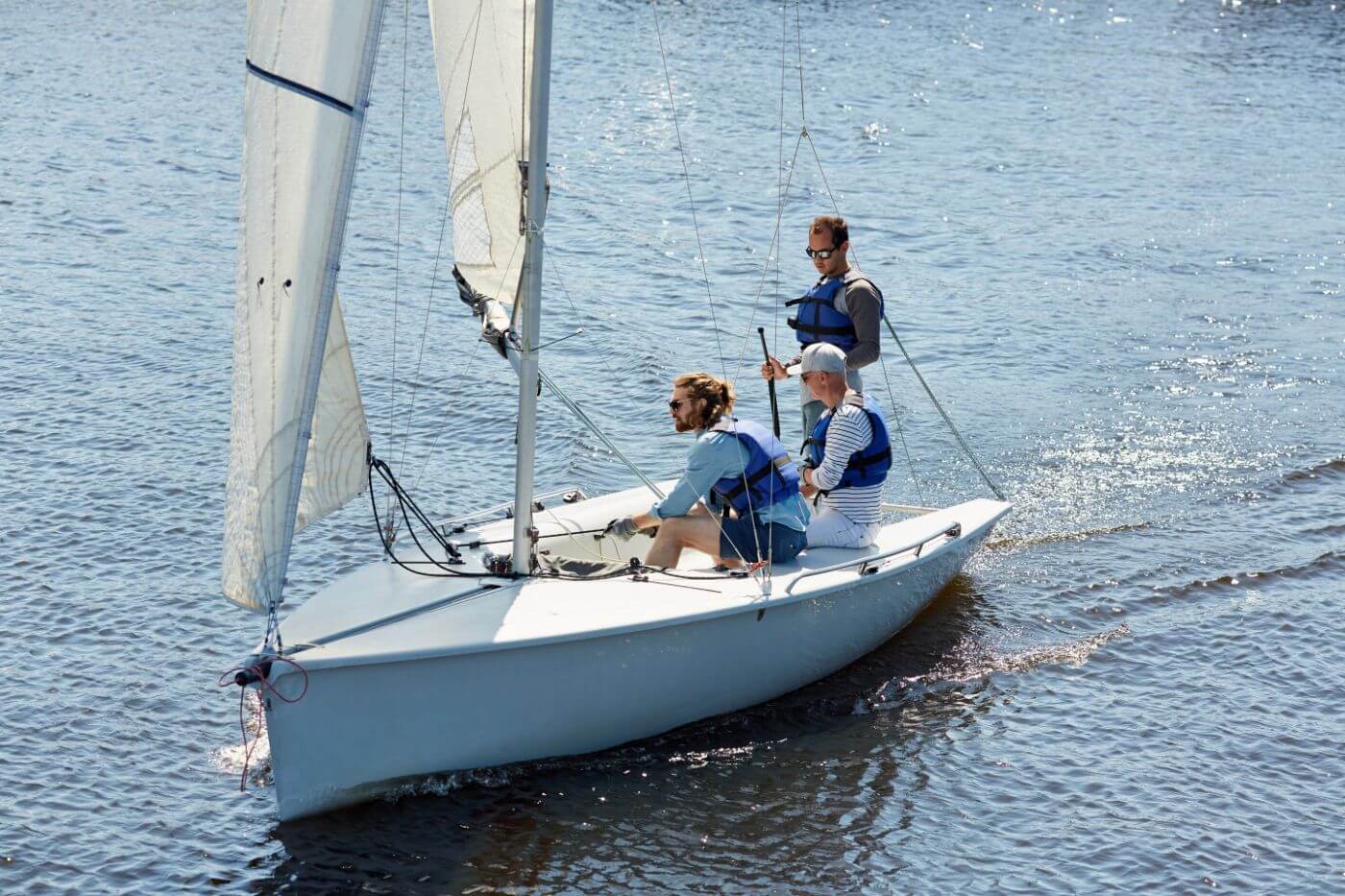

You can set sail within a couple of months
Learning to sail can take anywhere between 50 - 500 hours, depending on what level of skill you require. Coastal sailing and ocean passages require a lot more knowledge and experience. In contrast, you can learn to sail your recreational lake in light winds pretty quickly.
You can get started today
It's okay to not be the best sailor straight away. As with any skill worth learning, it's worth doing badly at first. As long as you don't get in anybody's way and stay safe, you can try and fail all you want. That's great because it means you can start today. You don't need hundreds of lessons before setting out on your own.
Some people like to pretend sailing is some mysterious superpower. Sure, doing something really well is always hard, and so is sailing really well. But in the end, we're just catching wind with a piece of cloth. Let's not make it harder than it is.

You probably don't even need a license
In some states, you don't need any licenses in order to sail your boat in inland waters. Most states only require you to take a short boater safety exam, which you can do online for roughly $50. After that, you're officially good to go. If you don't require to get a safety license, I still recommend getting one. It's so cheap and easy to get, and it's better to be safe than sorry.
I do recommend getting some basic training before hitting the waters, as operating a boat can be nerve-racking if you're new, and it's just safer if you know the basic rules of the road. More on how to do that later.
For coastal and international waters, you do need multiple licenses, which will take money and time to pass. But when first starting out, you probably want to gain a lot of experience on small bodies of water first.

Okay, so apparently you don't need a huge budget, you don't need dozens of licenses, and you don't need hundreds of lessons before sailing your first boat. You can start today, and nothing's holding you back - you probably get that by now. Except, something is holding you back. Where the heck do you start?
Well, let's start with learning the essential skills before doing anything else.
I have written a very simple approach to learn to sail for practically free (I have linked to it before). Besides being cheap, it's also a good overview of how to go about learning these essential skills. Here's the gist of it:
My 5-step bootstrap plan for new sailors
1. lay the theoretic groundwork.
- Start with free online introductory courses
- Read up on the essential knowledge on Improve Sailing
- Spend time playing Sailaway Sailing Simulator
- Read my recommendation for free courses here .
2. Test where you stand
Now that you have some theoretic knowledge, take two sailing lessons to test where you stand. Don't go overboard on lessons, just get a feel for how quick you learn and how much you know (or don't) already. That way, you don't break the bank and can change your plan accordingly.
3. Gain experience
Next, we want to make sure we have enough experience to stay safe and confident.
- If you are a quick learner , take a 1 or 2-day sailing course. This is a bit more expensive, but it pays off to spend a longer time with someone experienced.
- If you feel like you need more help at first, I recommend trying to become a ship's mate first. This is free and you learn a lot quickly. You can be a ship's mate for a day, a week, or an entire season.

4. Optional: get your license
If you need any licenses, be sure to get them now. In most states, you just need to take a basic boater's safety exam .
5. Set sail
Once you have the basic theoretic knowledge and practical experience, you can finally set sail on your own. I suggest hiring (chartering) a boat at first. This doesn't have to be expensive at all and is a great way to learn what you like and dislike.
General tips when setting sail for the first time
- Start with small boats (under 24') for better feedback
- Sail with light winds of 7 knots or less
- Start small and work your way up
- Safety is always your priority, speed comes second
Let's take a look at the precise skills you need to develop in order to become a good sailor. Below is a quick overview of essential skills and important information, and I'll link to which articles will help you out.

Essential sailing skills
- Marine navigation
- Weather interpretation
If you learn the fundamentals of these five skills, you should be able to stay safe while navigating through most situations. We'll walk through each of those skills, what it involves, and how to learn it below.
Other useful skills that are not essential at first are general boat maintenance, diagnosing electrical issues, and maintaining your boat's engine.
How to learn basic sailing skills
I recommend reading up on basic sailing skills. We have created a special page that shows you what articles we recommend when first starting out . Reading up on sailing skills might seem unnesseccary, but believe me, it really helps to boost your confidence if you have read about all those moving parts ahead of time. It will also save you precious lesson time.
NauticEd offers Basic Sail Trim as one of their free introductory courses , so I recommend taking that course, as well as playing Sailaway, which will really prepare you for trimming sails in real life.
Here's a great beginner sail trim video:
The most important way to learn basic sailing skills, of course, is going out and practising them on the water. I would want to have at least a basic grasp of sail trim and navigation before sailing single-handed (alone).
How to learn marine navigation
I recently wrote a complete guide on how to learn marine navigation . I suggest you start there - it's a very comprehensive guide and great for beginners. I specifically wrote it for people who don't know where to start. In it, I explain the fundamentals and link out to more in-depth articles, so you can explore on your own. Marine navigation is a skill you can train at home especially well.
How to learn anchoring
This is more of a practical skill, but I still recommend to read up on it first (it doesn't cost you anything). William has written a couple of solid articles on anchoring:
- 9 Easy Expert Tips for Anchoring a Boat Near Shore
- How Much Anchor Chain Should You Let Out When Anchoring?
- Can I Moor & Anchor My Boat Anywhere?

Essential knowledge
Even though sailing is a very hands-on skill, you do need some theoretical knowledge as well.
- Boat Safety Standards
- Rules of the Road - essential in avoiding collisions and dangerous situations
This information is included in one of the free introductory courses offered by NauticEd , and I believe ASA also has a free course on collision rules.
Useful knowledge
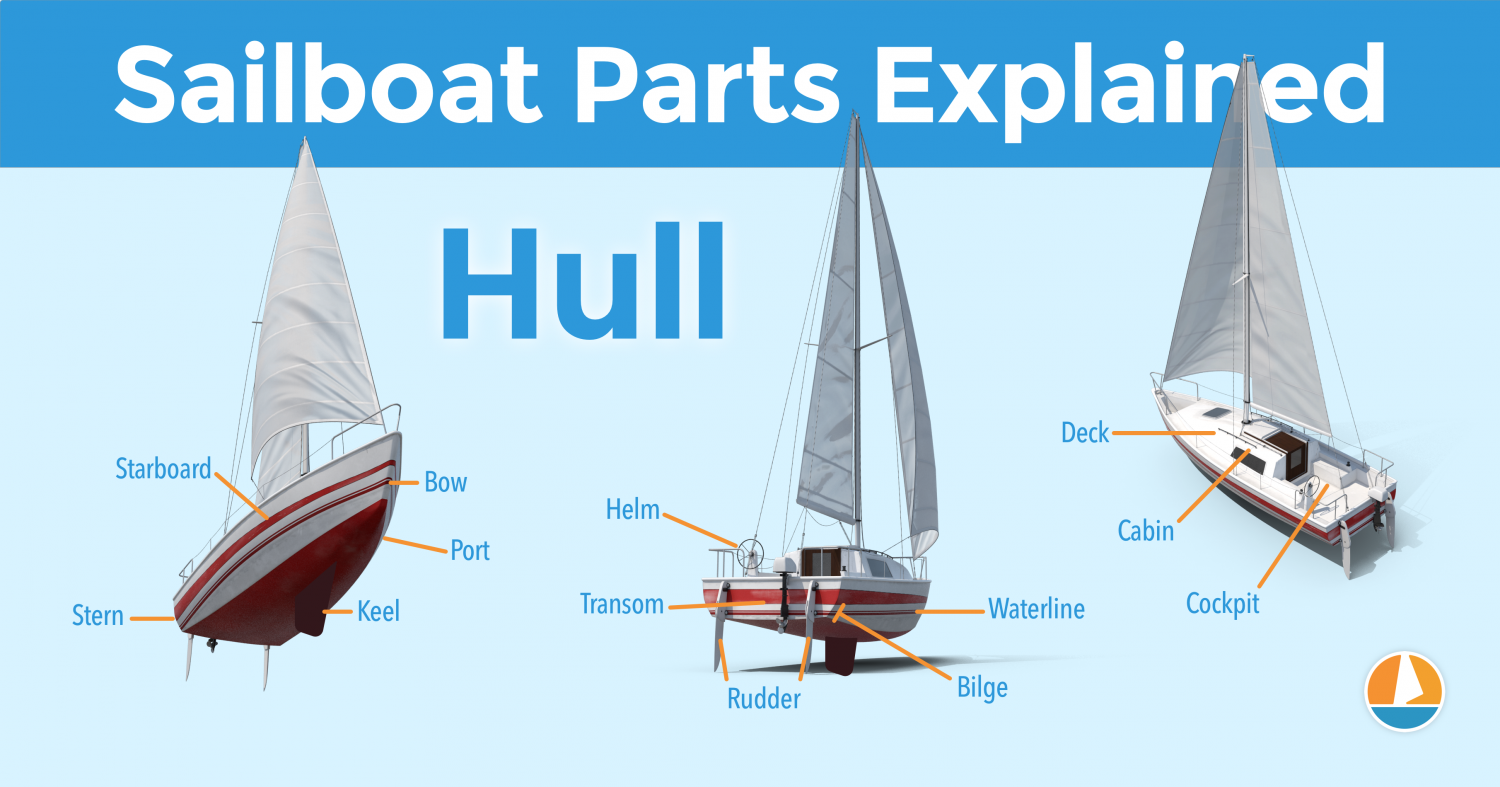
Besides this essential information, there are also things that are simply handy to know. It really pays to invest some time into learning the most important sailing terms. I recommend you learn the following at the least:
- Basic parts of sailboats - has great diagrams
- Basic sail names - illustrated guide with examples
- Most common sailing terms - extensive database
Understanding the basic names of things comes in handy when shouting orders at your crew (or being shouted at!), and avoiding any confusion. However, you can definitely sail a boat without knowing the name of everything on it.
There is some basic gear you probably want to have as a first-time sailor. Luckily, there isn't a lot of speciality stuff you have to have when renting your first sailboat.
- suitable shoes & clothing
- basic navigation tools
- optional: plotting tools

Suitable shoes
If you're just going out sailing for some odd days here and there, you only need suitable shoes to wear onboard. Or you could not wear any shoes at all, which is cheaper obviously. It can pay off to invest in something to protect your pinky toe.
- Here's What Shoes to Wear Sailing (and which not )
Sailing gloves
If you're planning on sailing more often, or longer days, you might want to consider getting a good pair of sailing gloves. Those will really help protect your hands from fatigue, blisters, and rope burn.
I highly recommend getting some kind of headwear. Make sure it has a strap or is a tight fit. Protecting yourself from the sun is important on the water. You get sunburn quickly.
Suitable clothing
You can wear regular clothing. Make sure to bring multiple layers, as temperatures on the water can change quickly. If you have clothes that are lightweight, comfortable, dry quickly, and optionally break wind, that's perfect. You could of course buy special sailing jackets, but these tend to be pricey, and you only really need them if you're on the water a lot.
Here's an expert tip: always bring dry clothes and wrap them in a plastic bag.
- Here's What to Wear Sailing in the UK
If you're looking for good quality sailing gear, I have articles on gear I like. You can check them out on the recommended gear section of this site. It has all the sailing gear I love most.
Navigation tools

When renting a boat, you want to bring some basic navigational tools:
- handheld magnetic compass
- nautical charts
Most people won't need plotting tools at first, but if you're planning on sailing longer legs, you might want to get them:
- parallel rulers
You might also need to show your skipper's license, or at least your boater's safety license.
Getting into sailing doesn't have to be complex at all. If you bookmark this article, you can get back to it (and the resources I link out to) and work your way through them in your own time. Taking your time to learn the fundamentals right first will greatly speed up your practical learning experience.
While sailing is a practical skill, and more traditional skippers will argue that you can't learn it on paper, I disagree. There is a lot of information that is especially suited to learn online or practice at home. By doing so, you'll feel more confident once you set foot on board. However, you probably shouldn't postpone bolstering your practical experience either. You want to see where you stand as quickly as possible. A lot of people put it off indefinitely, and if there's one thing true about the internet - actually, two -, it is this:
- You can keep reading indefinitely.
- It can't replace the real thing.
Instead, use it as a helpful resource to speed up the process and cut cost. It's a great place to do homework. But now, it's time to step aboard - good luck, and smooth sailing!
Leave a comment
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Water Sports
A Beginner's Guide to Sailing a Sailboat
Key Information for Beginners and Sailors
There are many ways to learn to sail:
- You can just jump in a boat with a friend and try to learn from experience
- You can sign up for a formal course at a sailing school
- You can buy or borrow a small sailboat and do it all on your own
No matter which way works best for you, it helps to understand the boat and what's involved in sailing first before you're out on the water, where suddenly you might get into trouble.
The Basic Steps of Sailing
Sailing involves both specific knowledge and skills. The following are the basic steps of learning to sail- as much as you can learn while not actually on a boat. You don't have to follow this order; skip ahead if you already know some of the basics. If you're mostly new to sailing, you might want to proceed through these steps like chapters in a manual.
- Understand Basic Sailing Terms. To get into sailing, you have to understand the words that are used to talk about the sailboat and the skills used to sail. Start here with a review of basic sailing terms. Don't worry about memorizing everything as many of these terms and concepts will become clearer as you read on about how to do it.
- Learn the Parts of the Boat. Before you go on the boat, it's helpful to know the words used in different parts of the boat. Even if you have an instructor, he or she won't say "Grab that rope over there and pull it," but instead will say "Haul in the jib sheet!" Review the basic boat terms you'll need to know.
- Start an Online Course. Now you're ready to learn more about what all those parts of the boat are used for. Here you can start an online learn-to-sail course by learning more about the parts of the boat along with a lot of photos, so you'll see what to do.
- Rig the Boat. Read to go sailing now? Hold it a minute- you have to rig the boat first by putting on sails and making other preparations. Here again are a lot of photos of what to do on a typical small sailboat used by beginners.
- Review Basic Sailing Techniques. OK, now you have the boat ready- so what do you do now to make it go? Manage the sails to go in the direction you want by learning basic sailing techniques.
- Discover How to Maneuver. Sailing in a set direction is reasonably easy, but eventually, you'll have to change direction. That often involves tacking and gybing. Take a moment to learn what's involved in these critical maneuvers.
- Recover From a Capsize. Now you've got the basics down. But did anyone ever tell you that small sailboats often tip over if the wind is gusting? Be prepared and carefully see how to recover from a capsize .
- Dock or Anchor the Boat. Now you're out there sailing and you've got the boat under control. Learn how to go faster, dock or anchor the boat and use some of the equipment you've ignored so far. Take a look at some of these additional sailing skills.
- Practice Tying Knots. For thousands of years, sailors have used times where it is cold or raining by doing things like tying knots. Knots are important on a sailboat and you will need to learn at least some basic sailing knots to sail at all.
- Sail Safely. At this point, plus practice on the water, you're good to go. However, it's good to remember that water is a dangerous place. Learn the basics about sailing safety. Staying safe makes it easier to keep having fun out there.
Related Articles
More related articles.

How to Sail: The Ultimate Sailing Guide for Beginners
Learning to sail can seem like a daunting process. Besides just learning how to sail a boat, the terminology of boating is completely different, and most of what needs to be learned can only be acquired by doing, meaning practice is required. But before you head out on the water, you can increase your knowledge by reading up on sailing , which will further help to keep you safe while on your boat. Discover our ultimate sailing guide for beginners !
(Guide via Jen Reviews )
Sailing Defined
Sailing is the art of taking a boat, turning off the motor, and harnessing the power of the wind to make the boat go where you want it to go. It might seem difficult, but it is really very simple, provided you take the time to understand how the boat utilizes the power of the wind. More than likely your boat will also have a motor (for times when there is no wind), but we will mainly focus on the actual process of sailing, and how that can be achieved.
Before you leave the dock
Before you head out on your own boat (or before you go to purchase a boat), search online and find the nearest sailing school or yacht club. You can find the local sailing school where you can take one on one sailing lessons, or even take an instructor out on your boat to show you the ropes, and how to safely sail. There are also free classes you can take online, which can better prepare you for learning the basics of sailing.

Make sure and check the weather before heading out. If there is a storm headed your way, or in the direction you want to go, it might be prudent to wait a few days until calmer weather is in the forecast. It also can be quite boring to head out on the water if there is no wind, as you will be forced to motor the entire time.

Dress for the weather, but be sure and bring lots of layers. Even if it’s hot out, while out on the water there is nothing to shield the wind, so it might seem colder than on land. Always have a jacket , hat, sunscreen, long pants and or shorts, shoes, and bring lots of water and snacks. Better to be over prepared than under prepared.

Make a Checklist
Make a checklist for necessary equipment you will want to bring with you on the boat (or even things that are US Coast Guard required). This could include items such as:
- Life Jackets
- Drinking water and snacks
- Sunglasses, hat, jackets, extra clothing
- Engine fuel and spare parts
- Chart ( handheld GPS as well)
- Bucket (can be used to bail water, clean off the boat, or as a restroom if need be)
- USCG required equipment for the boat
- Sound signals (whistle or fog horn)
- Fire extinguisher
- Visual distress signals (flares or flashlight at night )
- Navigation lights (required at night, or if visibility is reduced)
- Anchor and chain/line
- Extra line (mooring or various other uses)
- Fenders (Plastic hard ‘balloons’ that keep your boat from bumping on the dock)
- VHF radio and cellphone
- First-Aid Kit and booklet
- Tool Kit and Knife
- Lifesling or throwable buoy
- Radar reflector
- Ditch kit (full of life saving necessities in case you have to abandon ship)
- Life raft of some sort (depending on where you are sailing, and the size of your vessel)
These are all useful and necessary items to have stocked on your boat: some are required by the Coast Guard , and some are just common sense. It might also be helpful to bring a sailing buddy when you head out, to assist with docking, hoisting the sails, or just giving a second opinion in case something should occur.
Know your boat
Before heading out on the water, make sure and inspect as much of your boat as you can: understand where the lines (ropes) are going, how the sails are hoisted (lifted) and lowered, and where the safe places to walk or sit will be once you are out on the water. This article will discuss the basic terminology (with important words defined in bold), and try to explain as much as you need to know about the basic parts of your sailboat.
Let’s start with the simple terminology first .
When you get on your boat, and are facing towards the front of the boat, that would be forward, with everything behind you being aft. The very front of the boat is the bow, with the aft part of your boat called the stern. The left of the boat is the port side (think left and port both having four letters), with the right side being the starboard side. That seems simple, right? So let’s keep going.
The mast is the vertical pole that supports the sail. If you only have one big sail, there will only be one mast. Some boats have more than one mast, but sailboats always have at least one. The horizontal pole that comes off the bottom part of the mast is called the boom (which is also the sound it makes when it hits you in your head… be careful of this one!).
The tiller is a horizontal lever arm that turns the rudder (steers the boat), and is either by itself or is attached to the wheel, which is what you use to steer the boat. Standing in the boat you will be on the deck, but if you go inside the boat you will be below-deck. The sides of the boat are called the hull, and the draft is the distance from the surface of the water to the deepest part of the boat underwater (important to know if you don’t want to run aground).
The lines that hold up the mast on the starboard and port sides up to the top of the mast are called the shrouds, while the wire that runs from the mast to the stern is called the backstay, and the wire that runs from the mast to the bow is the forestay (also called the headstay). The beam is the width at the widest point of your boat, and the total length overall is the horizontal length from the tip of the stern to the tip of the bow (necessary to know depending on where you want to dock or store your boat).
It may seem like quite a few terms to know, but while being on a sailboat everything is called something different. But we are only concerned with the most important terms at the moment.
When you start putting up a sail, you will be pulling on a halyard . If you are putting up the mainsail (largest sail that is attached to the mast), you will be pulling on the main halyard. To let the sail move towards the starboard or port side of the boat, you will let out the main sheet (line that is attached to the bottom aft section of each sail, which moves it side to side). You may need to use a winch, which is a round drum that increases your power capabilities to pull on a line (rope).
Top 15 places sailing around Mediterranean Sea this summer
10 sailing tips essentials to make you a better sailor, taking your sailboat on holiday: a comprehensive guide to boat shipping, how to avoid a gybe broach – video tutorial, live your passion, subscribe to our mailing list.
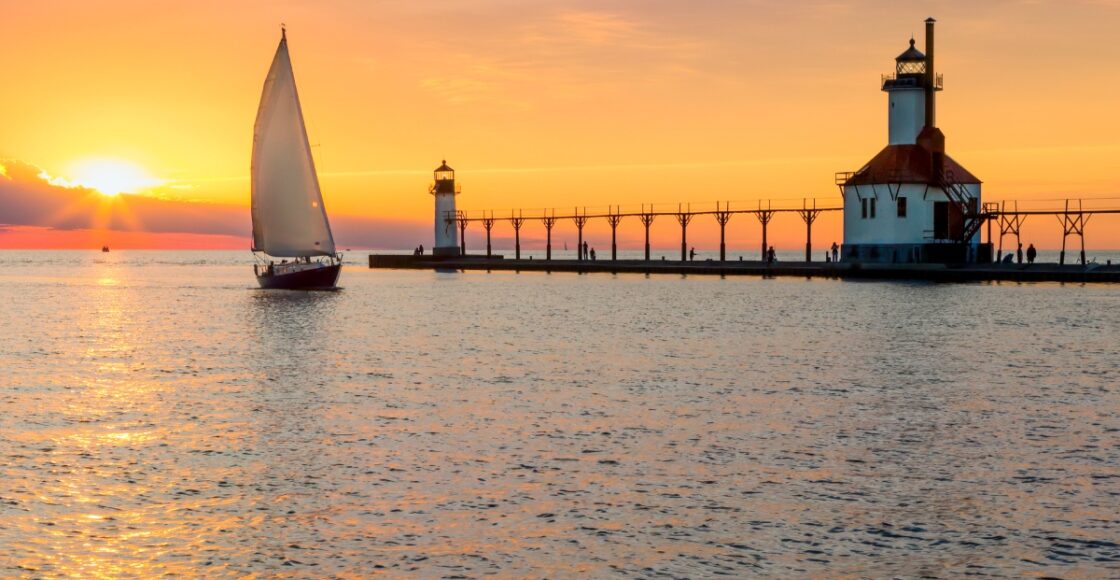

Lake Michigan Boating Guide

Table of Contents
Last Updated on August 23, 2024 by Boatsetter Team
With over 1,600 miles of coastline to explore, Lake Michigan can’t be beat for gunkholing, cruising, and sailboat racing. One of the five Great Lakes, this giant body of water is over 300 miles long, has more than 22,000 square miles of surface area, and borders four sates so there’s always somewhere to go and somewhere to rent a boat with a sharing service like Boatsetter. From Indiana to Chicago and Milwaukee to Mackinac, there are dozens of secluded anchorages, state parks, and charming waterfront towns to visit.
Where to Go

You could spend years of summers exploring all that Lake Michigan offers but if you have just a few days of boat rental each season, consider checking out some of these destinations.
Grand Traverse Bay is well-protected and generally calm even if Lake Michigan itself is less so. Learn about Ernest Hemmingway who was from the area or explore the town of Charlevoix that is split in two by a canal which leads to Round Pond and Lake Charlevoix. Bring or rent bikes and ride the 26-mile Little Traverse Wheelway for some exercise.
Visit scenic Door County in Wisconsin on the lake’s western shore. The Door County Lighthouse Festival is popular as are July 4 th fireworks in Egg Harbor. And you don’t want to miss the Sturgeon Bay Harvest Festival in late September. Harbor hopping in this area can’t be beat.

Beaver Island is the opposite of busy Mackinac. This remote island is 35 miles from Charlevoix on the mainland and tends to be a quiet respite with an unpretentious municipal dock and fun toy museum. The beaches are pristine and you won’t want to miss the Whiskey Point Lighthouse and the Beaver Head Lighthouse for their spectacular views. Check the weather before crossing from the mainland so you don’t get caught in 30-mile winds which are not uncommon here.
Activities & Highlights
Whether you’re in Milwaukee, Chicago, or Door County, there’s much to do during the summer including live music, wine tastings and art festivals. One big draw is the Chicago Air & Water Show that takes place in August and on a boat, you’ll have front row seats to the action. Another can’t miss event is the Playpen boat party which is like a giant tailgate party for boaters that draws in excess of 800 boats in late July.
There are also sailing regattas like the famous “Mac” race that runs from the Chicago Yacht Club to Mackinac Island. This race takes place in July, is over 300 miles long, and over 125 years old. Join the sailboat send off in Chicago or welcome them at the finish line at the island and partake of all the activities and celebrations on both sides of this classic event.
Lake Michigan is long and it can build up seriously large waves when a northerly wind runs along its entire length. Always check the weather before departing, especially if you’ll be boating farther south around Chicago where the weather and sea state can get gnarly. Freshwater forms steeper waves than saltwater because it’s less dense and running into a wall of square waves is no fun.
It can also get very cold in winter with temps below freezing in January near the Windy City. Target to rent a boat in the area from May to October but be ready to change course or cruising plans, especially in spring and fall when the weather may be iffy. Dress appropriately, bring lots of layers, pack flashlights in case you’re caught out after dark, and don’t forget some extra food and water.
Rules & Regulations
There are a few things to know before you untie the dock lines. Like in most other states, the Coast Guard requires all children under 13 to wear a lifejacket when aboard a vessel under way, and there must be a sufficient number of PFDs for the rest of the people aboard as well. You as the operator, cannot bring the boat within 150 feet of a person in the water for safety reasons – unless you’re participating in watersports.
Also, Lake Michigan is located in its entirety within the United States which means there are no check-in requirements for Canadian immigration or customs. You’ll have a bureaucracy-free run of the whole lake.
Serious Boating
Just because it’s called a lake doesn’t mean you should take it less seriously than coastal boating on the ocean. The Great Lakes are massive bodies of water and Lake Michigan can be nearly 200 miles across so it will take some time to traverse. Be boating savvy and prepared. All this said, there are great anchorages, wonderful beaches, and much to do on its shores so book a boat and have fun all summer long
Boatsetter is the leading online marketplace for boat rentals and on-water experiences. Download the Boatsetter app ( App Store | Google Play ) and follow us on Instagram .

Zuzana Prochazka is an award-winning freelance journalist and photographer with regular contributions to more than a dozen sailing and powerboating magazines and online publications including Southern Boating, SEA, Latitudes & Attitudes and SAIL. She is SAIL magazines Charter Editor and the Executive Director of Boating Writers International. Zuzana serves as judge for SAIL’s Best Boats awards and for Europe’s Best of Boats in Berlin.
A USCG 100 Ton Master, Zuzana founded and manages a flotilla charter organization called Zescapes that takes guests adventure sailing at destinations worldwide.
Zuzana has lived in Europe, Africa and the United States and has traveled extensively in South America, the islands of the South Pacific and Mexico.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

10 Best Gift Ideas for Anglers for 2023

Zachary Shares How His Sons Amplify His Love For The Water

5 Best Lake Minnetonka Restaurants on the Water

7 Best Places to Catch a Florida Sunset this Fall
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- Email Newsletters
- Boat of the Year
- 2024 Freshwater Boat and Gear Buyers Guide
- 2024 Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Water Sports Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Pontoon Boat Buyers Guide
- Cruising Boats
- Pontoon Boats
- Fishing Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- Water Sports
- Boat Walkthroughs
- What To Look For
- Watersports Favorites Spring 2022
- Boating Lab
- Boating Safety
- Ultimate Boat Giveaway

Guide to LED Pontoon Boat Lights
- By Elliott Stark
- August 20, 2024

Whether on the lake, river or bay, nothing packs a party quite like a pontoon boat. Recent advancements in LED lighting take the pontoon boat party to a whole new level. What follows is our take on dialing in your pontoon boat led lighting setup.
What Lights Does a Pontoon Boat Need?
Like all vessels, the right pontoon boat LED lighting setup involves a combination of lights that you’re required to have and those that make the experience more fun. Whether navigation lights, spreader bars, underwater lighting or light strips around the deck, LED lights are functional, versatile and quite a bit of fun.

LED setups offer a number of customization possibilities. For instance, they may be:
- Dimmable: You can control and adjust the brightness and lumen output via apps on your marine electronics or smartphone.
- Multi-color changing: The same bulb can produce an incredible variety of colors. Previous lighting options, if they had the ability to change color at all, were extremely limited.
- Syncable with sound: With the right setup and installation, you can make the lights on your pontoon boat change in brightness and color to music. LED light strips like these are really cool for kids and adults alike.

Lighting for Pontoon Boats: Legal Requirements
The exact lighting setup you will need depends on the length of your pontoon boat. Be sure to check the legal requirements for your situation. The requirements include the number of lights, angle of light emitted, and visible range of the light.
At its most basic, your pontoon boat needs the following:
- Masthead lights: These are typically white lights that are mounted in a place that is visible to other boats. This base-mounted, fold down LED pole light is a great example.
- Navigation lights: These are the classic red and green lights mounted on the bow of your boat. In addition to being required by law, they let other vessels know which direction you are traveling at night.
- Stern lights : You also need stern lights mounted on the back of your boat and an all-around light.

‘Nice-to-Have’ Lights for a Pontoon Boat
Beyond the lights required by law, you can outfit your pontoon with an incredible variety of exciting LED lighting options. Consider illuminating the dock, installing courtesy lights along pathways and steps, and adding submersible underwater LED lights .

You also have many options when it comes to deck lighting. For instance, you can mount a series of recessed LED lights along the walls or beneath the covering boards. You can also mount an LED light strip to run the length of your pontoon boat.

Other great varieties of pontoon boat LED lights include:
- Spreader lights to illuminate where you’re going
- Utility livewell lights
- Tube lights that light the console
Boating’s Top Spotlights for Boaters provides a breakdown of spotlight options for your pontoon boat.

Benefits of LED Lights for Pontoon Boats
LED lights for pontoon boats provide a wide ranging number of benefits. They provide a significant energy savings and produce less heat than other forms of lighting.
The primary benefits include:
- Energy efficiency : LED lights draw less battery power to produce the same number of lumens than do halogen or incandescent lights.
- Longevity and durability : When properly maintained, LED lights last longer and stand up to the elements. If you do need to replace a bulb, they’re more consistent between lights than other types of lighting.
- Brightness and visibility : LED lights produce more light in smaller packages than other types of boat lighting.
- Versatility in color: LED lighting systems allow you to customize the color of your boat’s lighting. You can also control many LED light kits with apps.

Installing Pontoon Boat LED Lights
Just as there are many LED lighting products, you have a range of installation options. Hire a professional, or install them yourself. Integrate all your pontoon boat LED lights into a single circuit, or install and control them individually.
Check out the 2024 Pontoon Boat Buyer’s Guide for some design inspiration. This review of the SunCatcher Elite provides some additional perspective.
Marine Mounting Considerations
Where and how you mount your LED lighting systems depends on your boat’s setup and the look you’re after. You can install a series of individual recessed lights or mount an LED strip on a track .

Professional vs. DIY Pontoon Light Installation
Most LED lighting systems are wired into your pontoon boat’s battery system. If you are technical, you may be able to install a new lighting system or modify the one you have.
Professional installation is a great option, too. Professionals understand your boat’s voltage (and can make sure to install the appropriate lights). Most LED manufacturers make them in 12V and 24V options.
How you install LED lights on your pontoon boat also depends on how complex and feature-rich you’d like your system to be. When you start including dimmability and app control, or integrating different LED lighting components, the installation gets more complex.
Maintaining LED Pontoon Lights
When properly maintained, your pontoon boat LED lighting system will last a long time. Clean and dry the lights after use to keep them in ship shape. Make sure that your connections are secure and that the wiring and batteries stay dry.
If you use your pontoon boat in saltwater, take extra care to avoid corrosion. Also, be sure to test your navigation lights before you leave the dock. Being in the middle of the lake at night is no time to find out that your lights are out.
Make a Safe Investment in LED Pontoon Boat Lights
So you’ve got your pontoon boat. You know the many benefits of LED lighting setups. Now it’s time to bring a fully customized, brighter LED setup to the biggest party on the water. Pontoon boats are great. They’re even better with LEDs.
What lights should be on when boating at night?
You’ll need navigation lights (a red and green light on the bow), stern lighting on the back of your boat, a masthead light, and an all-around light. These are the basics, and you can of course add to this.
Where do the lights go on a pontoon boat?
To satisfy the law, you’ll need lights on the bow, on the stern, and atop the console. From there, you could illuminate the deck, any steps, and maybe even beneath the water’s surface under your pontoon boat. Where you place them depends on the design you’re after.
Will lightning strike a pontoon boat?
Any time you are on the water, you should be aware of the weather. If there is lighting in the vicinity, you should consider heading to shore. Lighting can strike boats of all kinds, pontoon boats included.
- More: Affiliate , Gear , Lighting , Pontoon Boats

Choosing the Right Tools for Boat Repairs

What Are the Best Trolling Motor Batteries for Your Needs?

ReLiOn RB100-HP Starting Battery

Boating’s Deals of the Week

Installing Retractable Transom Straps

Decoding the Horsepower Ratings of Electric Motors

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Boating may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Boating Firecrown . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
- Santiago de Chile
- Santiago de Compostela

Bosphorus Boat Tour with an English Speaking Guide
Cruise along the Bosphorus and enjoy the stunning landscape of Istanbul with an English-speaking guide
Thank you! Your support means more to us than we can express in words. Chris Sandeman and the SANDEMANs Live Community
Give anything you want
Wrong price format. Please enter a valid price.
Please enter a price greater than 0.
Payment is secured with

Great choice! Your favorites are temporarily saved for this session. Sign in to save them permanently, access them on any device, and receive relevant alerts.
- Sailboat Guide
1985 O'day 35
- Description
Seller's Description
If you’re looking for a capable and spacious vessel, this 1985 O’day 35 is an excellent option. It’s equipped for smooth navigation with a Raymarine e7D chartplotter connected to an EV-100 Autopilot, i50 Depth, i50 Boat Speed, and i60 for wind speed and direction.
The autopilot can maintain the point of sail, even with shifting winds. The Furlex 200S make it easier to manage and deploy sails, especially in changing wind conditions
The boat’s spacious cockpit, comfortable cabin, galley area, head compartment and ample storage compartments make it a great choice for any avid sailor. Additionally, it comes with Atwood EHM 6SM water heater.
Rig and Sails
Auxilary power, accomodations, calculations.
The theoretical maximum speed that a displacement hull can move efficiently through the water is determined by it's waterline length and displacement. It may be unable to reach this speed if the boat is underpowered or heavily loaded, though it may exceed this speed given enough power. Read more.
Classic hull speed formula:
Hull Speed = 1.34 x √LWL
Max Speed/Length ratio = 8.26 ÷ Displacement/Length ratio .311 Hull Speed = Max Speed/Length ratio x √LWL
Sail Area / Displacement Ratio
A measure of the power of the sails relative to the weight of the boat. The higher the number, the higher the performance, but the harder the boat will be to handle. This ratio is a "non-dimensional" value that facilitates comparisons between boats of different types and sizes. Read more.
SA/D = SA ÷ (D ÷ 64) 2/3
- SA : Sail area in square feet, derived by adding the mainsail area to 100% of the foretriangle area (the lateral area above the deck between the mast and the forestay).
- D : Displacement in pounds.
Ballast / Displacement Ratio
A measure of the stability of a boat's hull that suggests how well a monohull will stand up to its sails. The ballast displacement ratio indicates how much of the weight of a boat is placed for maximum stability against capsizing and is an indicator of stiffness and resistance to capsize.
Ballast / Displacement * 100
Displacement / Length Ratio
A measure of the weight of the boat relative to it's length at the waterline. The higher a boat’s D/L ratio, the more easily it will carry a load and the more comfortable its motion will be. The lower a boat's ratio is, the less power it takes to drive the boat to its nominal hull speed or beyond. Read more.
D/L = (D ÷ 2240) ÷ (0.01 x LWL)³
- D: Displacement of the boat in pounds.
- LWL: Waterline length in feet
Comfort Ratio
This ratio assess how quickly and abruptly a boat’s hull reacts to waves in a significant seaway, these being the elements of a boat’s motion most likely to cause seasickness. Read more.
Comfort ratio = D ÷ (.65 x (.7 LWL + .3 LOA) x Beam 1.33 )
- D: Displacement of the boat in pounds
- LOA: Length overall in feet
- Beam: Width of boat at the widest point in feet
Capsize Screening Formula
This formula attempts to indicate whether a given boat might be too wide and light to readily right itself after being overturned in extreme conditions. Read more.
CSV = Beam ÷ ³√(D / 64)
Similar to O’DAY 34 but with swim ladder on extended stern which accounts for extra length. Shoal draft: 4.25’/1.29m See O’DAY 34.
This listing is presented by PopYachts.com . Visit their website for more information or to contact the seller.
View on PopYachts.com
Embed this page on your own website by copying and pasting this code.
- About Sailboat Guide
©2024 Sea Time Tech, LLC
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Perfect Looping Boat for Your Family Find the boat that best suits your family's needs and cruising plans for America's Great Loop.
Learn about the different types of sailboats, their origins, and what they're used for. Compare monohulls, multihulls, and various rig types, and find out their strengths and weaknesses.
17 Sailboat Types Explained: How To Recognize Them Written by Shawn Buckles Sailed a Cornish Crabber across the great Dutch lakes in Beginner Info
The Perfect Looping Boat for Your Family Find the boat that best suits your family's needs and cruising plans for America's Great Loop.
Explore the ultimate sailboat guide for 2024. Discover tips on choosing the perfect sailboat, maintenance advice, and sailing destinations.
Learn how to choose the best sailboat for your needs and preferences from this comprehensive guide. Compare different types, styles, sizes, materials and features of sailboats and find out what suits you best.
Learn about the basics of sailboat design, including hull types, keel types, and mast configurations. Explore the different rig types and sail types used on various sailboats and how they affect sailing performance and handling.
It's a good idea to consider the popularity of a sailboat before choosing. Common sailboats have lots of user data available on sailing forums, so you can get an idea of how it handles.
Small sailboats are perfect for kids to sail on, and massive sailboats are used to cross oceans in style. In between, there are daysailers, racers, and cruisers.
The term sailboat includes many different sizes, shapes, and hull types. Here's how to identify most of the common ones.
Learn everything you need to know about sailboats, from the different types of sails and hulls to the fastest and most luxurious models. Find out how to choose the right sailboat for your needs and budget, and how to operate it safely and enjoyably.
With good sails, great design, and regular maintenance, sails and rigs are an important part of a sailboat.
Sailboat Guide is a comprehensive and accessible database of sailboats ever built, with data on 7874 sailboats, 751 yacht builders, and 558 yacht designers. You can discover your dream boat, learn about its history, and find techniques and gear to improve your boat.
How to sail a boat. Here's a step-by-step beginners guide to sailing. Learn about parts of a sailboat, sailing terms, sailing lines and wind direction.
A veteran sailing writer and experienced cruising and racing sailor explains the basics needed to get you out on the water and under sail.
A book by John Vigor that compares 20 old fiberglass sailboats that are seaworthy, cheap, and suitable for ocean crossings. Learn about their designs, handling, weaknesses, and tips from experienced owners.
The Average Cost of Buying & Owning a Sailboat I have compared thousands of sailboat prices, and the cost of ownership. In this guide, we'll go over every dollar it will cost to own a boat. If you are unsure what it costs to buy and own a boat (and what's possible on your budget), this is a great resource for you.
Here's what you need to know to get out there and sail. Learn the basic steps of sailing in ten simple steps, from rigging the boat to tying knots.
The first step to becoming a sailor starts with knowing the rules and basic vocabulary associated with sailing and then moving on to more hands-on training with your sailboat. Sailing is one of the most invigorating sports or hobbies out there; almost everyone has dreamed of sailing the seas at one time or another.
SailboatData.com …is a database that contains information on over 9000 production and semi-production sailboats dating back to the late 1800's.
Besides just learning how to sail a boat, the terminology of boating is completely different: read our ultimate sailing guide.
Explore 99 sailboats with rich histories and offshore capabilities in this collection by Sailboat Guide. Find detailed summaries, design and construction features, and sailing characteristics of each blue water boat.
The Recipe Guide Gravy Boat is a stunning addition to your dining table. Made from high-quality glass, this gravy boat exudes elegance and sophistication. Its unique feature is the recipe guide exterior, which adds a touch of charm and functionality. Measuring at 4" x 7 1/2", this gravy boat is the perfect size to hold and serve your delicious ...
With over 1,600 miles of coastline to explore, Lake Michigan can't be beat for gunkholing, cruising, and sailboat racing. One of the five Great Lakes, this giant body of water is over 300 miles long, has more than 22,000 square miles of surface area, and borders four sates so there's always somewhere to go and somewhere to rent a boat with ...
Lighting on your pontoon boat can enhance safety and ambiance. Boating Magazine. Whether on the lake, river or bay, nothing packs a party quite like a pontoon boat. Recent advancements in LED lighting take the pontoon boat party to a whole new level. What follows is our take on dialing in your pontoon boat led lighting setup.
Bosphorus Boat Tour with an English Speaking Guide. Cruise along the Bosphorus and enjoy the stunning landscape of Istanbul with an English-speaking guide. Homepage. Tours. Istanbul. Bosphorus Boat Tour with an English Speaking Guide. View photos. TOUR SCHEDULES MAP. Book this tour. Adult: € 15.
The higher a boat's D/L ratio, the more easily it will carry a load and the more comfortable its motion will be. The lower a boat's ratio is, the less power it takes to drive the boat to its nominal hull speed or beyond. Read more. Formula. D/L = (D ÷ 2240) ÷ (0.01 x LWL)³ D: Displacement of the boat in pounds. LWL: Waterline length in feet