

What is a Properly Lit Sailboat at Night? (A Guide to Safety Regulations)

Have you ever been out on the open water and seen a sailboat with its lights on at night? It’s a beautiful sight to behold.
But did you know that there are specific safety regulations in place for properly lit sailboats? In this guide, we’ll be looking at the importance of having a properly lit sailboat, what types of lights are needed, how to install them, and how to test for proper operation.
Let’s get started and learn how to stay safe on the waters!
Table of Contents
Short Answer
A properly lit sailboat at night is a boat that is equipped with the correct navigation lights, which are required by law.
These lights must be visible for two miles and should include a green light on the starboard side, a red light on the port side, and a white light aft.
Additionally, the boat must also have a white masthead light that is visible for three miles.
The masthead light should be mounted at least two meters above the hull.
What Are the Safety Regulations for Properly Lit Sailboats?
When it comes to sailing at night, safety is of the utmost importance.
Properly lit sailboats ensure that they are visible to other boats, which reduces the risk of collisions and other accidents.
In order to ensure that a sailboat is properly lit at night , there are certain safety regulations that must be followed.
First and foremost, the sailboat must have the correct lighting equipment installed and in good working order.
This includes running lights (red and green lights found at the bow and stern of the vessel), an anchor light (a white light mounted on the masthead or the bow of the vessel), a stern light (a white light placed at the stern of the vessel), and a masthead light (a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel).
The running lights, anchor light, and stern light must be visible for at least 3 miles in clear conditions.
This allows other boats on the water to easily spot the sailboat, even in the dark.
The masthead light must be visible for at least 2 miles in clear conditions.
This ensures that the sailboat is easily seen from all directions.
In addition to having the correct lighting equipment, sailboats must also be equipped with a white all-round light.
This light must be visible for at least 2 miles in clear conditions and must be mounted on the mast at least 9 meters (or 30 feet) above the waterline.
The all-round light is an important part of a sailboats lighting system as it allows other boats to easily spot the sailboat from any direction.
These are just a few of the safety regulations that must be followed when it comes to properly lit sailboats.
Following these regulations will help to ensure that a sailboat is visible to other vessels on the water and will help to reduce the risk of accidents and collisions.
It is important that all sailors understand and adhere to these regulations in order to remain safe on the water.
Types of Lights Needed for Proper Lighting

When it comes to lighting a sailboat at night, there are a few key components that must be in place in order to ensure the safety of the vessel and the crew.
The most important of these components is the correct type of lighting equipment.
This includes various running lights, anchor lights, masthead lights, and stern lights.
Running lights are the red and green lights that are mounted on the bow and stern of the vessel, and are used to show the direction of travel of the boat.
They must be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions, making it easier to spot the boat in the dark.
Anchor lights are white lights that are mounted on the masthead or the bow of the vessel, and are used to show that the boat is anchored.
They must also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
The stern light is a white light placed at the stern of the vessel.
This is used to show the direction of travel of the boat and should also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
Finally, the masthead light is a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel.
This light is used to help identify the boat to other vessels on the water, and must also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
Having all of these lights in good working order is essential for the safety of the boat and the crew.
It is important to make sure that all lights are visible from a distance of 3 miles in clear conditions, as this will make it easier to identify the boat in the dark.
It is also important to make sure that all lights are regularly inspected and maintained in order to ensure that they are in good working order.
How to Install the Lights
Installing the lights for a properly lit sailboat at night is an essential part of staying safe while sailing.
It is important to ensure that all of the lights are in good working order and that they meet the safety regulations for visibility.
The first step is to select the right lights for your vessel.
There are two main types of lights running lights and anchor lights.
Running lights are the green and red lights found at the bow and stern of the vessel, while anchor lights are white lights mounted on the masthead or bow of the vessel.
Once the lights are selected, the next step is to install them.
Start by attaching the anchor light to the masthead or bow of the vessel.
The anchor light should be securely mounted and wired in accordance with the manufacturers instructions.
Next, attach the stern light at the stern of the vessel.
This should also be securely mounted and wired in accordance with the manufacturers instructions.
Finally, attach the running lights.
These should be mounted at the bow and stern of the vessel.
It is important to test the lights after installation to make sure they are working properly.
Make sure that the lights meet the visibility requirements of 3 miles in clear conditions, as this is the minimum distance that the lights must be visible from.
Once the lights are installed and tested, youre ready to set sail in the dark!
Importance of Properly Lit Sailboats

When it comes to sailing, safety is of the utmost importance.
This is why it is essential for all sailboats to be properly lit at night.
Having the correct lighting equipment installed and in good working order is a critical component to ensure visibility and the safety of everyone on the water.
Not only does having properly lit sailboats maintain the safety of the sailors on the boat, but it also helps to prevent collisions with other vessels.
It is much easier to spot a sailboat on the water at night when it has the correct lighting equipment, such as running lights, anchor lights, stern lights and masthead lights.
All of these lights should be visible for at least 3 miles in clear conditions, making it much easier to spot a sailboat on the water.
Additionally, having properly lit sailboats at night is also important for law enforcement and marine patrol officers.
It makes it easier for them to identify and inspect boats, ensuring that all safety regulations are being followed.
This helps to keep the waterways safe for all boaters.
For these reasons, it is important for all sailboats to be properly lit at night.
By having the right lighting equipment installed and in good working order, it can help to maintain the safety of everyone on the water, as well as help to prevent collisions with other vessels.
It also makes it easier for law enforcement and marine patrol officers to identify and inspect boats, helping to keep the waterways safe for all boaters.
Different Types of Lights and Their Functions
When it comes to lighting a sailboat at night, there are several different types of lights that must be installed and in good working order in order to ensure the safety of the vessel and its occupants.
The most common types of lights used on sailboats are running lights, anchor lights, stern lights, and masthead lights.
Running lights are the green and red lights found at the bow and stern of the vessel.
These lights are typically used to signal the direction of the boats movement, and must be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
The green light is typically placed on the port side (left side) of the boat, and the red light is placed on the starboard side (right side).
Anchor lights are white lights mounted on the masthead or bow of the vessel.
They are used to indicate that the boat is at anchor, and must also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
Stern lights are white lights placed at the stern of the vessel.
These lights indicate the boats direction of travel, and must be visible for 2 miles in clear conditions.
The masthead light is a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel.
This light is typically used in conjunction with the stern light to indicate the direction of travel, and must be visible for 2 miles in clear conditions.
In addition to these lights, boats may also be fitted with a variety of other lights such as tricolor lights, sidelights, all-round lights, and deck lights.
These lights are typically used to indicate the presence of the vessel in low-visibility conditions, and must be visible for 2 miles in clear conditions.
It is important to ensure that all lights on a sailboat are in good working order and visible from a distance in order to make the vessel visible to other boats and comply with safety regulations.
A properly lit sailboat at night is one that has the correct lighting equipment installed and in good working order.
Benefits of Properly Lit Sailboats

Having a properly lit sailboat at night is essential for staying safe on the water.
With the right lighting equipment installed and in good working order, you can be easily seen by other vessels and prevent possible collisions.
Additionally, having the right lights on your sailboat can help other boaters determine your vessels size, direction, speed, and even your intentions on the water.
Having the right lights can also give you a sense of security while youre out at night.
Knowing that youre visible to other vessels reassures you that youll be able to be seen and spotted if you need assistance or if theres an emergency.
When youre out on the water at night, having a properly lit sailboat can also make navigation easier.
By having the correct lighting equipment installed, youll be able to easily spot buoys, markers, and other vessels, making it easier for you to stay on course and reach your destination in a timely manner.
Having the proper lights also helps to keep your sailboat in compliance with safety regulations.
If youre stopped by the coast guard or other law enforcement, having the right lights can help to avoid any potential fines or penalties.
Overall, having a properly lit sailboat at night is essential for staying safe on the water.
Not only does it make it easier for other vessels to spot you, but it can also help with navigation and make sure that youre in compliance with safety regulations.
Properly lit sailboats can also give you a sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that youre visible to other vessels in the area.
How to Test Lights for Proper Operation
Testing lights on a sailboat at night is an important part of ensuring that the craft is properly lit and visible to other vessels.
It is essential for safety, as well as compliance with regulations set by the United States Coast Guard.
Before each voyage, it is important to inspect all of the lights and make sure that they are in proper working order.
The first step to testing lights is to turn them on and check that they are functioning correctly.
It is important to make sure that all of the required lights are present and that they are bright enough to be seen in clear conditions for up to 3 miles away.
The running lights should be a green light at the bow and a red light at the stern, while the anchor light should be a white light mounted on the masthead or the bow of the vessel.
The stern light should be a white light placed at the stern, and the masthead light should be a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel.
Another important step in testing lights is to make sure that they are not obstructed in any way.
This includes checking for any wires, cables, or other objects that could block the lights from being visible.
This is especially important for the masthead light, as it needs to be accessible in order to be seen from a distance.
It is also important to check the wiring of the lights to make sure that they are securely connected and not corroded or damaged.
Finally, it is important to check the bulbs of the lights to make sure that they are all functioning correctly.
It is important to check the wattage of the bulbs to make sure that they are bright enough to meet the standards set by the United States Coast Guard.
It is also important to make sure that the bulbs are not cracked or damaged in any way, as this could affect their visibility.
Following the steps outlined above will help to ensure that all of the lights are in proper working order and can be seen from a distance in clear conditions.
This is important for safety, as well as compliance with regulations set by the United States Coast Guard.
Final Thoughts
Having the correct lights installed and in proper working order on your sailboat is essential for safety and visibility on the water at night.
Knowing what type of lights you need, how to install them, and how to test them for proper operation is key.
While it may seem daunting to install and maintain all these lights, the benefits of having a properly lit sailboat at night far outweigh the effort.
So take the time to review safety regulations, and make sure you have the right lights installed and operating correctly to ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
James Frami
At the age of 15, he and four other friends from his neighborhood constructed their first boat. He has been sailing for almost 30 years and has a wealth of knowledge that he wants to share with others.
Recent Posts
When Was Banana Boat Song Released? (HISTORICAL INSIGHTS)
The "Banana Boat Song" was released in 1956 by Harry Belafonte. This calypso-style song, also known as "Day-O," became a huge hit and remains popular to this day for its catchy tune and upbeat...
How to Make Banana Boat Smoothie King? (DELICIOUS RECIPE REVEALED)
To make a Banana Boat Smoothie King smoothie at home, start by gathering the ingredients: a ripe banana, peanut butter, chocolate protein powder, almond milk, and ice. Blend the banana, a scoop of...
Sailboat Navigation Lights: A Guide to Safe Nighttime Sailing
by Emma Sullivan | Jul 26, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance

==Short answer sailboat navigation lights:== Sailboat navigation lights are essential safety features that help vessels communicate and avoid collisions at night. These lights, such as the red and green sidelights and white stern light, allow sailors to determine the direction and status of approaching boats.
Understanding the Importance of Sailboat Navigation Lights
Sailing, with its air of romance and adventure, is a timeless pursuit that has captured the hearts of seafarers for centuries. While sailing enthusiasts revel in the sense of freedom and connection with nature that this activity provides, it is crucial to recognize that safety should always be a top priority when out on the open water. Among the many precautions taken to ensure safe navigation, sailboat navigation lights play an essential role.
These lights serve as beacons in the darkness, guiding both sailors and other vessels on their watery voyages. They are particularly vital during low visibility conditions such as fog, twilight, or nightfall when discerning a sailboat’s presence can be challenging. By understanding the importance of sailboat navigation lights, sailors can take proactive steps towards avoiding collisions and mishaps while enjoying their time at sea.
First and foremost, these lights serve as a communication tool between vessels. Just as traffic signals guide drivers on roads, sailboat navigation lights communicate a vessel’s navigational status to others nearby. These lights convey critical information about a boat’s direction of travel and whether it is under power or relying solely on wind propulsion. This enables other boats to predict potential collision courses and adjust their own paths accordingly.
In terms of regulatory compliance, having properly functioning navigation lights is not just recommended; it is required by international maritime laws like The International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGS). These regulations provide clear guidelines for different types of watercraft around the world to standardize safety measures. Following these rules ensures that every sailor speaks the same language when at sea, diminishing misunderstandings and encouraging mutual respect among mariners.
Furthermore, sailboat navigation lights contribute significantly to situational awareness – an invaluable asset in any seafaring endeavor. By displaying specific colors and configurations such as red/green sidelights and a white stern light visible from 135 degrees, sailors can discern the orientation of approaching vessels even in complete darkness. This knowledge empowers sailors to make informed decisions about altering their course or speed to avoid potential dangers.
In addition to enhancing navigation safety, sailboat navigation lights also add a touch of elegance and charm to nighttime voyages. Picture yourself sailing under a summer moonlit sky, with the soft glow of your vessel’s navigation lights casting mesmerizing reflections on the water’s surface. These lights not only provide reassurance but also create an enchanting ambiance for both sailors and onlookers.
While it may be tempting to dismiss the importance of sailboat navigation lights as just another cumbersome boat regulation, understanding their indispensable role is crucial for every sailor’s peace of mind and for ensuring uninterrupted enjoyment of our beloved pastime. So next time you set sail, remember that these little beacons serve as more than mere accessories – they are your allies in darkness, silently guiding you towards safe passages and unforgettable adventures on the open sea.
How to Properly Install and Operate Sailboat Navigation Lights
When it comes to sailing, safety should always be a top priority. And one of the essential safety measures on a sailboat is proper navigation lighting. Sailboat navigation lights help other vessels identify your boat’s position and course, especially during low visibility conditions or at night. In this blog post, we will guide you through the correct installation and operation of sailboat navigation lights to make your sailing adventures safe and enjoyable.
Installing sailboat navigation lights may seem like a simple task, but there are several key factors to consider for optimal functionality. First and foremost, familiarize yourself with international regulations regarding navigation lights. These regulations ensure consistency across different countries and improve communication between vessels on the water.
Before starting the installation process, carefully choose high-quality LED lights specifically designed for sailboats. LEDs offer numerous advantages over traditional incandescent bulbs, including energy efficiency, higher light output, longer lifespan, and reduced heat emission. Additionally, LEDs are more durable and resistant to vibrations commonly experienced while sailing.
To begin installing your sailboat navigation lights:
1. Determine the appropriate locations: Positioning your navigation lights correctly is crucial to maximize their visibility and effectiveness. Refer to your boat’s owner’s manual or consult with a marine electrician to identify the ideal mounting points for each light.
2. Prepare wiring routes: Plan out the wiring routes before drilling any holes or mounting fixtures. Concealing wires within the boat’s structure not only enhances aesthetics but also minimizes potential damage caused by exposure to external elements.
3. Drill strategically: Using an appropriately sized drill bit, carefully create mounting holes following the instructions provided by the manufacturer of your chosen navigation lights.
4. Connect electrical components: Install a waterproof junction box near each light fixture to protect wires from moisture and corrosion. Make connections following color-coded standards (red wire – positive; black wire – negative), ensuring proper polarity is maintained throughout the circuit.
5. Securely attach fixtures: Once all wiring connections are made, attach the navigation light fixtures to their designated mounting positions. Double-check that they are secure and properly aligned to maintain optimal visibility.
With your sailboat navigation lights installed, it’s time to understand their operation. Different situations call for specific combinations of lighting:
1. Underway with power: When sailing under engine power, display both a red (port side) and a green (starboard side) light visible from dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft each beam. A white stern light should also be shown.
2. Sailing without power: When solely relying on wind propulsion, display just the red and green sidelights in the same manner as during powered navigation.
3. At anchor: If you’re moored or anchored, only exhibit an all-around white light at a location high enough to illuminate unobstructed from every angle.
4. Restricted maneuverability: In situations where your sailboat’s maneuverability is impaired (e.g., towing another vessel), use three shapes—two balls vertically aligned above one diamond—to indicate restricted movement.
Lastly, always ensure proper maintenance of your sailboat navigation lights:
1. Regularly inspect for damage: Routinely check for signs of wear and tear on the electrical connections, housing seals, lenses, and reflectors. Replace any damaged components promptly.
2. Clean for maximum visibility: Keep lenses clean from dirt, grime, salt residue, or any other obstructions that could limit the effectiveness of your navigation lights.
3. Carry spare bulbs/batteries: Be prepared by carrying backup LED bulbs or batteries in case of failure during extended voyages.
By following these installation steps, understanding proper operation techniques according to maritime regulations, and maintaining your navigation lights diligently; you can cruise confidently knowing your sailboat is equipped with highly visible and functional navigation lighting system—an important feature enhancing safety while enjoying the open water at any time of day or night. So, set sail with peace of mind and navigate the seas safely while embracing the thrilling adventures that await you!
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up Sailboat Navigation Lights for Safe Sailing
Welcome aboard, fellow sailors! Today, we are going to dive into the nitty-gritty of setting up sailboat navigation lights for safe sailing. As you know, proper navigation lights are an essential part of ensuring your safety on the water, especially during low-light conditions and at night. So grab your cup of coffee, sit back, and prepare to learn how to illuminate the seas like a professional.
Step 1: Know Your Lights Before we jump into the technicalities, let’s familiarize ourselves with the different navigation lights required on a sailboat. These include the red port light on the left side, green starboard light on the right side, white stern light at the rear, and if our boat is longer than 20 meters (or 65 feet), a white masthead light at its highest point. Having this knowledge sets you up for success in navigating effectively while abiding by maritime regulations.
Step 2: Choose Your Lighting System Now that we’ve covered the basics, it’s time to decide which lighting system is most appropriate for your sailboat. You have two options: traditional incandescent bulbs or modern LED lights. While both serve their purpose well, LED lights are more energy-efficient and tend to last longer – a win-win situation!
Step 3: Gathering Materials To ensure smooth sailing throughout this process (pun intended), gather all necessary materials beforehand. This includes navigation lights (either incandescent bulbs or LED lights depending on your preference), wiring connectors, heat shrink tubing (to protect connections from moisture), electrical tape, wires (preferably color-coded for easy identification), wire strippers/cutters, and mounting hardware suitable for your boat.
Step 4: Planning Placement Consideration of placement plays a crucial role in setting up navigation lights effectively. Ensure visibility from all angles without obstructing other boat equipment or compromising aesthetics onboard. Take note of any manufacturer guidelines provided with your purchased lights for optimal placement. Remember, safety doesn’t mean sacrificing style!
Step 5: Wiring Your Lights Now we’re getting hands-on! Let’s start with the stern light. Attach the wires of your chosen light to the existing electrical system using appropriate connectors and ensure a secure connection. Utilize heat shrink tubing and electrical tape to safeguard against any moisture-induced malfunctions. Repeat this process for both port and starboard lights.
Step 6: Don’t Forget the Masthead Light If your sailboat exceeds 20 meters in length, you’ll need a masthead light too. Carefully mount this light on top of your mast using suitable hardware. Then, run additional wires through the mast to connect it securely with your electrical system.
Step 7: The Proof is in Testing After successfully wiring all navigation lights, it’s time for a crucial step – testing! Double-check that all connections are secure and operational before venturing out onto the open water. Be meticulous; don’t let a faulty bulb ruin your sunset cruise or impede your journey under a moonlit sky.
Congrats, sailors! You’ve now mastered the art of setting up sailboat navigation lights for safe sailing. Remember, maintaining these lights should be an essential part of regular boat maintenance as well. With proper illumination, maritime rules adhered to diligently, and cautious seamanship skills mastered, you can enjoy many breathtaking nights on tranquil waters without compromising safety. So go forth into the starry night with confidence and raise anchor towards new horizons! Bon voyage!
Frequently Asked Questions About Sailboat Navigation Lights, Answered!
Title: Frequently Asked Questions About Sailboat Navigation Lights, Answered!
Introduction: Navigating a sailboat safely and responsibly requires understanding and adhering to various rules and regulations. One vital aspect of sailing is ensuring proper use of navigation lights. These lights not only aid in visibility but also help communicate with other vessels on the water. In this blog post, we will delve into frequently asked questions about sailboat navigation lights, offering detailed professional answers infused with wit and clever insights.
1. Why are navigation lights necessary for sailboats? Navigation lights serve as visual signals that enable sailors to identify vessel types, positions, and movements at night or in low visibility conditions. They are crucial for promoting safety on the water by helping prevent collisions and aiding in the communication between boats.
2. What are the different types of navigation lights found on a sailboat? Sailboats typically feature three main navigation lights: red (portside), green (starboard side), and white (stern light). The red light tells other sailors that your boat’s portside is facing them, while the green light indicates that your starboard side is visible. The white stern light illuminates the rear of your vessel, making it easier for others to determine your direction of travel.
3. When should I turn on my sailboat’s navigation lights? According to international rules of collision avoidance at sea, all vessels must show proper navigation lighting between sunset and sunrise or during periods of restricted visibility such as fog or heavy rain showers. It’s essential to remember that even during daylight hours if visibility drops due to poor weather conditions, switching on navigational lights can greatly enhance safety.
4. Are there any additional requirements regarding sailboat navigation lighting? Yes! Aside from displaying the three main distinct navigation lights mentioned above, it is crucial for sailboats under power or motorsailing – using engine power alongside sails – to display an additional white forward-facing masthead light apart from the stern light. This masthead light helps identify the sailboat as a power-driven vessel, providing further clarity to nearby boaters.
5. Can I use LED lights for navigation purposes on my sailboat? Absolutely! In fact, LED lights are highly recommended for their energy efficiency and prolonged lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. However, it is essential to ensure that any LED navigation lights you use adhere to relevant maritime regulations concerning color, visibility range, and intensity.
6. How can I check if my sailboat’s navigation lights are working correctly? Regular maintenance and testing of your navigation lights are vital to guarantee their functionality when needed the most. Before every outing, visually inspect each light for signs of damage or corrosion. Additionally, switch on all navigational lights while docked or at anchor to verify they illuminate brightly according to the appropriate standards laid out in navigational lighting regulations.
Conclusion: Understanding sailboat navigation lighting not only ensures your safety but also promotes effective communication with other vessels on the water. By knowing when and how to properly utilize these lights, you contribute to maintaining a harmonious sailing environment. Remember, navigating with wit means being informed and cleverly enhancing your skills as a sailor while keeping safety at the forefront of your adventures!
Top Tips and Best Practices for Maintaining Sailboat Navigation Lights
Maintaining Sailboat Navigation Lights: Expert Tips and Best Practices
Picture this – you’re out on the open water, gliding along with the wind in your sails. As the sun dips below the horizon, darkness begins to envelop your sailboat. This is when maintaining proper navigation lights becomes paramount for both safety and legal compliance. In this blog post, we will dive deep into top tips and best practices for ensuring that your sailboat’s navigation lights are not only functioning but also showcasing their brilliance.
1. Regular Inspections are Key: To ensure your sailboat navigation lights are in prime condition, regular inspections should be conducted. Make it a habit before every trip to thoroughly examine all lights, from bow to stern. Look out for any loose connections, cracked lenses, or water intrusion that could hamper their effectiveness.
2. Ensure Proper Power Supply: One common issue faced by sailors is inadequate power supply to navigation lights, leading to dimness or complete failure at crucial times. Check that the wiring system is correctly connected and working optimally. Additionally, consider installing a voltage monitor or battery analyzer to keep tabs on power levels during extended journeys.
3. Choose LED Lights: When it comes to choosing sailboat navigation lights, opt for LED technology without hesitation. LEDs offer brilliant luminosity while consuming minimal power compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Their longevity and durability make them ideal for equipping your vessel’s masthead light, sidelights, stern light, and anchor light.
4. Cleaning is Essential: Navigation lights on a sailboat accumulate dirt and grime over time due to exposure to various elements like saltwater spray or bird droppings (we all know how seagulls love making our boats their restroom). Regularly clean the lenses with a soft cloth and mild soap solution followed by drying with a lint-free towel. Keeping them crystal clear will maximize their output and visibility range.
5. Protect Against Moisture: Water ingress can be a persistent menace, harming the functionality of your sailboat’s navigation lights. To combat this, ensure watertight seals around light fixtures and wiring connections. Applying silicone lubricant or dielectric grease to connectors further enhances protection against moisture.
6. Carry Spare Bulbs and Fuses: Murphy’s Law states that anything that can go wrong, will go wrong – especially in the middle of nowhere. Imagine how disheartening it would be if one of your navigation lights suddenly fizzles out on a moonless night! Always carry spare bulbs and fuses suited for your specific lighting system to avoid such predicaments and keep your journey uninterrupted.
7. Stay Familiar with Navigation Regulations: Being updated on marine regulations regarding navigation lights is not only essential for your safety but also ensures compliance with local laws. These regulations dictate the placement, colors, and timings for displaying navigational lights based on different conditions such as underway, anchored, or sailing near other vessels at night.
In conclusion, maintaining sailboat navigation lights might seem like a mundane task; however, its significance cannot be undermined when it comes to safety during nighttime voyages. Regular inspections, adequate power supply, LED technology adoption, cleanliness, moisture protection, carrying spare bulbs/fuses, and adhering to maritime regulations should become second nature for any seasoned sailor. By following these top tips and best practices meticulously, you’ll be able to navigate the vast expanse of dark waters with confidence while ensuring a safe voyage each time.
Exploring Different Types and Designs of Sailboat Navigation Lights
When it comes to sailing at night, having the right navigation lights on your sailboat is absolutely crucial. Not only do they help you stay safe and avoid collisions with other vessels, but they also ensure that you are compliant with maritime regulations. In this blog post, we will be exploring different types and designs of sailboat navigation lights, so you can make an informed decision for your own vessel.
One of the most common types of sailboat navigation lights is the sidelight. These lights are usually mounted on either side of the boat and emit a green light on the starboard (right) side and a red light on the port (left) side. The purpose of these lights is to signal the direction in which your boat is moving to other vessels in the vicinity. Additionally, sidelights should be visible at a distance of at least two nautical miles, ensuring that other boats have ample time to react accordingly.
Another important type of navigation light for sailboats is the sternlight. As its name suggests, this light is mounted at the back or stern of the boat and emits a white light. The sternlight helps other vessels determine if you are moving away from them or approaching them from behind. It should be visible from a distance of at least two nautical miles as well.
In addition to sidelights and sternlights, sailboats also require an all-round white light, commonly known as an anchor light. This light serves as both an anchoring indicator and a warning signal to other boats that your vessel isn’t under power and may be stationary. Typically mounted atop the mast or another elevated point on the sailboat, this white light must be visible from all directions within two nautical miles.
Now that we’ve covered the main types of sailboat navigation lights, let’s delve into their designs. While traditional incandescent bulbs were once widely used for their simplicity and affordability, LED technology has revolutionized marine lighting. LED navigation lights are highly energy-efficient and have a considerably longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs. Additionally, LEDs emit a bright and focused light, making your sailboat more visible to others even in adverse weather conditions.
Furthermore, many LED navigation lights come with built-in features that enhance safety and convenience. Some models have automatic sensors that adjust the brightness of the lights depending on the ambient lighting conditions. This means that if you’re sailing during twilight or dawn, when visibility is reduced, these lights will automatically become brighter for better detection by other vessels.
Moreover, some innovative designs include combination lights that incorporate both sidelights and sternlights in one compact unit. These multifunctional lights save space on your boat while still ensuring compliance with regulations. Additionally, there are folding or telescopic navigation lights available that can be easily stowed away when not in use, further optimizing your deck space.
In conclusion, choosing the right types and designs of sailboat navigation lights is crucial for safe night sailing and regulatory compliance. Sidelights, sternlights, and anchor lights are essential components of any sailboat’s lighting system. Consider opting for energy-efficient LED technology that offers enhanced visibility and longevity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Moreover, explore innovative designs such as combination lights or folding options to optimize space onboard your vessel. By equipping your sailboat with the right navigation lights, you can navigate confidently through the darkness while captivating other sailors with your illuminated elegance on the open sea!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
Boat Navigation Lights Rules: Illustrated Beginners Guide
When navigating at night, the lights on other boats are your first clue about the moving dangers around you. And your navigation lights are your first line of safety in avoiding collisions in the dark, and they tell others vessels what you are and what you are doing. The rules sound complex, but with a little understanding you can get the basics for any situation.
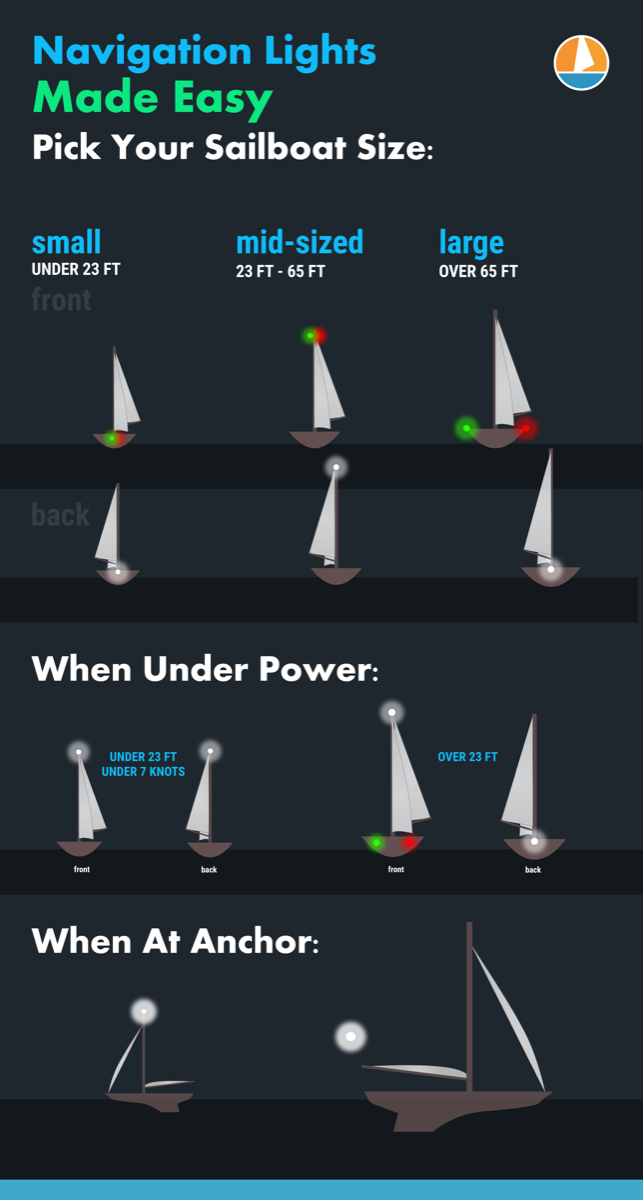
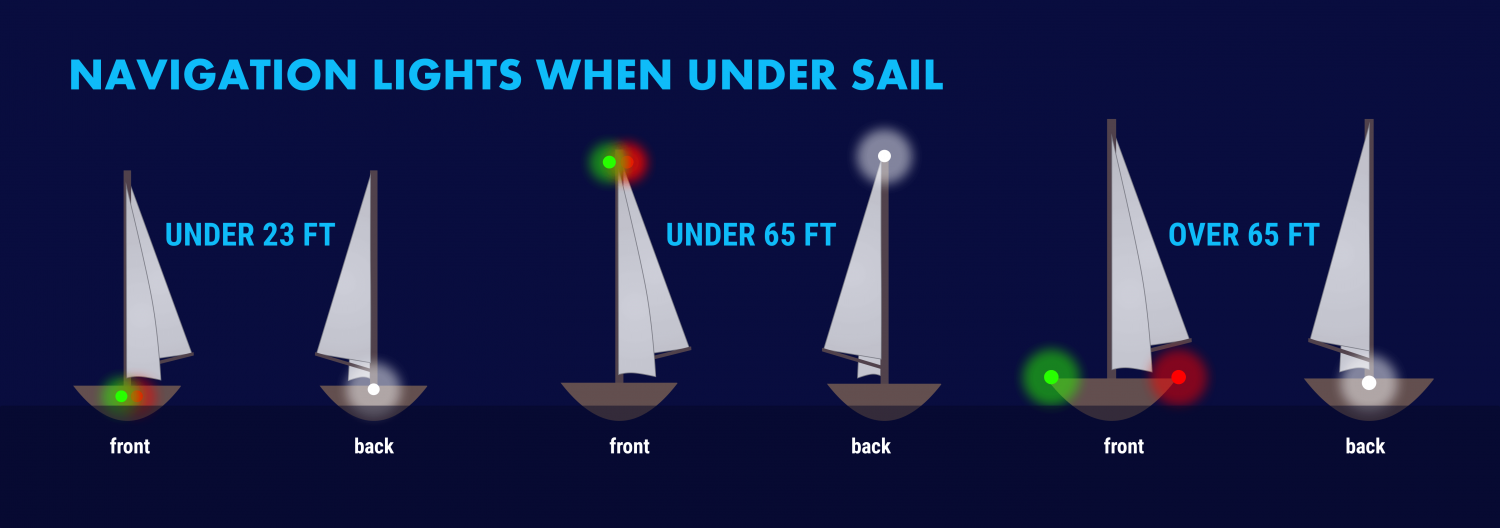
So what are the basic navigation light rules? For most small vessels, motoring requires red and green (port and starboard) lights, and a white light visible in all directions around the boat. This is almost always a stern light and a masthead light on sailboats. Boats under sail require port and starboard lights, and a white stern light. Sailboats below sixty-five feet may show a tricolor light at the masthead instead of side and stern lights when sailing.
That's it, in a nutshell. There's a little more to it, as the rules change with different sizes and there are some specifics about angles of display for the colors. Identifying other ships at sea requires more study, but the basics are the same. And it's not much trouble to make sure you've always got the proper lights on your vessel.
On this page:
What are the official colregs rules for your sailboat, what about the uscg (united states coast guard) rules, lighting at anchor, identifying the boats around you.
The International Regulations for the Prevention of Collision at Sea , abbreviated "COLREGS" is very specific about the lights required, their shapes and sizes, and the distance they must be visible. For the smaller boat, the following definitions apply.
- Masthead Light - a white light placed centerline on the boat showing an arc of 225 degrees with 112.5 degrees either side of the front of the vessel.
- Sidelights - A red light on the port side and a green light on the starboard. They must show an arc of 112.5 degrees from centerline of the bow.
- Stern light - A white light on the stern of the boat showing an unbroken arc of 135 degrees from centerline of the vessel.
- All-round light - A light showing in an unbroken arc of 360 degrees.
The good news is you need not measure these angles. Any properly installed USCG or COLREGS approved light which will cover the correct arcs. If you have to replace the original light from your boat, make sure it's with an approved replacement.
Lights When Sailing
The specific rules for a sailboat under sail are in COLREGS Rule 25 and vary slightly with the size of the boat. A sailboat powering is considered a power boat and falls under in Rule 23.
- Under 23 feet (7 meters) - side lights and a stern light, possible. If these lights can not be displayed a light must be kept at hand to help avoid a collision. This can be a bright flashlight.
- Over 23 feet - Side lights visible to one nautical mile and stern light visible for two.
- Vessels under 65 feet may combine both sidelights into a single lantern on the bow.
- May show a tricolor light on the masthead instead of sidelights and a stern light. It's one or the other though, do not show these lights at the same time .
- Masthead light must be visible for three nautical miles, all other lights must have a two nautical mile visibility.
- Side lights must be separated.
- May not show a masthead tricolor light.
- Masthead light must have five nautical mile visibility, all other lights must be visible for two nautical miles.
- Optional masthead lights - any vessel under sail may display a red light over a green light at the masthead with sidelights and stern light. The red over green may NOT be displayed with a masthead tricolor light. It's one set or the other.
Lights When Motoring

For all navigational purposes a sailboat under power is considered a power boat. This includes motor sailing - if the engine is on and providing propulsion you are on a power boat, even if the sails are up . This applies to navigation lighting, sound signals in fog and limited visibility, and rights of way.
Sailboats under 50 meters under power need to show:
- A masthead light
- Stern light
A power-driven vessel under 23 feet (7 meters) that does not exceed seven knots of speed may display an all around white light, though sidelights should be used if available.

The USCG has published its own "Rules of the Road" that are based on the COLREGS. In addition, it has rules for the "Inland Waterways" for rivers, inland lakes and the Great Lakes.
The good news is this has no impact on what you have to do with your own boat.
They mostly relate to lighting changes on towed vessels like barges and tugs. For example, a vessel towing or pushing another vessel in the ocean under COLREGS shows two masthead lights, sidelights and a stern light, whereas in Inland Waterways the towing or pushing vessel displays two yellow towing lights instead of a white stern light.
If you sail on lakes, rivers or the Great Lakes where towed commercial traffic is common you should learn the inland lights, but coastal or ocean sailors will never see these.
When you anchor outside a designated mooring field, you should display an all around white light at the masthead or as high in the boat as practical.

If your boat is large and has a very tall mast, you may wish to display another light closer to the waterline. Boats approaching in the dark may not see a light on a mast sixty or seventy feet in the air when they are close to your boat.
We use a simple garden path light on our stern when we anchor, left in a rod holder or flag socket. It comes on automatically at dusk and is a cheap and easy way to be more visible. There is no specific rule stating you can not display more lights than required, or the nature of any lights beyond the required all around light.
The COLREGS also specify that a round black "daymark" should be displayed in the rigging of any vessel at anchor. Very few small vessels observe this, however it is the correct display for a vessel in an anchorage.
If you tie to a mooring in a marked mooring area you are not required to display anchor lights, but there is no harm in doing so.
The other important reason to know your lights is to figure out what's going on around you at night. The water may be ablaze with white, red, green and other lights at night and they are your first key to avoiding collisions and problems.
All combinations of lights for fishing boats, commercial vessels, and so on are outside this post‘s scope. The odds are small you will encounter a submarine, seaplane or hovercraft at night, but there are regulations regarding specific lighting for each of those vessels!
There are a few fundamentals to help you figure out what that is you see on the horizon, which way it is going, and whether it is a danger to you.
Port Wine is Red
The fundamental rule is that red sidelights will ALWAYS be on the port side of a vessel, and green lights will always be on starboard. However, some vessels can use all around red and green lights for other purposes, though those will be higher than sidelights.
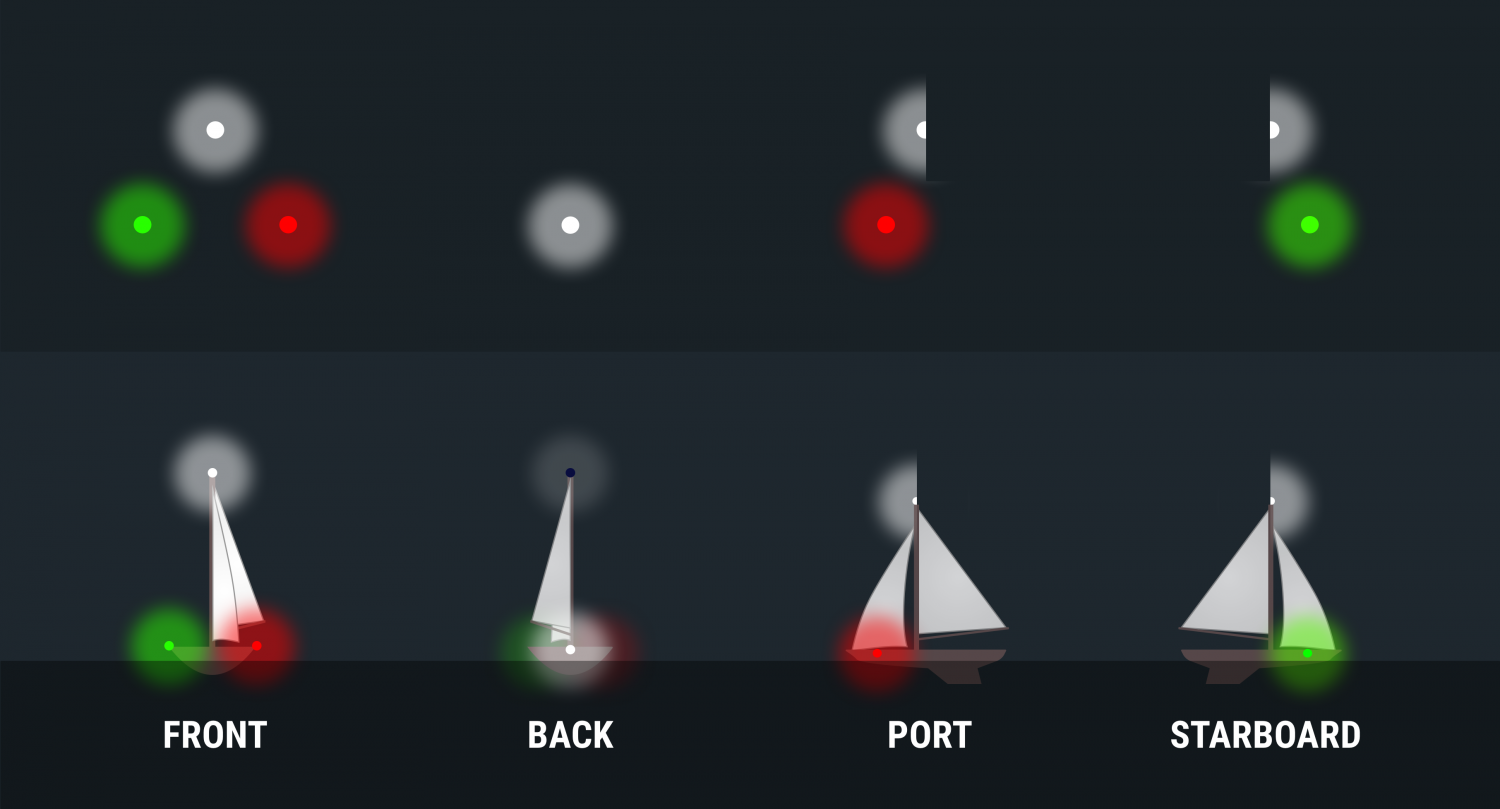
The light‘s on a ship is not important, some large tankers and freighters will have their sidelights far aft and put them on the superstructure for better visibility. It is not safe to assume that sidelights you can see are on the bow of large vessels .
When you can see the color, you know which way the bow is pointing. If it's red, it's pointing more or less to the left and will travel in that direction. A green light shows it is heading more or less to your right.
If you can see the red and green lights at the same time, you are looking directly at the bow of the vessel. When you are far away, this isn‘t as alarming as if you are close crossing. Seeing red and green lights together on a vessel is something you never want to see for long.
Be aware of red and green lights used in combination with other red, green and white lights. These may not be running lights and could have other significance.
Tankers, Freighters and Large Ships
Tankers, freighters and large ships will have side lights, a stern light and a masthead light. In addition, on vessels over 50 meters there will be a second masthead light further aft and higher than the forward light. The masthead light positions are a better tipoff to the bow direction and how far from the bow the sidelights might be. Remember - on a large vessel the sidelights may not be at the bow or even close to it.
USCG Inland Rules allow for a second all-around white light on large vessels on the Great Lakes instead of a second masthead light.
Fishing Boats
Fishing boats engaged in fishing will have more complex light displays. When they aren't fishing, they will show lights like any power vessel, but Rule 26 spells out light combinations that vary by the fishing activity being done. In general:
- Boats which are Trawling but not making headway will display a green all-around light over a white all-around light , and a masthead light aft of these lights. Boats making headway while trawling will show these lights, plus sidelights and a stern light.
- A vessel fishing other than trawling will show a red all-around light over a white all-around light . When making way they will also show sidelights and a stern light.
- If a vessel has gear more than 150 meters away from the boat, it will show a second all around light in the direction of the gear. The best rule is to give fishing boats as wide a berth as you can at night. They're easy to pick out if you check the top light configurations but their course may be difficult to predict.
Towing and Pushing
Towed vessels can be the most dangerous to cross, but they have the most lights to tell you what is happening. Refer to COLREGS or the USCG Rules of the Road Rule 24 for all combinations You can pick a tow/push vessel out with the following lights:
- Two or three masthead lights in a vertical line. Three masthead lights shows a tow over 200 meters. Additional masthead lights may show for larger tow vessels.
- A towing light (yellow light with the same characteristics as a stern light) directly above the stern light.
- The will also have side lights and a stern light.
- The towed vessel will show sidelights and a stern light. Lighting may vary under USCG inland rules, where towing lights may replace stern lights. Learn these differences if this is your regular cruising ground. If you think there is a tow ahead of you, always go well behind the aft most set of lights. Never go between a tow and avoid crossing ahead if possible as it may restrict their maneuverability.
Special Situations
There are several rare situations you may encounter. As a general rule, if there are a lot of lights and you don't understand them look for the sidelights on a moving vessel. If you can find them and figure out the direction it is moving, it makes the vessel easier to avoid. Stay well clear of lights you do not understand if you can avoid them without risk.
Most of these signals are used by larger, commercial vessels and you will not need them.
They use these light combinations with other light combinations. For example a towing vessel may also be restricted in maneuverability, and a vessel constrained by draft will show running lights if moving.
- Not Under Command - two all around red lights in a single line
- Restricted in Ability to Maneuver - red, white then red in a single line
- Constrained by draft - three all around red lights
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: 2e4c7e31-634e-11ef-ab7c-7b16e4fbcdb9
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.
- How to sail at night
Captains are often asked if it's possible to sail at night. In the vast majority of cases, the answer is yes, unless you are just starting out. You just need to know the specifics of night sailing — the rules of boat lighting, beacon signals, have navigation and nautical charts handy, and most importantly, follow basic safety rules on board. So, do you know what night sailing entails?
You can't do it without the correct lights
While on land, lights are primarily there to help us see, at sea it's the other way around. All boats must be properly lit for other vessels to see. And, a boat doesn't work like a car either, where we shine our headlights on the road ahead to see what's in front of us. At sea we rely on navigation, nautical charts, lighthouses and the captain's knowledge.
Basic boat lights include running lights, steaming lights and anchor lights. There are clearly defined and standardized rules for lighting a ship under sail at night . So the question of how to light a yacht at night has a very simple answer. Running lights, or side lights, show other vessels where your port and starboard sides are, with red indicating port and green starboard, and you must also have a white stern light on.
Lighting the yacht at night is very important because, unlike during the day, the helmsman cannot judge the distance and direction of other boats by sight. Running lights make the position and direction of the surrounding vessels visible, as well as their approximate distance, and helps to avoid possible collisions. Radar is also highly practical in this respect, as it shows the size and distance of the vessel.
However, when sailing there can be situations where the sails need to be lowered, and with that, the lighting also needs to be changed. If travelling under motor power , a steaming light (masthead light) must be turned on , which shines at the same angle as the side lights. When a sailboat is not under sail, it has to abide by the rules set out for power boats by COLREG (The International Rules for Preventing Collisions at Sea).
Lighting regulations when at anchor are again different. When at anchor at sea , only the anchor light should be on . According to the regulations this could be either a 360-degree white light atop the mast, or a light suspended from the boom, above the foredeck or on a furled genoa. If the boat is moored in port, the light is not normally used.
Navigation, GPS and maps
Nowadays, GPS and navigation aids integrated into the boat or that work as mobile apps are commonly used to determine the position of the boat. Modern technology is very accurate and reliable, but it is still worth understanding, reading and checking your position on paper nautical charts . After all, almost any skipper will tell you that their GPS or navigation system has at some point told them they were on land, even when tens or hundreds of metres from shore.
Thanks to nautical charts, you will not only know of possible danger spots, but also lighthouses , enabling you to easily and accurately determine your position with the help of a compass. Each lighthouse is different, being lit and flashing in a unique way. A nautical chart will tell you how to identify a lighthouse by the number of flashes, their frequency and the colour of the light. To determine your exact position, you’ll then need two lighthouses in sight that serve as reference points for each other.
YACHTING.COM TIP: Lighthouses are not only practical, but they are often buildings with impressive architecture that are well worth stopping off at. Take a look at 15 lighthouses you must visit .
Safety is paramount when sailing at night
Even during the day, there are clear rules regarding the movement of the crew on board. Basically, the crew should not stand unless they are engaged in manoeuvres. In all other cases, they should be sitting on benches, at the side of the boat when heeling, or in the cabin. Apart from the fact that a standing crew member could obstruct the helmsman's view, it also poses a greater risk of falling overboard . If you're interested in getting to know this subject in more detail, check out our article Sailing Etiquette A to Z .
At night, the rules are even stricter to ensure the crew remain as safe as possible and avoid damaging the yacht. If a crew member is on deck at night while sailing, they should wear a lifejacket and ideally be attached to the boat with a lifebelt or harness.
Except for really experienced seafarers, the rule of thumb is that there should be at least two people on board when sailing at night. And the captain should schedule shifts so that there are always two rested crew members on board. After all, you need to be doubly vigilant when sailing at night, and staying awake all night is certainly not conducive to alertness — especially when manoeuvring or entering port. For the same reasons alcohol is prohibited when night sailing. While during the day, crew members other than the helmsman can toast Neptune or have one glass of wine or beer, drinking alcohol is not permitted during a voyage at night. By all means celebrate a successful journey upon arrival in port at a local tavern, but it definitely pays to keep a clear head at sea.
Specifics of night sailing and boat handling
Steering and controlling the boat is not particularly different during the day and at night. There are just a few nuances to make sailing that bit smoother. If you're on a vessel you know well, that’s one thing, but if you're on a charter boat , it's worth marking the sheets and other lines so that you know your way around in the dark.
Sailing at night, it is also important to assess the weather conditions well. What you would normally do during the day can be significantly more challenging at night and requires a more careful assessment of weather conditions and weather patterns. It is always better to choose smaller sails and if you have even the slightest doubt about anything, postpone the trip.
When entering a harbour or sailing close to shore, be doubly cautious. There are several risk factors. During the day, the surrounding boats, the rocks and the potential hazards on the surface and below are visible. At night you have to rely on navigation, charts and lighting. When entering the harbour, charts and GPS can provide you many clues but lights can cause issues. For example, you might get dazzled by the light from the shore, the anchor lights of other boats are easily confused with the lights on land, and, last but not least, you may encounter poorly lit fishing boats. However, if you keep in mind all of these potential risks, you will arrive safely in the harbour.
The magic of night sailing
When compared to sailing during the day, night sailing places more demands on the captain's experience and knowledge of sailing regulations. But it is also a truly romantic experience. Millions of stars glistening in the night sky and the waves sparkling in the moonlight. If you're lucky, sailing out of the mist from land on a clear night with a near full moon, it will seem almost like daylight.
If you're serious about sailing and steering your boat, there are other benefits to night sailing. Navigating at night sharpens the senses and enhances the sailing experience as well as your experience of the sea itself. It truly gives a whole new meaning to sailing. But if all you want is to just enjoy yourself, night sailing is one of the most romantic experiences you can have. Check out our article on how to enjoy romance on board a yacht charter .
Are you new to the sea? We will recommend experienced captains who will take care of you on the ship. Give us a call.

Denisa Nguyenová
Faq how to manage a night sailing.
- Members Forum
- Log In / Create Account
Navigation Lights at Night
by Harbor Sailboats | Dec 4, 2020 | Blog | 1 comment

Great article! Boat lights are the means of communication between sailing vessels. These lights are also a tool to let my presence known even from a distance.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Latest Blog Posts
- Talk and Walk
- Sailing Lessons in San Diego
- Water in the Bilge
- Bow Standing
- Gear then Steer

Navigation Lights for Sailboats (And How To Read Them)

Last Updated by
Capt Chris German
June 15, 2022
Navigation lights on a sailboat can be confusing. If you understand the reason behind why they are the way they are however, they can make a lot more sense.
At their heart, sailboats are really just a power boat and as such must adhere to all power boat rules such as navigation lights. Other times however, a sailboat is classified in a special category. They have a set of additional lights they CAN show as an option, but are not always required to do so.
That’s about as clear as mud if you ask me and I contend that that is where the confusion about lighting a sailboat begins.
Just because you can show a light to identify yourself in times of low visibility, does not mean you have to and then we add in a little sibling rivalry between power and sail and things get downright adversarial when it comes to navigation and the night.
Table of contents
The USCG says You’re a Power Boat Whether You Like It or Not
Much to the consternation of many a sailor who has earned a commercial license to drive their sailboat, when you received your credential from the USCG it says you are a master of steam and power across the top with no mention of wind as a source of propulsion.
It is not until you read the back pages of your little red book that feels like a passport and looks like a US Sailing credential, that you will see the term “sail auxiliary”. That is because most of the time the U.S. Coast Guard knows that you are primarily reliant on your mechanical power to propel your vessel.
It's a sad thing, but the days of commercially viable sail boats are done and all but the most select few even have sails let alone use them as their primary power source. All sail boats by law are powerboats, but not all powerboats are sailboats.
Navigation Lights for a Power Boat
As a power boat, you are required to show certain lights and have been required to do so before power was even invented.
In the days of man powered vessels like the viking ships who relied on oars while in close quarters to power their vessels, they needed to show other boats, friend or foe, where they were by showing lanterns in the dark to identify themselves. As you know, it is a time honored rule among all the nations of the world both past and present, that you must avoid a collision at all costs while at sea and even the viking knew that you should not run into things.
By lighting the front and back of your boat, you could warn other boats of your presence as well as identify which way you were heading. As such there is a very specific rule in the Code of Federal Regulations Number 46 (CFR46 by common name) that spells out with detail how many, the color, the luminosity or brightness, the angle of visibility and the location of all of the lights required for navigation on every single boat, seaplane, submarine and other nondescript vessel conceived by man to date that they must show while underway in reduced visibility.
And there is no flexibility in the rules.
As such a power boat, and by extension all sailboats, MUST, without question show one green light on the starboard bow and one red light on the port bow and one all around white light or lights while operating in reduced visibility. These lights should shine at all 360 degrees of visibility with the bow lights shining at an angle of dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam and the stern lights shining 225 degrees dead aft. A forward facing masthead light that is white in color shall shine forward to comply with the directive that all vessels must carry an all around white light. For more read here .
As you can see, there isn’t much wiggle room when it comes to lights that must be shown.
Sailboats get a little flexibility with lights
Sailboats however, are a little different when they are in fact sailboats, which is only when you are entirely reliant on the wind for power and in no way reliant on any mechanical or manual means of propulsion. And for good reason.
Back in the day when men were men and sailboats were wooden, fire was a major concern. Sails were coated with wax and other flammable substances and the wood on boats was saturated with oils and grease. Even the ropes were plant materials saturated with oils to keep them pliable and strong.
Add those highly flammable substances to a parching environment like the sea and you had what was essentially a giant floating tinderbox.
Then tell that giant floating tinderbox that they need to identify themselves to the world at large at night using oil lamps with flames because batteries and lights were not invented yet. It didn't take very long or very many ships burning to the water line for the Governments to say to the sailboats, you get to do things a little different.
As such, sailboats are given special dispensation when it comes to lights aloft. They don't have to show an all around white light in their rigging because no one wanted to set their rig on fire with oil lamps 60 feet up in their rig.
However, when a sailboat takes their sails down such as when they are powered or at anchor, they must resume the display of an all around white light or lights aloft. That became a real challenge with aluminum masts and the disappearance of rat lines on the shrouds because there was no easy way to climb the rig and check the bulbs up the mast on a regular basis.
Red over Green Sailing Machine
I have no idea where the history of this particular light comes from, but if you ever take a deck exam with the USCG, you better remember this mnemonic. An all around red light over an all around green may be displayed on a vessel during times of reduced visibility to indicate that a vessel is operating under sail power alone.
I won’t even speculate on how or why they came up with this particular light configuration, but if you want to use these lights as a sailing vessel, you can do so, but that means that you will need three all round lights at the top of your mast, an all around white, an all around red and an all around green, just in that order.
The red over green is to be displayed in addition to the running lights or the red and green bow lights with the 225 degree stern light. As always, when the motor comes on, so does the steaming light or the forward facing white light that is also usually about ¾ of the way up on your mast to complete the requirement of an all around white light that indicates a power vessel.
What is a “steaming light” and why are you mentioning it now?
Most sailboat electrical panels will have a switch that is labelled “steaming light” and it will only come on when your anchor light is off. This is probably the most confusing part of sailboat navigation lights so if you are confused about this, you're in good company as most people are.
A “steaming” light is named thusly, going back to the days of steam powered sailboats where when they fired up their boilers and doused the sails, they became a power boat once again. There aren’t too many steam powered boats, let alone steam powered sailboats, but the name stuck and it is a vestige of a bygone era.
Either way, when you fire up your motor, you turn on your “steaming light” and that locks out the all around white light which is used for anchoring to minimize the number of switches on your panel and reduce the number of wires in your mast. The fewer wires, the less chance of something not working or becoming disconnected.
The steaming light and the anchor light both go up the mast, but you can’t use an all around white light while using the 225 degree stern light at the deck level because to other boaters you would look like you have two white lights from the stern and that would be confusing.
The anchor light is used exclusively for anchoring while the steaming light is used to indicate you are a power vessel while underway.
As to why I am mentioning it now in the article, is because this would have blown your mind if I started with this subject cause it can be really confusing stuff.
Aspect Recognition with Lights
Remember when I said earlier that lights can help you tell others which way you are heading as well as tell you which way other boats are heading? That is called the aspect of the vessel and the USCG tests you on this for your deck exam as well.
Knowing that the bow lights go 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on both sides or 112.5 degrees on each side, and the stern light faces 225 degrees aft for a total of 360 degrees of visibility, you can tell a lot about where a boat is heading and who has the right of way.
One thing that's easy to remember is red means stop and if you see a vessel's red light, it means stop as you are the give way vessel and approaching the other vessel from his port side. Conversely it works with green as well as that means you are approaching from the other vessel's starboard side and you are the standon vessel.
If you see a red and green light equally low on the horizon, that means your heading dead on into another vessel's path and conversely if all you see is a white light low on the horizon, it means you are overtaking another vessel power or sail, we don’t care because it is an overtaking situation. However, any time you do see a white light aloft in addition to the red and green bow lights, you know you are encountering a power boat.
Then there are angular approaches as well, where you see white and red or white and green light low on the horizon. You know in that case you are seeing a portion of the bow lights and stern lights from the side approaches of a vessel. Based on which direction those lights are heading, you can deduce which way that boat is going in relation to your boat.
So put it all together and you see a green light and a white light low on the horizon with a red over green light aloft, you know that you are approaching a sailboat that is traveling to your port and that might make you the standon vessel. That is of course, if we didn’t concern ourselves with windward and leeward and port tacks and starboard tacks, but that is a discussion for another article. So stay tuned when we talk about sailing rules and the right of way. But for now, do good, have fun and sail far.
Related Articles
Capt Chris German is a life long sailor and licensed captain who has taught thousands to sail over the last 20 years. In 2007, he founded a US Sailing-based community sailing school in Bridgeport, CT for inner city youth and families. When Hurricane Sandy forced him to abandon those efforts, he moved to North Carolina where he set out to share this love for broadcasting and sailing with a growing web-based television audience through The Charted Life Television Network.
by this author

Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
Daniel Wade
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

How To Drive A Pontoon Boat
Jacob Collier
December 19, 2022
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

Navigation Lights
- You are required to display the appropriate lights at night or during times of reduced visibility.
Navigation lights are used to prevent collisions at night or in times of reduced visibility, and are an essential tool in keeping you and your vessel safe. Nav lights allow you to see other nearby vessels, and allow other vessels to see you.
Nav lights also provide information about the size, activity, and direction of travel. By understanding the characteristics of Nav lights, you can determine an appropriate course of action as you approach another vessel.
On any vessel, navigation lights have a specific color, (white, red, green, yellow, blue), arc of illumination, range of visibility, and location, as required by law and regulations. For the purposes of this course, we will concentrate on pleasure boats under 65 feet in length. Knowledge of navigation lights is important to a small-boat skipper for separate, but important, reasons.
- You are legally responsible for displaying lights of the proper color, intensity, location and visibility on your boat.
- Knowing the type and heading of another boat.
Legal Requirements
Vessels are required to show the proper navigation lights from sunset to sunrise in all weather conditions, good and bad. During these times, no other lights that could be mistaken for lights specified in the Rules of the Road can be displayed, nor any lights that impair the visibility or distinctive character of navigation lights, or interfere with the keeping of a proper lookout. The Rules also state that navigation lights must be shown in conditions of reduced visibility, and may be shown at other times considered necessary.
It's Your Responsibility
It is the responsibility of the owner/operator of a vessel that she show the proper navigation lights for her size and the waters in which she is operating. It is not the responsibility of the manufacturer, importer, or selling dealer. Many boats are delivered with lights that do not meet legal requirements with respect to technical characteristics or placement on the vessel. Remember also, that the angles of visibility must be met when the boat is underway-if your boat rides at a significant bow-up angle, take that into consideration when installing and/or checking your lights.
Navigation Lights for Powerboats
Power driven vessels underway shall exhibit a masthead light forward, sidelights and a stern light. Vessels less than 12 meters in length may exhibit an all around white light and side lights. Power driven boats on the Great Lakes may carry an all around white light in stead of a second masthead light and stern light combination.

Sidelights - Colored lights - red on port and green on starboard - showing an unbroken arc of the horizon of 112.5 degrees, from dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on each side.
Combination lights - Sidelights may be combined in a single fixture carried at the centerline of the vessel.
Stern light - A white light showing over an unbroken arc of the horizon of 135 degrees, centered on dead astern.
Navigation Lights for Sailing

A sailing vessel of less than 7 meters in length shall, if practicable, exhibit regular navigation lights, but if not practical, she shall have ready at hand an electric torch or lantern showing a white light which shall be exhibited in sufficient time to prevent collision.
Diving Lights
Another light display that you may see in resort areas, or waters that have wrecks or reefs, is the night diving configuration. This has three vertical masthead lights, that have a red-white-red sequence. You must maintain a good distance from these vessels, and you should also be aware that there may be divers near you.
Interpreting what you see

It's great that you're learning the basics of lights - what is required and when they're required. But, this in only the beginning. You must also learn how to interpret the navigation lights that you see when you are underway at night- and for your safety-learn it well.
For instance, if you see a vessel approaching that shows a light pattern such as the ones to the right, you immediately know that you are in a crossing situation, and that you must yield to the other vessel - that's why it is red.

Seeing a green light over a white light indicates a fishing vessel actively trawling. You not only need to avoid the vessel, but you also need to remember that it could potentially have a very large net deployed that you will also need to avoid.
And there are numerous other lights and combinations of lights that you must be able to instantly recognize - the lights for a sailboat that is privileged over a motorboat, the special lights of various fishing vessels, a dredge or a vessel not under command. Study the requirements for navigation from the viewpoint of a "looker" as well as a boat owner.

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge

7 Tips for Night Sailing
By: Pat Reynolds Cruising Tips , Learn To Sail , Safety
Now that we’re into the summer months, lots of you might want to stretch your skill set and do a bit of night sailing. It’s a bit of a different animal so we’ve cobbled together seven things to keep in mind as you head off into the wild black yonder.
- Dress accordingly It may be obvious for some, but don’t forget the big ball of yellow heat will be replaced by a cold little white ball that will not help the warmth cause at all. Your ability to enjoy the pleasure that a gorgeous night on the water can provide is directly proportionate to you being dressed for the environment. Don layers, with a spray jacket on top and life should be good.
- Carry a decent searchlight Night boating involves becoming accustomed to the available light and acclimating to it. It’s actually one of the cool things to experience during a sail in the dark, so constantly shining a spotlight like you were hand-holding your car’s headlights is not where it’s at. That said, there are instances where having a high-powered light on board can make things considerably safer. Coming into a harbor, verifying a navigational aid or identifying something foreign in the water are all common situations that benefit from a good light.
- Stand a watch Of course someone should always be keeping an astute lookout whenever the boat is underway, but this is hyper-important during the restricted visibility that night sailing involves. If you’re lucky enough to have a bright full moon than things are a bit easier but short of that, it’s dark out there folks! Someone needs to keep a mandated watch. By the way, if that person is you, be prepared to have one of the most quality “alone-times” you’ve ever had. People are known to find the meanings of their lives on night watches. You might well return from your nice sail and promptly quit your job, dump that angry spouse and finally get in shape!
- Don’t push Many old salts attach a different attitude and mentality for night sails. During the day the fun might be to vigilantly trim and adjust, catch lifts, shift weight and monitor that knot-meter for that rewarding uptick – 3/10s of a knot – Yes! “ Herman are you secretly racing that little boy in the sabot? ” “ No, of course not. ” But Herman is racing that little boy in the sabot! Anyway, at night it’s good to downshift and run the boat at a lower percentage. Enjoy the serenity this time of day has to offer and understand that downsizing the operation a little will make for a safer and more fulfilling experience.
- Make sure Waypoints are Clear & Safe Most sailors rely on electronic aids to see them around the waterways and at night they become even more important. They can also, in certain situations, make things less safe. A few years ago, the famous Newport to Ensenada race reported their first deadly accident when a group of sailors ran into a small island off the coast of San Diego. After an investigation, it was determined that the sailors, in all likelihood, didn’t account for the land-mass (island) when they entered in their waypoints. They might have been sleeping or just not paying attention when their cruising boat tragically ran up on the rocks. This would never have happened during the day, but sailing at night brings with it these kinds of considerations.
- Know the Light Patterns Fortunately charts and boats are all set up for sailing at night so it’s absolutely essential that the skipper and at least some of the crew know what the language of lights is saying out there. Boats are equipped with lights situated in such a way that other boats can tell what’s going on and charts are filled with light-related information that will clue mariners in on where they are. It can be confusing to look into a harbor located outside of a city and try to understand what is going on. “ Why is that harbor entrance light switching from green to red like that? Oh, that’s Washington blvd… ” Know what to look for and how the lights behave and the confusion will be greatly reduced.
- Wear a PFD We understand that not everyone wears their pfd for whatever reason – it’s not comfortable, it’s filthy from lying on the floor for the past month, it sucks away at your already limited sex appeal – we get it. We don’t agree with the decision, but okay. For night boating, swallow your reasoning and put that thing on. Things can get slick on the boat at night and God forbid you end up in the drink, that little pea head of yours is very hard to see in the night. If you’re floating around for a while screaming “over here!” things are vastly better. Attach a battery powered personal beacon/light to it while you’re at it. Follow our advice and should you end up overboard you’ll be back in the boat in no time!
Related Posts:

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login
The Nighttime Navigation Gear Checklist
Embarking on a nighttime sailing adventure can be exhilarating, but it also comes with unique challenges. Read on to discover the essential nighttime navigation gear checklist to ensure a safe and enjoyable journey under the stars.
Embarking on a nighttime sailing adventure can be an exhilarating experience, but it also comes with its own unique set of challenges. To ensure a safe and enjoyable journey, it’s essential to be well-prepared with the right gear and knowledge. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the essential nighttime navigation gear checklist, providing you with the tools and information you need to confidently set sail under the stars.
Table of Contents
Introduction, navigation lights, gps and chartplotter, flashlights and headlamps, personal locator beacon (plb), lifejackets and harnesses, additional nighttime sailing tips.
Sailing at night can be a magical experience, with the stars above and the phosphorescent glow of the water below. However, it also presents unique challenges, such as reduced visibility, disorientation, and the need for heightened situational awareness. To ensure a safe and enjoyable nighttime sailing experience, it’s crucial to be well-prepared with the right gear and knowledge.
In this guide, we’ll cover the essential nighttime navigation gear you’ll need to have on board, as well as some additional tips for a successful night sail. Let’s dive in!
Essential Nighttime Navigation Gear
Proper navigation lights are crucial for nighttime sailing, as they help you to see and be seen by other vessels. At a minimum, your boat should be equipped with the following lights:
- Bow lights : Red (port) and green (starboard) lights mounted on the bow of your boat, visible from at least one mile away.
- Stern light : A white light mounted on the stern of your boat, visible from at least two miles away.
- Masthead light : A white light mounted on the mast, visible from at least three miles away.
It’s essential to regularly check and maintain your navigation lights, ensuring they are functioning correctly and are visible from the required distances.
Radar is an invaluable tool for nighttime navigation, as it allows you to detect and track other vessels, landmasses, and potential hazards. A radar system can help you maintain situational awareness and avoid collisions in low-visibility conditions.
When selecting a radar system, consider factors such as range, power consumption, and ease of use. Additionally, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with your radar system’s operation and capabilities before setting sail at night.
A reliable GPS and chartplotter system are essential for nighttime navigation, providing you with accurate position information and helping you plot your course. Ensure your chartplotter is up-to-date with the latest charts and software updates, and familiarize yourself with its operation before setting sail.
Consider investing in a chartplotter with a night mode or dimmable display, as this can help preserve your night vision while still providing you with essential navigation information.
An Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a valuable addition to your nighttime navigation gear, as it allows you to receive real-time information about other vessels in your vicinity. This information can help you avoid collisions and maintain situational awareness, particularly in busy or congested waterways.
When selecting an AIS system, consider factors such as range, compatibility with your existing navigation equipment, and ease of use. As with any navigation gear, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with your AIS system’s operation and capabilities before setting sail at night.
A VHF radio is a crucial piece of safety equipment for any sailing adventure, allowing you to communicate with other vessels, marinas, and emergency services. Ensure your VHF radio is in good working order, and familiarize yourself with the proper procedures for making distress calls and communicating with other vessels.
Additionally, consider investing in a handheld VHF radio as a backup, in case your primary radio fails or loses power.
While electronic navigation tools are incredibly useful, it’s essential to have a reliable, non-electronic backup in case of equipment failure or power loss. A traditional magnetic compass is a must-have for any nighttime navigation gear checklist, providing you with essential directional information in any situation.
Ensure your compass is properly mounted and calibrated, and familiarize yourself with its operation and any potential sources of interference on your boat.
A good pair of binoculars can be invaluable for nighttime navigation, allowing you to spot navigation aids, other vessels, and potential hazards more easily. When selecting binoculars for nighttime use, consider factors such as magnification, field of view, and light-gathering capabilities.
Additionally, consider investing in a pair of image-stabilized binoculars, which can help reduce the effects of boat movement and provide a clearer, more stable image.
Having a variety of flashlights and headlamps on board is essential for nighttime sailing, providing you with illumination for tasks such as checking charts, adjusting sails, and performing repairs. Ensure you have a selection of both white and red lights, as red light helps preserve your night vision.
Consider investing in waterproof, durable flashlights and headlamps, and ensure you have spare batteries on hand.
A Personal Locator Beacon (PLB) is a small, portable device that can be activated in an emergency to send a distress signal and your location to search and rescue services. While a PLB is a valuable piece of safety equipment for any sailing adventure, it’s particularly important for nighttime sailing, when the risk of man-overboard incidents and other emergencies may be higher.
Ensure your PLB is registered and up-to-date, and familiarize yourself with its operation before setting sail.
Properly fitting lifejackets and harnesses are essential safety gear for any sailing adventure, but they’re particularly important for nighttime sailing when the risk of man-overboard incidents may be higher. Ensure all crew members have a properly fitting lifejacket with a built-in harness, and consider investing in lifejackets with additional features such as reflective tape, strobe lights, and whistle.
Additionally, ensure your boat is equipped with jacklines and tether points, allowing crew members to safely move around the boat while clipped in.
- Maintain a proper lookout : Ensure at least one crew member is always on watch, actively scanning the horizon for other vessels, navigation aids, and potential hazards.
- Preserve your night vision : Minimize the use of white light on board, and allow your eyes time to adjust to the darkness before setting sail.
- Monitor the weather : Keep a close eye on the weather forecast and be prepared to adjust your plans if conditions deteriorate.
- Communicate with your crew : Ensure all crew members are aware of the nighttime sailing plan, and establish clear communication protocols for emergencies and routine tasks.
Nighttime sailing can be a thrilling and rewarding experience, but it’s essential to be well-prepared with the right gear and knowledge. By following this nighttime navigation gear checklist and implementing the additional tips provided, you’ll be well-equipped to confidently set sail under the stars and enjoy the unique beauty and challenges of sailing at night.

Educational
Sailing at night: common questions for beginners, is it possible to sail at night.
Absolutely. Sailing at night is not only possible but also a unique and exciting experience. With the right preparation and skilled crew, night sailing can be as safe and enjoyable as daytime sailing.
Is Sailing at Night Safe?
Safety is the primary concern for newcomers. We ensure all safety measures are in place, with well-trained crew adept in night navigation and emergency procedures. The sea at night is a different world, demanding respect and caution.
What to do at night when sailing?
Nighttime on a sailing vessel can be magical. Activities range from watchkeeping, navigating, and steering to enjoying the tranquillity of the sea, stargazing, and observing nocturnal wildlife.
How Do You Navigate in the Dark?
This is a key question. Alongside modern tools like GPS and radar, we emphasise the traditional, non-electronic methods. Over 100 years ago, the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) in London developed a system of lights to identify vessels, ships’ lights, and navigation marks, including lighthouses. This system allows sailors, even beginners, to understand what’s around them in the sea, using simple visual cues. We teach our guests to interpret these lights, connecting them to a century-old tradition of maritime navigation.
How do you sail in the dark?
Sailing in the dark involves a combination of using navigational tools, understanding maritime light systems, and relying on the heightened senses and experience of the crew. It’s a skill developed with practice and guidance. Lights are used on the deck and in the rigging when the sails need handling or changing.
How do big ships sail at night?
Larger ships use similar principles as smaller sailing vessels but with additional resources like advanced radar, more extensive crew for watchkeeping, and often more sophisticated weather tracking systems.
What About Sleep and Watchkeeping?
Managing sleep on overnight voyages is a common concern. We use a watch system to ensure there are always alert eyes on deck, balancing rest with responsibility. Learn about the Watches
What Can I See at Night?
The night sea offers a unique spectacle, from bioluminescent trails to starlit skies. Night watches are not just a duty but an opportunity to witness these marvels.
What Should I Wear?
Nighttime calls for practical, warm, and waterproof clothing. Safety gear like life jackets are worn if the skipper requires or you are more comfortable wearing them.
How Do You Deal with Sea Sickness at Night?
Sea sickness can be more challenging at night. We recommend preventative measures and have remedies on hand, advising guests to stay on deck and focus on the horizon or stars.
What If There’s Bad Weather?
We monitor forecasts meticulously and have contingency plans, teaching guests about reading weather patterns and respecting the sea’s moods.
Can I Participate in Night Sailing?
Participation is encouraged. Guests learn everything from steering to sail adjustment, under the guidance of experienced sailors.
What Wildlife Might We See?
Night time brings a different array of marine life, from nocturnal fish to dolphins in the ship’s wake, but it is more difficult to see. You might hear a whale breathing, or a flying fish may land unexpectedly at your feet.
How Different is Sailing at Night Compared to Daytime?
Night sailing feels more intimate and elemental. It’s about the stars, the sound of the water, and the feel of the wind, offering a unique and enriching experience.
Sailing at night is not just a journey across water, but a voyage into a world where traditional skills and modern knowledge meet. It’s an opportunity to connect with the sea in its most enigmatic form and to learn navigation skills that have guided sailors for centuries.
Oh and going off watch after watching a spectacular sunrise for a hearty well earned breakfast is a real treat that few get to experience, enjoy.

Blog search
Latest Posts
08/02 Special Offers
Hooray! It’s the Classic Sailing Summer Sale
02/28 Educational
2024 – Classic Sailing’s Year of Skills: Confident Crew
08/11 Announcing New Voyages
Skippers Logbook: Fetes Maritimes Brest 2024
07/20 Inspiration
What an evening!
Provident Customer Reviews
Embracing the Night: The Unseen Joys of Overnight Sailing
More Stories

02/08 Special Offers
Things are looking up! It’s time for the Classic Sailing Summer Sale: our collection of fantastic voyages with fantastic savings

28/02 Educational
Throughout 2024, we’re shining the spotlight on the various ways our customers get more with a Classic Sailing booking. Sailing on a traditional vessel

11/08 Announcing New Voyages
Tallulah’s skipper Debbie Purser reports back on Brest Festival of the Sea 2024 Anarchic behaviour out of the water, and sometimes like a sea

20/07 Inspiration
A couple of weeks back I had a wonderful evening that only came about in a very ad hoc sort of way. One of

Night Sailing: Seven Main Tips to be Safe and Happy

If you plan to do a bit of night sailing , there are several things that you need to consider. Here are several tips to keep in mind if you’re going to be sailing at night .
Personal Flotation Device
We understand that life jackets might not be comfortable, but when you’re sailing at night it’s a very good idea to have your personal flotation device on. Some personal flotation devices can have a beacon or light attached to them which makes it easier to find you in the water if you happen to fall overboard. by using a personal flotation device, you simply improve your safety when on the water at night time.

Clear and Safe Waypoints
You should make good use of your electronic sailing aids to ensure boating safety at night. You should also make sure that the waypoints you have entered your navigational aid are correct so you don’t have any mistakes while sailing at night. Make note of your surroundings such as islands and other obstacles to ensure that each one of your waypoints from point A to B is going to be safe for you to sail through.
Know Light Patterns
When you sail at night you may encounter other boats, so it’s critical that you understand the lights on other boats. This will let you understand what is going on out on the water. When you understand what the various lights mean and what they are doing, this will help keep you safe and reduce confusion.

Dress for Weather
At night you’re naturally not going to have the warmth of the sun so you should dress according to the weather. On the water at night time, it can become quite chilly even if the daytime temperatures have been hot. If you want to enjoy your time on the water, make sure you have proper attire for nighttime sailing.

Have a Watch
While you want to enjoy sailing at night you should also have someone as a lookout and a watch. There’s going to be restricted visibility so even though moonlight might give you some light, you should still have somebody watching things as you sail. It might be boring being on a watch, but it’s essential to ensure safety. If you boating alone, you’re going to be the person on the watch so you must not only steer your boat but be cautious of where you’re going.
No Need to Rush
At night time it’s a good idea to run your boat a little slower. At night time you want things to be safer and you can have a better experience if you’re not sailing as fast as you might say out during the day. You won’t have as much reaction time at night so it’s a good idea to keep things slow and easy during a nighttime sail.
Good Searchlight
Your eyes will become accustomed to sailing in the darkness, but you still want to have a good Searchlight in case of emergencies. You may need the flashlight when you want to verify a navigational aid, come into the harbor to park your boat, or try to identify something in the water that might be foreign such as a log or other small obstacle that might be dangerous to your boat. You should have a good searchlight for all situations because you never know what you might encounter in the water at night time.
Top 15 places sailing around Mediterranean Sea this summer
10 sailing tips essentials to make you a better sailor, taking your sailboat on holiday: a comprehensive guide to boat shipping, how to avoid a gybe broach – video tutorial, live your passion, subscribe to our mailing list.
- Competitions
- British Yachting Awards
- Southampton Boat Show
- Print Subscription
- Digital Subscription
- Single Issues
- Advertise with us
Your special offer
Subscribe to Sailing Today with Yachts & Yachting today!
Save 32% on the shop price when to subscribe for a year at just £39.95
Subscribe to Sailing Today with Yachts & Yachting!
Save 32% on the shop price when you subscribe for a year at just £39.95

Top tips for sailing at night
When most boats have moored up for the night clive loughlin ventures out into a different world.

There is something rather magical about sailing at night, and I love it.
In many ways very little changes – the chart plotter, depth sounder, log, AIS and radar still work just as they do in daytime, and yet somehow everything is different.
Although you can sail at night with your eyes glued to an electronic screen, it is much more fun (and safer) to supplement technology with traditional techniques, and I hope the following will help you brave the dark.
Not to be undertaken lightly
Probably the single most significant safety measure is to make sure that your eyes have adapted to night vision before you set off (see box).
Most saloon and cabin lights are far too bright to be left on at night, and yet it is important to be able to pop down below without stumbling around. I like to use a bicycle rear light, or other torch switched to red mode, and reflecting off the saloon coachroof to provide a dim bordello-like atmosphere.
Switch on compass and instrument backlights and dim chart plotter displays to their lowest setting. They may look too dim at first but they will soon seem brighter as your night vision kicks in.
Dressing for the occasion
It gets cold at night so you must wrap up warm, and a woolly hat and gloves are essential.
Over the years I have spent a fortune on ‘sailing’ gloves and been disappointed. I now use industrial gloves designed for people working in refrigerated warehouses. These give me the dexterity I need, and are warm and very low cost.
A man overboard is really really bad news in daylight, but in the dark it is a literal nightmare. So always wear a lifejacket and clip on.
The eyes have it
The sensitivity of our eyes increases the longer they are in the dark and it typically takes 30-45 minutes for maximum sensitivity to be acquired, and the improvement is dramatic. Unfortunately it can be lost in a few seconds of exposure to bright lights.
Eyes have cones that are used for colour vision in daylight, and more sensitive rods that come into their own at night. The rods are not sensitive to red light and this means that if you switch to red illumination (or red ‘Steampunk’ goggles) your eyes can continue to adapt while you move around the boat.
Each eye adapts separately and pirates used to wear an eye patch so that one eye was always adapted to darkness. This enabled them to move easily between the bright Caribbean sunlight and the vestigial gloom below decks.
The bad news for those of pensionable age is that your eyes will only be about a third as sensitive to low light as in your youth. Binoculars will boost illumination by about fifty times and go a long way to redressing the balance; but it still pays to have your youngest crew on lookout.
Paper charts still reign supreme in a number of areas and one of these is the display of lights, and in particular the sectored lights that are so crucial for our safe arrival into harbour.
I simply cannot get on with having a red light at the chart table. The same goes for chart plotter ‘night modes’ where the colour palette is changed to something gothic. I much prefer a very dim white light so I can view charts as nature intended.

A cunning plan
A pilotage plan on a whiteboard in the cockpit is handy for the navigator and crew to refer to and saves countless trips to the chart table. I like to use a book light clipped to the whiteboard. A standard book light is far too bright, but can be made useable with a few layers of primary red nail varnish or a wrap or two of masking tape.
A pilotage plan wants to be the simplest you can come up with that will safely do the job; and with a few backup strategies in case the main one doesn’t work out for any reason.
Don’t assume that a navigation mark is lit, as most, including some cardinal marks, are not.
Yellow buoys (seasonal special marks) may not be there at all, but you are generally pretty safe to assume that port and starboard lateral marks, cardinals, sectored lights and lighthouses are all present and correct.
As with daytime pilotage, you cannot beat a forward or back transit for keeping you on track.
Around harbours most lit navigational buoys will have a visible range of 2-5nm, while main channel markers and important cardinals will have a 5-10nm range and lighthouses can be visible at 25nm.
Cautious sail plan
Moving around on deck should be avoided whenever possible and so it makes sense to only have out sails that are well within the conditions at the time.
In busy areas I also like to have quite a bit of the headsail rolled away as this improves visibility looking forward.
Light spotting
Towards shore the horizon will likely be a confusion of lights and it can be very difficult to spot the one you are after. One trick is to work out the bearing that the light is meant to be on and get the boat heading in that direction. Then the crew can restrict their searching to just 10 degrees either side of the bow, and this narrows the field considerably.
The biggest danger comes from deciding that a light is the one you are looking for simply because you want it to be. The green light you are actually looking for may be as yet too dim to be seen, but a bright alternative on ‘more or less’ the correct bearing must surely be it?
Judging distance can be very tricky as well. Is that a bright light a long way off or a dim one much closer?
Lights can also come up on you in a bit of a rush. On numerous occasions I have been heading for a mark for half-an-hour or so with it seemingly never getting any closer and then suddenly it is 50m off the bow and evasive action is called for. Ships are even worse.

Look behind you
My crew is often surprised by just how few lights are provided in anchorages and rivers. If there is nothing ahead to guide you then full use must be made of back bearings.
For example, the very popular anchorage in Newtown River on the Isle of Wight has no lights at all within, but it does have the smallest lit west cardinal known to man just a few cables out from the entrance.
Fishing pots have been in the news a lot recently with the Cruising Association campaigning for them to be made easier to spot. Whatever happens in the future it is likely that they will always be difficult to see at night, and the crew need to be on their guard and looking ahead on both sides of the hull, especially if under engine.
Silhouettes
Although shore lights can be a distraction for most nocturnal navigation, if you happen to be looking for an unlit buoy or mark (a popular task for Yachtmaster candidates), plan the approach so that the mark is between you and the lights ashore.
A good torch
For close-quarters maneuvering you simply cannot beat having a trusty crew on the foredeck armed with a powerful narrow-beamed torch. They need to be careful never to shine the torch on the deck or headsail, as this will blind everyone on board, but they can quickly earn their rum ration by scanning the torch around to highlight any obstacles that threaten the boat’s safe passage.
One of my first outings as an instructor included a night time pilotage up the river Beaulieu in January. This is a sparsely lit passage at the best of times, but on this occasion there was no Moon and the few navigation lights had been removed for winter maintenance. My fledgling career was saved by the rapid deployment of a ridiculously powerful torch that was able to pick out the red and green reflective marks on the piles in sufficient time before we ploughed into them.
I would be remiss if I did not caution against head torches. They are fine for the person wearing them but are a menace to everyone else.
Thanks to: Trusty crew Tracy, Vivien, Paul, Alexandre and Davide.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

America’s Cup Boats: What it’s like helming an AC75

How to Sail on a Budget: Tom Cunliffe’s Column

Anchoring Masterclass: How to Anchor like an Expert

Offering a wealth of practical advice and a dynamic mix of in-depth boat, gear and equipment news, Sailing Today is written cover to cover by sailors, for sailors. Since its launch in 1997, the magazine has sealed its reputation for essential sailing information and advice.
- Telegraph.co.uk

ADVERTISING

© 2024 Chelsea Magazine Company , part of the Telegraph Media Group . | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
Boating at night - Navigation lights to display in Canada Requirements in Canada
- Boating Safety Equipment
- Types of navigation lights
- Boat Navigation Lights rules and requirements at night
Powerboats navigation lights at night
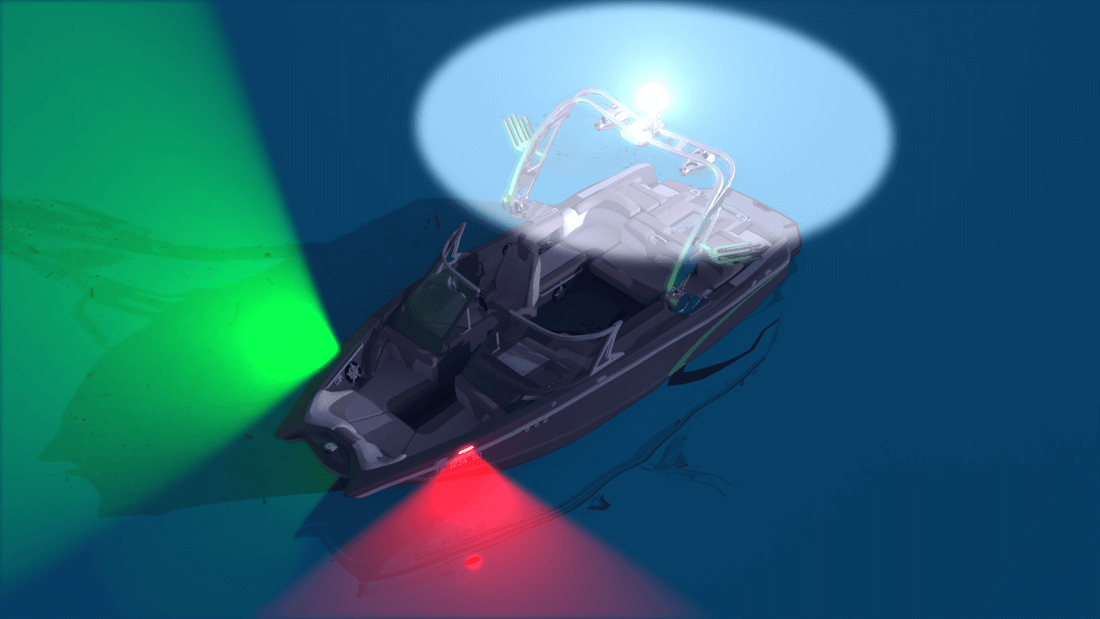
- Powerboats less than 12 meters (39,4") in length
- Powerboats of 12 meters (39,4") and over in length
- Powerboats at anchor
Properly lit sailboat at night
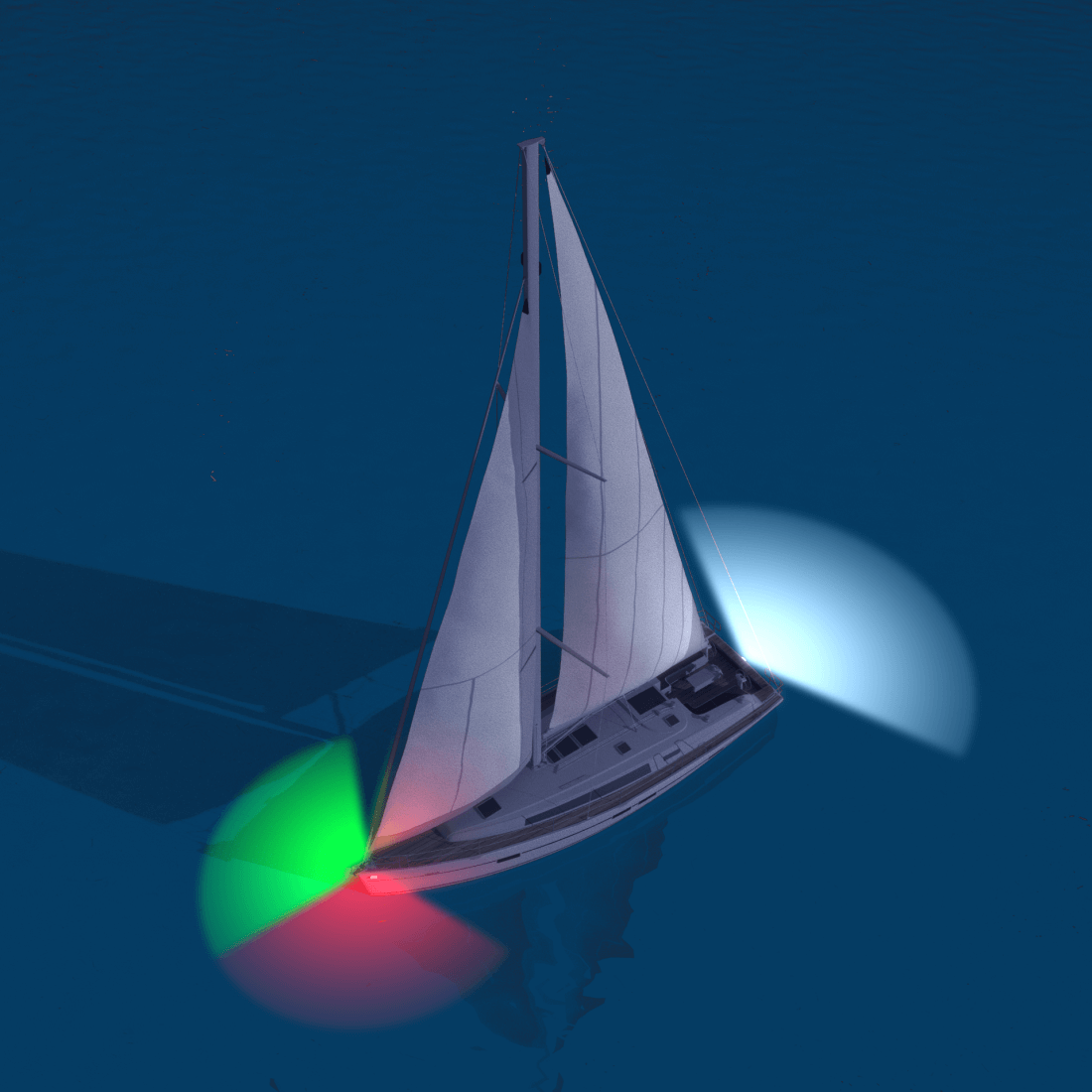
- Sailboats under 7 m (23’)
- Sailboats from 7 m (23’) to under 20 m (65’7”)
- Sailboats 20 m (65’7”) and over
- Sailboats operating under motor power
- Sailboats at anchor
Commercial boats navigation lights at night
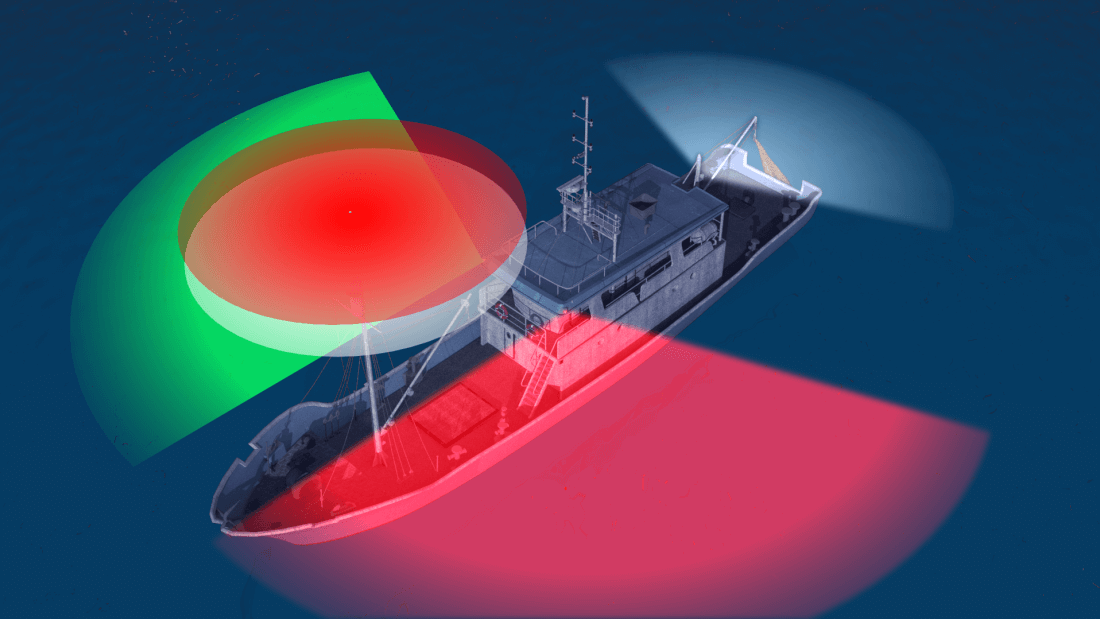
- Navigation lights for a vessel engaged in fishing
Navigation lights for a vessel engaged in trawling
Navigation lights for a power-driven vessel when towing.
- Navigation lights for a government vessel
Navigation lights for powerboats less than 12 meters (39,4") in length
A power driven vessel of less than 12 meters in length, and underway, may display, from sunset to sunrise:
All-round light (white) forward and,
Sidelights (red – green).

Navigation lights for powerboats of 12 meters (39,4") and over in length
A power driven vessel of 12 meters and over in length, and underway, may display, from sunset to sunrise:
Masthead light (white) forward,
Sternlight (white) and,
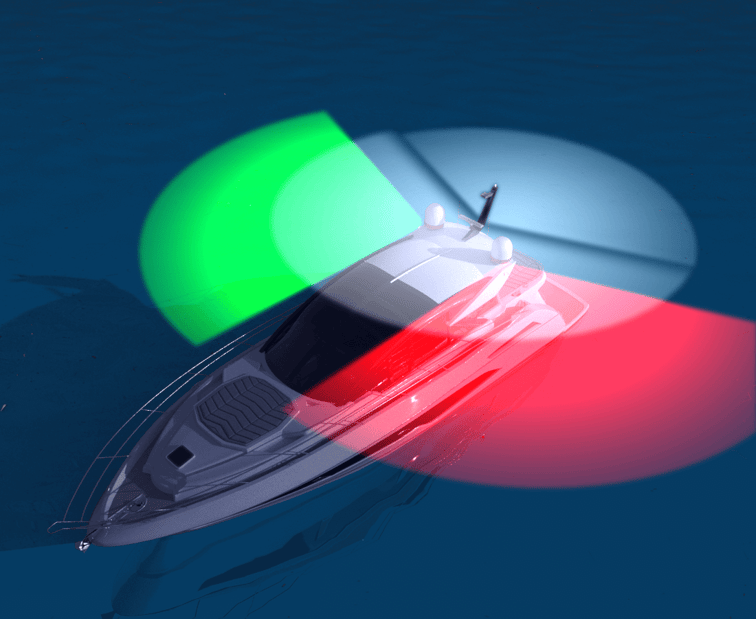
Navigation lights for powerboats at anchor
At anchor, the operator of a pleasure craft shall display, from sunset to sunrise, in the fore part, an all-round light . A powerboat anchored at night must display an all-round light .
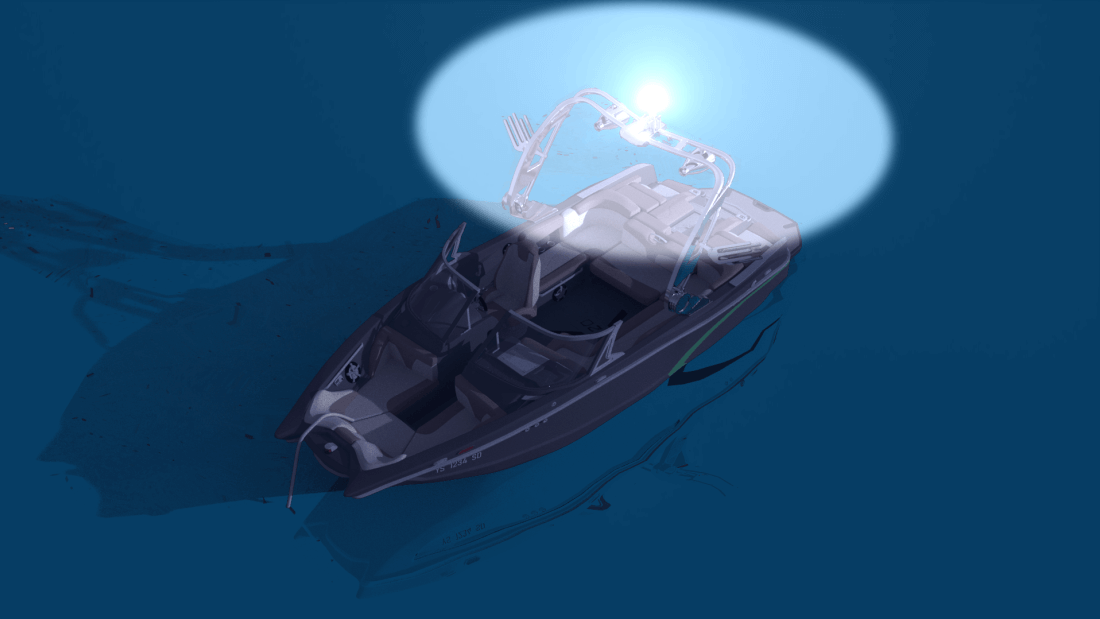

What is a properly lit sailboat at night?
Navigation lights for sailboats under 7 m (23’).
and underway, may display, from sunset to sunrise:
Sidelights (red – green) and,
Sternlight (white).
- 1 lantern, combining the sidelights and stern light above.

Navigation lights for sailboats from 7 m (23’) to under 20 m (65’7”)
- Sternlight , and
- 1 lantern, combining the sidelights and stern light above

Optional - A sailing vessel may exhibit at or near the top of the mast, two all-round lights in a vertical line: the upper one red and the lower one green. These lights are shown along with the sidelights and sternlight.
Navigation lights for sailboats 20 m (65’7”) and over

Navigation lights for sailboats operating under motor power
Sailboats are considered powerboats when they have the engines on - even if the sails are up.
Masthead light (white) forward,
Sternlight (white).
Navigation lights for sailboats at anchor

Navigation lights for kayak or canoe (human-powered vessels) at night
Navigation lights are also required for human-powered vessels (canoe, kayak) or for a sailing pleasure craft of less than 7 meters in length not under power. When underway, the operator shall, from sunset to sunrise, display, if practical, sidelights and a stern light, but if the operator cannot, he/she must have at hand , a flashlight or lighted lantern emitting a white light which must be lit in enough time to prevent a collision.

Navigation lights for a vessel engaged in fishing
Sidelights ,
Sternlight and
All-around light in a vertical line, the upper being red over white light. When making way through the water.

A vessel when engaged in trawling , which means dragging a dredge net or other fishing apparatus through the water, shall display:
Two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being green and the lower white. When making way through the water,
Sidelights and
Sternlight.
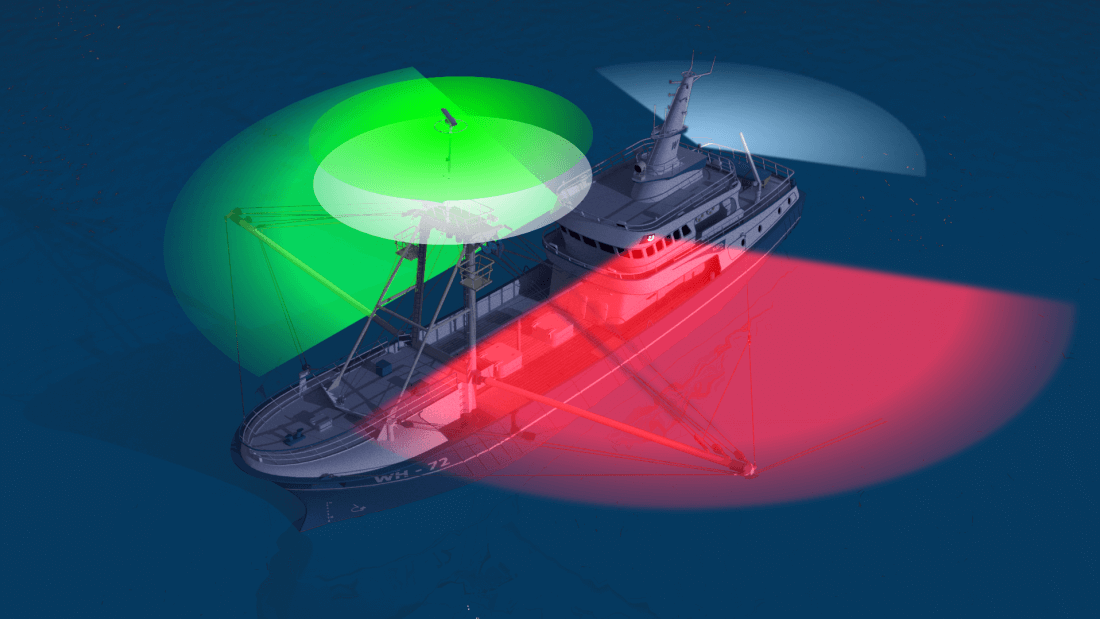
Navigation lights for a government vessel (Police boat)
Any government vessel or any vessel that is owned or operated by a harbor, river, county or municipal police force may display a blue flashing light to identify itself as such, in the following cases
When it is providing assistance in any waters to any vessel or other craft;
When it is engaged in law enforcement duties in Canadian waters.
Power-driven vessel when towing shall show sidelights, a sternlight, and a towing light in a vertical line above the sternlight, and two masthead lights in a vertical line. When the length of the tow, measuring from the stern of the towing vessel to the after end of the tow exceeds 200 meters, three such lights in a vertical line shall be displayed.
Apart from the regular navigation lights, when a boat tows another vessel in distress or in need of assistance for any reason, shall take all possible measures to show the relation between the towed vessel and the vessel doing the towing. A vessel towing must try to shine a light on the towing cable to make it as visible as possible, so that other boats do not come into contact with the cable.
A vessel being tow shall display sidelights and a sternlight. If it is not possible, it must display one all-around white light at each of the fore and aft ends.
Navigation lights for a power-driven vessel pushing another
A power-driven vessel, when pushing another , shall display the sidelights, a sternlight, and two superimposed masthead lights.
The vessel being pushed, and not part of a composite unit, must display its sidelights at the bow. When a vessel is pushing another, if both are connected in a rigid, composite unit, they will be regarded as one unit, thus showing the appropriate lights.
Navigation lights Examples
Sailing vessel seen from starboard side.
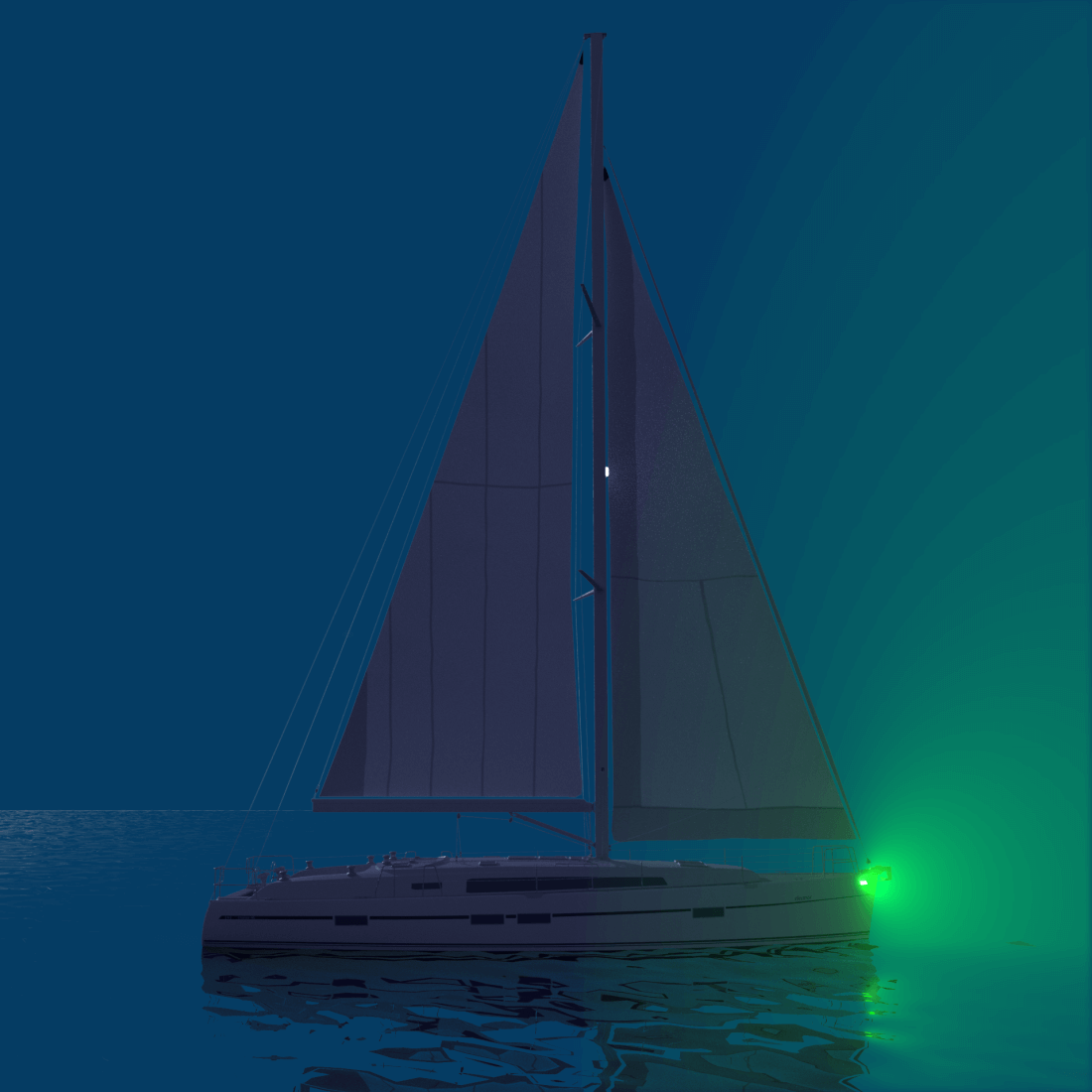

Sailing vessel seen from the front
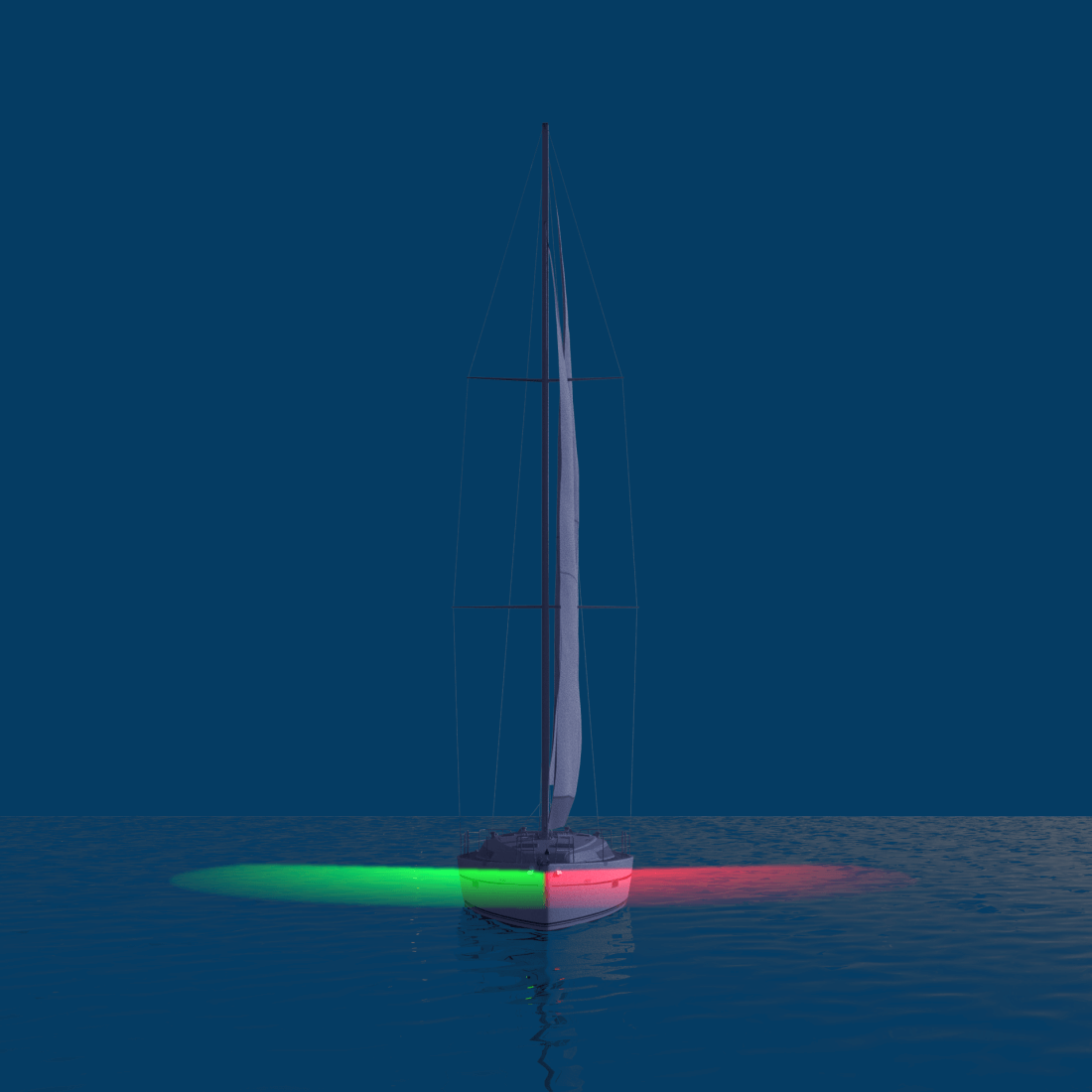

Power-driven vessel anchored

Power-driven vessel seen from starboard side
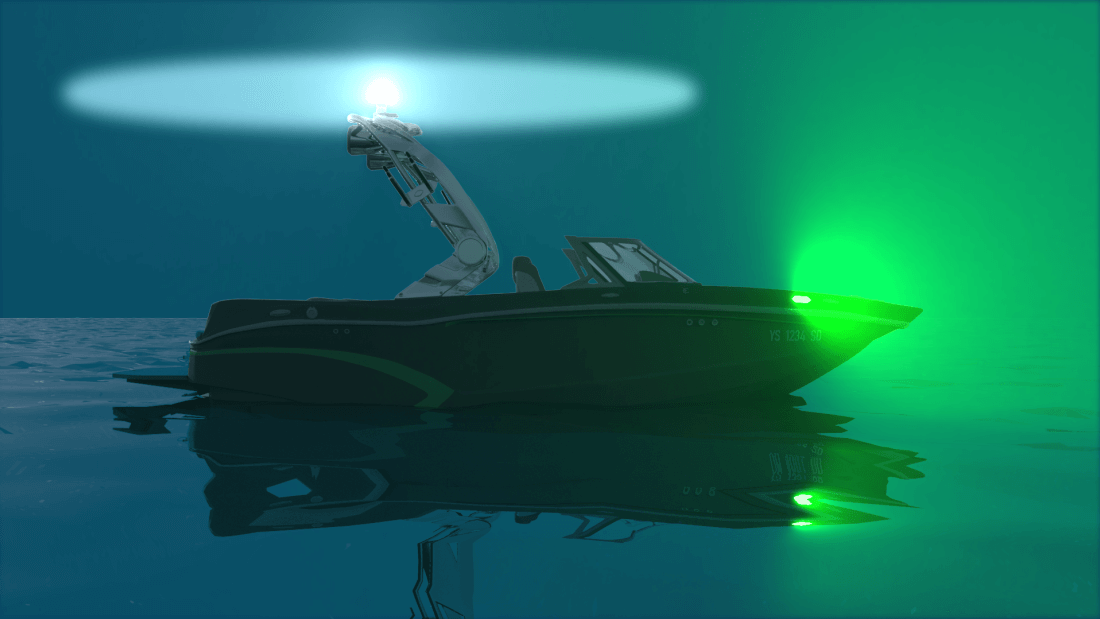
Power-driven vessel seen from port side
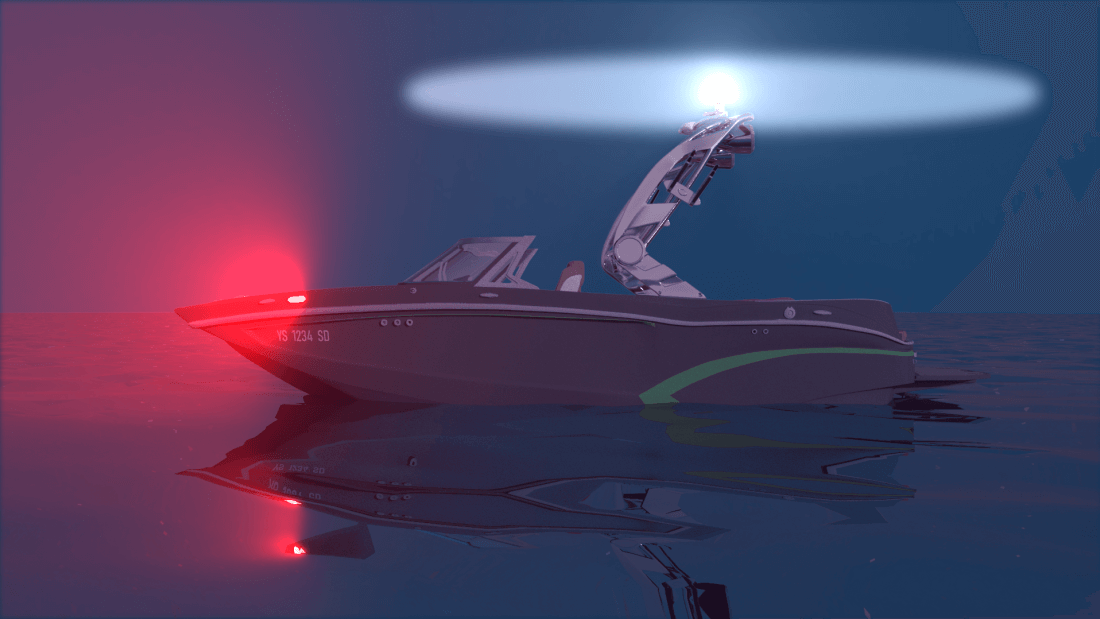
Power-driven vessel seen from the stern (back)
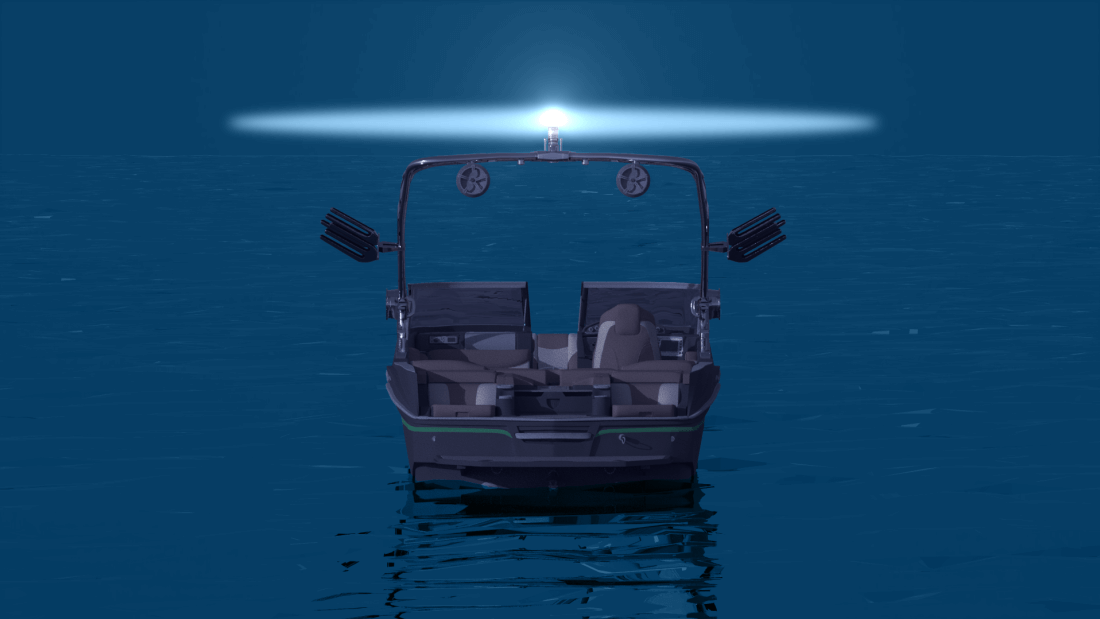

Would you like to learn more about boating safety and be able to drive a boat?
Aceboater s' boating safety course is accredited by Transport Canada to train students on the rules of navigation, buoys and their meanings, boating navigation lights, hazards, how to respond to emergency situations, boating laws and more.
Our course, once successfully completed, will give you the official pleasure craft operator card from Transport Canada, valid throughout North America.
I want my official Canadian boating license .

- Follow Ace Boater on YouTube
- Join Ace Boater on Facebook
- Contact Ace Boater
- AceBoater on Instagram
- AceBoater on X
Boating License & Pleasure Craft Operator Card online exam - Accredited Transport Canada
- Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy

22 Tips For Boating At Night: Helpful Guide (For Beginners)
Boating is an enjoyable activity. Most people think about boating during the day while the sun is shining, but others choose to boat during the evening.
Evening boating can be an entirely new experience whether you choose to watch the sunset over the water, watch a fireworks show, go out for a late meal, or any other night time activity.
When you are out on the water during the evening, you will want to make sure you know and follow nighttime boating navigation rules.
These rules are generally similar to the navigation rules during the daytime, but they are even more important, and there are special considerations to make.
There are also some tips to follow while out on the water in the dark.
These rules and tips can be found below!
Table of Contents
1. What Speed Can I Go When Boating at Night?

When boating during all hours of the day, there may or may not be a posted “speed limit.” Also, check local regulations to see if there is a nighttime speed limit.
This does not mean that you can or should always go as fast as you can.
The navigation rule in place for speed states that a vessel’s operator should always be traveling at a safe speed.
A safe speed is defined as a speed that allows the operator to take proper and effective action to avoid collisions. That will allow the operator to stop within a safe distance that is appropriate under each circumstance or condition.
This means that the operator will need to take certain factors into account when determining the proper speed.
These factors include:
- Traffic Density
- Maneuverability
- Background light available at night
- The proximity of potential hazards
- Vessel’s draft
- Radar limitations
- Weather conditions including wind, sea, and current
- Effect of wake on other boats or shoreline
This means that during periods with low visibility, such as heavy fog conditions, storms, or at night, you should be going slower than you would go on average during the day with perfect visibility.
Remember that while you are boating at night on a body of water that doesn’t have any lights to illuminate your way, you are relying on the small lights featured on the other vessels to determine where traffic is.
For this reason, if you are going too fast and you come around a bend, you might not see another vessel in time to stop.
Even with fancy equipment and your eyes on the lookout, you will likely not see anything or anyone else until they are too close.
Always make sure you are going at a speed that will allow you to stop whenever necessary, even at a moment’s notice.
You will also want to be sure that you follow any “no-wake” zone rules during the evening and in the daytime.
It is also a good idea to go slow in rivers or other shallow water during the evening. There can be large stumps, rocks, or other obstructions in shallow water or rivers that can damage your propeller.
Navigation LIGHT Rules at Night:
Boats are legally required to be equipped with the proper nighttime navigation lights . Even if you do not intend to take your boat out at night, you will still require these lights for your boat to be legal.
These lights are also needed during other periods of low visibility, such as thick fog or intense storms.
2. Navigation Light Requirements:
There are specific lights that are required for boats during times of low visibility.
Depending on the size of boat you are operating, here are the different lights you will need:
Boats less than 39.4 feet long or 12 meters:
These boats need 1 red light and 1 green light at both the front, port, and starboard sides of the boat.
You will also need one white light that can be seen from all angles up to 2 miles away.
Boats larger than 39.4 feet long or 12 meters:
These boats will still need the same red and green lights as the smaller size.
You will also need 2 white lights, 1 at the stern and 1 at the aft, that can be seen up to 2 miles away.
You will also need a red light on your port side and a green light on the starboard side that can be seen up to 1 mile away.
Sailboats or Unpowered Boats:
Unpowered boats that are under 23 feet only need 1 white light on them. These boats can include sailboats, rowboats, or kayaks. If you choose to, you can still add the red and green lights in their appropriate place. An effective way to safely sail at night is to shine a light on your sail if you hear a powerboat. You will be readily visible to other boaters.
Larger sailboats should have lights similar to the powered boat lights on the side and the aft, but there could also have a tri-color light on the masthead that can be visible up to 2 miles away. Sailboats must display a forward-facing, white light when motoring. This is commonly called a steaming light. When motoring, sailboats must abide by powerboat rules.
Never use red and blue lights on your vessel. These lights are reserved for official vessels.
3. What Does a Single White Light Mean on a Boat at Night?
When you see only a white light on a boat, you are headed straight for the other vessel; you are overtaking that vessel.
- Single White Light: If you only see the white light, the other boat is the stand-on vessel, whether underway or anchored. You should be able to go around it on either side.
- White and Green Light: If you see both green and white light, you are the stand-on vessel. This means you need to stand-on and let the other boat pass on either side. Be prepared to give way in case the other vessel does not know the proper navigation rules.
- White and Red Light: When you see both the red and white light, you are supposed to give way to the other vessel. You should either slow down and allow the vessel to pass, or you can turn to your right and pass behind the other vessel.
- Only Red or Green Lights: If you only see a red or green light, you may be approaching a sailboat or unpowered boat. You must always give way for a sailboat. A sailboat should always be the stand-on vessel.
For additional information about the navigation light rules during the evening, you should read this article where we go into great detail about rules for lights on the boat .
4. Navigation SOUND Rules For Boating At Night:

When your visibility is cut off, you will need to rely more heavily on sound. Because of this, you should know the proper navigation sound rules.
These rules include:
Sound Signals the Indicate Direction:
- 1 Short Blast : this indicates that you will pass on your port side.
- 2 Short Blasts : this indicates the plan to pass on your starboard side.
- 3 Short Blasts : this indicates you intend to back up.
Sound Signals that indicate Location:
- 1 Long Blast : this can be used to indicate you are coming around a bend in the river or you are leaving your dock or slip.
- 1 Long Blast then 3 Short Blasts : this indicates you are backing up.
- 1 Long Blast in intervals less than 2 minutes apart indicates that you are a power vessel when you are in blind areas or heavy fog.
Sound signals that indicate Danger:
- 5 Short Blasts: this indicates danger and can be used to indicate a potential collision.
For additional information about the navigation sound rules, follow the link below:
https://www.godownsize.com/boats-horns-signals-explained/
5. Follow Nighttime Navigation Rules:
Navigation rules are similar at night as they are during the daytime.
The only differences are:
- To reduce your speed.
- To place more emphasis on following sound signals.
- To know the proper light signals.
The evening can be darker with lower visibility, so it is even more important for you to know the navigation rules’ ins and outs and follow them.
A miscommunication about who has the right of way could be dangerous at any time, but especially at night.
If you cannot see other boats, you could have an issue seeing what the other boat is doing, and you could be less likely to react to them on time versus in the daytime.
Other Important Tips for Boating at Night:

There are tips for boating at night that are not necessary rules but can still help you during nighttime navigation.
These tips include:
6. Use Your Skipper:
The skipper is an important asset to have on a boat if something happens, and the operator needs someone else to take over.
In addition to this, the skipper can be very helpful while navigating at night. At night, the skipper can serve as an extra pair of eyes while boating in times of low visibility.
Even with excellent vision, your eyes can become tired while trying to see in the dark. If you get too tired, you can rotate the control of the helm with your skipper.
Your skipper can also help you look out for the lights that will be present on other boats. These can be harder to see than simply seeing the other vessel during the daytime.
An extra pair of eyes can mean that you see other vessels faster, which allows you to react faster.
Ensure you follow the navigation rules listed above when it comes to interpreting the lights on a boat.
7. Keep Your Ears Open:
With lower visibility, you should also keep your ears open while operating your vessel in the evening.
It can be beneficial to turn your radio off and make sure you are not utilizing headphones while boating at night.
You will need your ears to hear bells, markers, engines, or horns on any approaching boats.
Make sure you follow the navigation rules listed above when it comes to horn sounds.
8. Use Spotlights and Searchlights Appropriately:
Make sure that you do not immediately shine a spotlight or searchlight on a vessel.
Boats are not equipped with headlights similar to automobiles for a reason. If you try to flash your lights directly at other boaters, you could blind or disorient them.
Make sure you only use this tool when needed.
You might also be tempted to add headlights or continuously use a spotlight while out on the water. These don’t work because, unlike on the road, boats can be coming from any direction.
Also, you will be the only boat that is using a spotlight while out on the water. You will want to follow the navigation light rules that are already in place.
Spotlights can also cause an unnatural shining on the waves that can look like floats or debris, creating a sense of danger.
9. Ensure You Do Not Use Docking Lights as Headlights:
Your boat might have docking lights that look like headlights.
You will want to make sure that you do not mistake these or use these as headlights.
They do not cast as long of a beam as specific headlamps.
These lights are only supposed to be for maneuvering over close-quarter marinas or turning into docks or slips.
10. Drink Responsibly:
Whenever you are boating, but especially at night, you will want to make sure you are alert and boating safely.
This means that if you do choose to drink alcohol, you will want to do so responsibly.
Alcohol can lower your reaction time, your decision-making power and make your vessel’s operation more dangerous.
Most boating accidents are due to operator error, and many of them had alcohol involved somehow.
11. Turn Down Any Ambient Light:

It is a good idea to turn down any ambient light. Any light on your boat can reduce your ability to see off the boat.
Your eyes will adjust better to the darkness if you do not have any other light onboard your vessel.
Ambient lights can include:
- The chart plotter
- Courtesy lights
- Electronic devices
If you cannot turn a light off, you could drape a towel over it to drown out the light.
12. Don’t Spend a Lot of Time Looking at the Stars:
It can be disorienting to look at the stars in the dark while moving.
It can also cause vertigo to look at the stars while moving. Vertigo can even lead to seasickness if you are not careful.
If you want to look at the stars or even map them, you should do this while you are not moving to ensure that you do not get sick or disoriented.
If you anchor your vessel, looking at the stars while out on the water can be a really relaxing and beautiful experience.
While out on the water, you can see the stars better than while on land. This is because of a lack of light pollution while out on the dark water.
13. Novice Boating:
If you are a novice boater, you will want to be completely sure that you can handle anything that nighttime boating can throw at you.
Being fully confident on the water can be crucial at anytime but particularly at night.
User error is one of the main causes of boating accidents. This can be because of a bad call made by the operator or by an operator who was not fully knowledgeable about the navigation rules while boating.
If you are unsure about your operator skills, you might want to consider a boaters safety class.
Operator error is drastically reduced with operators who have completed a boaters safety course.
Knowing the proper rules and regulations can help you when it comes to interacting with other vessels, and it will also help you understand how others will operate their vessels.
It can also help to have an experienced boater on board with you in case of an emergency.
What to Pack for Nighttime Boating:
It is also important to make sure you pack the proper supplies for nighttime boating.
You will also want to pack for evening boating, even if you plan to be out at night. There is always a possibility for unforeseen circumstances.
14. Pack Emergency Light Gear:
At night there will be some specialized emergency gear that you will want to have on your vessel.
This can include:
- Flashlights
This is in addition to the safety equipment that you should always have on your boat .
Which includes life jackets, fire extinguishers, floatation devices, carbon monoxide detectors, and other equipment required by law.
15. Pack Warm Clothing:
It is important to pack warm clothing if you intend to boat at night.
The weather can feel chillier when the sun goes down, even on a summer’s night.
Long clothing can also help to deter bugs and the potential for insect bites.
Even if you do not end up needed the long clothing, it is better to have something and not need it than to need it and not have it.
You should also have clothing in case of foul weather, such as storms.
You will also want to bring towels if you get wet, even if you do not intend to.
16. Bring Sleeping Supplies When Necessary:
If you plan to stay out overnight, you will want to ensure that you have the proper sleeping equipment.
Even on a warm summer night, you will want to have a blanket if it gets cold.
You will also want to pack pillows and other comfort items.
17. Pack Bug Spray:
Like warm clothing that can deter bugs, you should also make sure you have bug spray to keep them at bay.
Bugs are often worse at night and can make any trip uncomfortable.
Bug bites are also uncomfortable in the long term, and you might regret not properly deterring them.
18. Bring Sufficient Food and Water:
Make sure when you are out on the water you have enough food and water for your trip. Even at night, you can suffer from dehydration in warm weather.
Like mentioned, accidents and unforeseen things can happen. If you end up being stranded, you will want to make sure you have the proper nutrients to sustain yourself until help arrives.
If you plan on staying out overnight, make sure you bring the proper food and water for all passengers.
19. Bring Chart Plotters, GPS Devices, and Radars:
A GPS device can help you see the direction you are heading, give you directions, and sometimes give you a scan of the coves that might be in the area.
You can get a chart plotter or buy a GPS device that comes with a chart plotter.
Chart plotters indicate where fixed objects are. These can be buoys and markers. This does not include other boaters.
The radar is a very reliable tool that can indicate the distance of something in the water.
You can also bring and utilize a compass. This can help you find your home port or destination when you cannot use landmarks to find your destination.
These objects are beneficial when it comes to navigation, but you will not want to rely on these devices solely. You will want to keep your eye out for yourself.
20. Pack the Proper Communication Devices:
You will want to make sure you have a communication device on board your boat at any time, day or night.
Anything can happen while you are out on the water, so you will want to make sure you can get help when you need it.
It is also a good idea to have a VHF radio on board if your cell phone is unable to get service or dies.
You will also want to make sure you know the proper emergency channels to get the proper assistance when needed.
21. Don’t Forget to Enjoy Yourself!
While you are trying to remember all the proper nighttime boating rules, do not forget to enjoy yourself.
Boating at night can be an entirely new experience versus boating during the daytime.
It is often quieter and offers a different experience to daytime boating.
Some unique experiences you can have during a nighttime boating outing includes:
- Watching the sunset.
- Looking at or charting the stars.
- Watching evening fireworks.
- Having a late dockside meal.
- Camping on your boat overnight.
Nighttime boating often offers an experience with less boating traffic and less overall noise.
You will also be able to enjoy the open water with a blazing or hot sun, cooler and breezy air, and calmer water without a wake.
22. Keep at It!
The final tip for boating at night is to keep at it. Experience is important when it comes to boating during the day as well as at night.
In the beginning, you should have another experienced boat operator on board in case of an emergency, as well as for the second set of eyes.
You will want to continue to practice boating at night to make sure you get the hang of it.
The saying “it’s as different as night and day” is highly applicable when operating a boat.
Once you get the hang of it and really know what you are doing, you can enjoy many relaxing and no stress evenings out on the water with you and your fellow passengers.
It is also beneficial to practice on nights that have a full moon or a bright moon. This can add additional light to see by while you get used to the difference that comes with nighttime boating and navigation.
Final Thoughts:
If you own a boat, you might be wondering how to get more use and enjoyment out of it. The solution for you could be to get into evening boating.
Boating at night can be a delightful and relaxing experience without the harsh sun and high boating traffic.
Evening boating can be quiet and relaxing as well as you can do many different types of experiences that you cannot do during daytime boating.
If you properly prepare, you can have an enjoyable experience for you and your passengers at night.
Preparations can include:
- Knowing the proper navigation rules regarding the right of way, light signals, and sound signals.
- Knowing the proper speeds for nighttime boating.
- Making sure you are confident in your operating skills.
- Bringing the proper safety equipment.
- Bringing the proper navigation equipment.
- Bringing the proper clothes, bug spray, towels, sleeping items, and other equipment.
- Preparing your boat to lower light and sound, so it isn’t distracting.
- Behaving safely when it comes to operation and the use of alcohol.
- Having an experienced skipper as a backup.
Make sure when you go boating at night, you remember the safety and navigation rules. Being safe out on the water should always be the top priority.
Reducing user error is a matter of being safe and taking the proper boater training classes to ensure you know the proper navigation rules, right of way rules, sound signals, and lighting signals and the proper time to use them.
Remember to have fun when you are out on the water, no matter what time of day. Having a boat is a fun activity and investment for you and your passenger. You will want to make sure you are enjoying it and using it to its full potential.
Click to share...
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

Night sailing tips for first timers
- Toby Heppell
- September 4, 2020
Cruising after dark doesn't need to be stressful. Toby Heppell shares his tops tips for night sailing

Sailing at night can be a magical experience. Credit: Paul Wyeth
Do you find night sailing stressful? It needn’t be if you follow a few basic rules and plan ahead.
Stay on deck while night sailing
As always with pilotage, the right place to be is on deck, not least to avoid uncharted objects such as other craft, mooring buoys and fishing pot markers.
Most pilotage errors occur at night rather than in the day so a thorough pilotage plan is essential.
Even with a navigation station filled with electronic aids it is still possible to become disorientated while trying to reconcile the view on deck with that on the chart.

Where possible, the right place to be is on deck. Credit: Paul Wyeth
You need a pilotage plan.
The most important principle is this: if you know the position of the yacht and you are armed with a chart (electronic or paper) and a compass, you know the range and bearing to the next mark.
This means that when you reach a known position, such as a navigation buoy, you know where to head to find the next one.
Simple, except that a surprising number of navigators waste time scanning the lights ahead with no plan to find the one they want.
Fishing pots
Unpredictable and unlit, these are the biggest danger at night.
Avoiding them is largely a matter of common sense.
Sometimes they are laid in deep water, but mostly they lurk in less than 50m.

Fishing pots, hard enough to spot in the daylight, become all but invisible at night
Avoid shallows if you can, especially near fishing harbours, and inside passages around headlands, even if you are confident of your position thanks to radar and plotter.
Even if you know where you are, there’s still the same risk of the engine stopping with a crunch, or finding yourself moored by the rudder or prop in a strong tide.
Light pollution
Light pollution is a well-known source of navigation stress, particularly when looking to enter an unfamiliar harbour after dark.
If it has been a while since you have done this, it is well worth returning to your own harbour after dark and noting the different complexion the various landmarks take on when not visible to the naked eye.
A large, unlit buoy may be sited just in front of a particularly well-lit hotel rendering it difficult to spot.
Another feature of light pollution (but of sailing at night more generally too) is the reduction in our ability to judge distances.
This is particularly acute when coming into harbour.
A navigation buoy’s light may well get lost in the background of a sea of lights when, during the day it would be clear and obvious the nav buoy was some way offshore.
Night vision
The sensitivity of our eyes increases the longer they are in the dark and it can take many minutes for maximum sensitivity to be acquired, and the improvement is dramatic.
Unfortunately it can be lost in a few seconds of exposure to bright lights.
Eyes have cones that are used for colour vision in daylight, and more sensitive rods that come into their own at night.
The rods are not sensitive to red light and this means that if you switch to red illumination your eyes can continue to adapt while you move around the boat.
The bad news for those of pensionable age is that your eyes will only be about a third as sensitive to low light as in your youth.

Is red light at night always best?
Binoculars will boost illumination by about 50 times and go a long way to redressing the balance.
However, it still pays to have your youngest crew on lookout.
It is worth noting too, that in this high-tech age, our cockpits are often filled with screens all giving off light.
Most of these screens can be dimmed or put into night mode, but sailing in the dark can be such a calm experience that the harsh light of screens can detract.
Keep your electronics on and functioning and use as appropriate.
If they are on and lit up in the cockpit they tend to draw the eye and can have the effect of making you less aware of that which is going on around you.
Poorly lit craft
Inshore, yachts can be hard to spot.
Coming into places like Southampton, Portsmouth or any other significant port with strong background lighting and a tight channel for leisure craft you are likely to be up against a significant confusion of lights.
Yachts are especially awkward if they opt for a tricolour at the masthead instead of proper running lights in close quarters.
You are looking ahead for trouble, not up in the sky!
Tricolours are great on passage though, increasing the likelihood of being spotted and minimising power drain – remember, do not use your tricolour when under power.
Fishing boats’ navigation lights are often made hard to see thanks to a bright deck light to enable the crew to work on deck.

Many larger ships are well lit up at night making them easier to spot. Credit: Colin Work
Watch them closely and expect erratic course changes.
Try to give them plenty of space to stay safe.
Around the UK other than the decklights making it hard to discern their heading from a distance, fishing craft should not cause too much worry.
But, you will want to avoid ending up astern of them in case they are trawling, so do take plenty of time to discern their direction of travel.
In some parts of the world fishing craft of various sizes do sometimes operate without proper lighting, so if you are entering a busy seaport always take it slowly.
Cruise ships and ferries are invariably lit up like Christmas trees.
It can be hard to pick out the red and green amongst the plethora of other lights onboard, so take time to work out what they’re up to and consult AIS if you have it.
Given their size, if you are close to shore even without seeing their nav lights it is usually fairly easy to make a decent guess at their bearing relative to you by glancing at your chart to get a sense of the main nav channels.
Safety on deck while night sailing
For the most part you will have your own rules about when lifejackets go on, whether that be worn the whole time, when the windstrength is above ‘x’ knots etc.
The strong recommendation is to always wear a lifejacket when on deck after nightfall, and this is sensible.
Some choose not to in calm weather and if they are in the cockpit.
As ever, what you decide will be between you and your crew.

Wearing a lifejacket when sailing after dark is advisable
For my part I would strongly recommend a lifejacket at all times after dark.
Clipping on via your harness is also strongly recommended.
If you are sailing a long passage at night then do be aware of your harness clip scraping along the deck if you are moving around – it’s a very irritating noise for those trying to get some kip below.
It’s not always easy to force discipline on yourself, but it really does make sense to call on your crew if you need to go up on deck for any sort of sail adjustment.
Safety is not about buying things.
It is about an attitude of mind.
We must constantly be on the lookout for trouble at night so that we can forestall it, just as we do in the daytime.
If you are setting out on a passage that may well extend into the night, it is worth considering what food you intend to take.
There is a lot to be said for preparing an evening meal before set off.
Something like a pre-made stew can be easily heated and give you a boost to cover the last miles.
It can also help you warm up on deck or make for a hearty meal once you are tied up.

Have snacks and hot drinks easily to hand
Whatever you choose, make plenty of it, that way you have enough to get you through the night, or you can have a bit to keep you going but still have a meal left when you arrive at your destination.
Hot drinks are axiomatic.
Boiling a kettle and having somewhere safe to place a mug while you make an instant coffee has to be easy.
If it isn’t and you are reduced to pre-heating thermos flasks, there is something wrong with your boat or your arrangements.
Keep the drinks coming.
They maintain morale and give people something to do.
Effect on weather
All air usually cools at night, even over the sea.
This will be more obvious when it has been a sunny day not far from land.
The result is that there are fewer gusts and a decrease in the average wind strength as the thermally enhanced breeze disappears.
On a night with low-lying cloud or hill fog, some lighthouses will not be visible.
Note the height of the lantern from the chart and be ready for the occasional disappointment.
Continues below…

Is red light at night best?
Dag Pike considers the age-old adage that using red light preserves your night vision

How to tackle a night passage short-handed
Worried about ‘things that go bump in the night’? Tom Cunliffe says night sailing is easier than you think –…

Night pilotage: How to enter unfamiliar harbours
James Stevens looks at how best to prepare for arriving at an unfamiliar harbour after dark and what to be…
Halos around the moon can be really obvious at night.
A big one is often a sign of an approaching front.
If the wind is light, think about starting the engine and keeping up boat speed.
In conditions when the air is moist, a degree or so of cooling after dark might be just enough to shut down poor-to- moderate visibility into mist or even fog.
Distant lightning is more easily seen at night, so don’t be too alarmed if you see it flashing around the horizon.
Sailing and sail handling while night sailing
Once darkness falls, moving around on deck should be reduced and so it makes sense to have out sails that are well within the conditions at the time.
Many skippers like to shorten sail before dark, regardless of conditions, so as to minimise the chance of having to handle sails at night.
However, you should still be willing and able to change sails, or take in or let out reefs, if necessary, particularly if you are on a long passage.
It is a very good idea to mark your halyards so that you can roughly get them in the right place for reefs etc.

Some skippers like to shorten sails as night falls to minimise the chance of sail handling. Credit: Graham Snook/YM
You should also have a working set of deck lights, so you can illuminate everything when doing big jobs.
If you are not far from your final destination and daylight is disappearing, it might be worth switching the engine on and getting sails down and tidy before the dark really takes hold.
But if you’re confident in your passage plan then this is far, far from crucial.
Reducing sail, however, helps with your own ability to see and be seen.
In busy areas many sailors like to have quite a bit of the headsail rolled away as this improves visibility looking forward – a good idea for busy ports in daylight too.
At the beginning of the night, the skipper should make sure everyone understands what adjustments can be made unsupervised by those on deck and when more crew should be called up to assist.
This may vary, depending on the crew’s experience.
Intuitive sailing
There are additional strips you can get added to sails that glow at night to allow you to properly set them at night, but this is really only necessary for racers and those looking to make very long night passages.
In truth, there is usually enough light to get some decent sense of how your sails are set, and if you have reduced sail before night falls, then the consequences of getting things wrong is just a slowing of pace.
Having a torch handy to check trim and telltales is a real help.

Toby Heppell got his first boat aged four and grew up sailing on the East Coast. He has been a sailing journalist for over 15 years. Credit: Richard Langdon
Though some are tempted to switch on the motor once dark falls, sailing in the dark is a really fun and tranquil experience and can improve your sailing skills during the day.
Without the ability to see gusts approaching on the water, your sail trim is going to be far more reactive than it might otherwise be.
Feel becomes key when sailing at night.
Sailing by feel is something of a specialism for blind sailors.
Lucy Hodges, Blind Sailing World Champion, once offered me this advice: ‘A key area for me when sailing are the hairs on the back of my neck. I always make sure that my neck is exposed. With a bit of practice you may be surprised how quickly you can lean to feel changes in wind pressure and direction.’
The key to sailing by feel, is using all of your senses.
Feeling the roll of a boat is essential, if you feel the boat is starting to heel, and if the hairs on your neck have not changed, the wind might not have altered and you probably want to adjust course slightly.
If the boat begins to heel and the hairs on your neck feel different, the wind may have increased so you might adjust trim.
Of course with visual inputs too, we do not need to sail entirely on feel when night falls, but it does stand as a great example of how different and rewarding sailing at night can be.
It can really help you feel more in tune with your boat.
For all the latest from the sailing world, follow our social media channels Facebook, Twitter and Instagram .
Have you thought about taking out a subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine?
Subscriptions are available in both print and digital editions through our official online shop Magazines Direct and all postage and delivery costs are included.
- Yachting Monthly is packed with all the information you need to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our expert skippers and sailors
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment will ensure you buy the best whatever your budget
- If you are looking to cruise away with friends Yachting Monthly will give you plenty of ideas of where to sail and anchor
3rd annual “Light Up The Fox” yachting event set for Saturday night
GREEN BAY, Wis. (WBAY) - Preparations are underway Saturday afternoon for the Green Bay Yachting Club’s third annual “Light Up The Fox” event.
The boat parade is free and open to the public for viewing. It starts at 9 p.m. on Saturday night.
Boaters will make their way from the mouth of the river through the Ray Nitschke Memorial Bridge on Main Street and the Bart Starr Memorial Bridge on Walnut Street bridge before looping back south.
The best places to watch, according to organizers?
The CityDeck, the Neville Public Museum, and Leicht Park.
Copyright 2024 WBAY. All rights reserved.

Green Lake County Sheriff’s Office asks boaters to avoid area of Green Lake on Saturday

Body of missing boater Bill Salnik recovered by Marinette County Sheriff’s Office

Authorities find body of man who fell into Wolf River in New London

More Central Wisconsin towns experiencing problems with missing mail

Reedsburg Area High School cancels two varsity football games due to an investigation

Green Bay woman busted with ‘6 pounds of meth’ gets 10 years in prison

Former President Donald Trump to hold Town Hall in La Crosse

Operation Football “Legit Play of the Week”
Latest news.

Green Bay Metro Fire Department puts out garage fire that homeowner didn't know was happening

Cudahy man walking hundreds of miles to raise money for recovering addicts

Appleton community gathers for workout in honor of former police officer, U.S. Marine

4th birthday party held for missing boy Elijah Vue

One person displaced following early evening structure fire in Kaukauna

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A properly lit sailboat at night is a boat that is equipped with the correct navigation lights, which are required by law. These lights must be visible for two miles and should include a green light on the starboard side, a red light on the port side, and a white light aft. Additionally, the boat must also have a white masthead light that is ...
Sailboat lights at night are a crucial part of safe navigating when it's too dark to see. Most accidents on the water occur because of a collision whether it's with a fixed object or another watercraft. The majority happen when visibility can become an issue, whether it's dawn or dusk.
==Short answer sailboat navigation lights:== Sailboat navigation lights are essential safety features that help vessels communicate and avoid collisions at night. These lights, such as the red and green sidelights and white stern light, allow sailors to determine the direction and status of approaching boats. Understanding the Importance of Sailboat Navigation LightsUnderstanding the Importance of
Red and green sidelights, one sternlight, and two all-round lights in a vertical line (upper red, lower green) also meet the navigation lights requirement for sailboats that are not operating under engine power (Rule 25). One combination red, green, and white light exhibited near the top of the mast meets the navigation lights requirement for ...
For most small vessels, motoring requires red and green (port and starboard) lights, and a white light visible in all directions around the boat. This is almost always a stern light and a masthead light on sailboats. Boats under sail require port and starboard lights, and a white stern light. Sailboats below sixty-five feet may show a tricolor ...
In addition to the navigation tips above, there are several safety precautions you should take when sailing at night: 1. Ensure Your Boat is Properly Lit. Make sure your boat's navigation lights are functioning properly and are visible from all angles. This will help other vessels see you and avoid collisions. 2. Wear Reflective Clothing and Gear
In this article, we'll discuss the proper sailboat lights at night. Sailboats are required to have three lights at a minimum: a masthead light, a red port light, and a green starboard light. The masthead light is white and is located at the top of the mast. This light should shine forward and aft and be visible from 2 nautical miles away.
Navigation lights requirements vary depending on the length of the boat. Larger boats are required to use lights with a higher visibility range and cannot combine sidelights into a single bi-color light. Powerboats and Sailboats When Under Power. The basic rule is that side lights, a masthead light and a stern light are required.
Here are some key steps to take before embarking on a night sailing adventure: Check your navigation lights: Ensure that your boat's navigation lights (red and green sidelights, white stern light, and white masthead light) are functioning correctly and are visible from the appropriate distances.
All boats must be properly lit for other vessels to see. And, a boat doesn't work like a car either, where we shine our headlights on the road ahead to see what's in front of us. At sea we rely on navigation, nautical charts, lighthouses and the captain's knowledge. Basic boat lights include running lights, steaming lights and anchor lights.
The most common of our navigation lights are our "running lights". This is a red light on the port side of the boat and a green light on the starboard side that shine from the bow to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam of the boat. This creates a 112.5-degree arc on either side of the vessel. To complete a 360-degree circle, our white stern light ...
As such a power boat, and by extension all sailboats, MUST, without question show one green light on the starboard bow and one red light on the port bow and one all around white light or lights while operating in reduced visibility. These lights should shine at all 360 degrees of visibility with the bow lights shining at an angle of dead ahead ...
Knowledge of navigation lights is important to a small-boat skipper for separate, but important, reasons. You are legally responsible for displaying lights of the proper color, intensity, location and visibility on your boat. You are required to display the appropriate lights at night or during times of reduced visibility.
Don layers, with a spray jacket on top and life should be good. Carry a decent searchlight. Night boating involves becoming accustomed to the available light and acclimating to it. It's actually one of the cool things to experience during a sail in the dark, so constantly shining a spotlight like you were hand-holding your car's headlights ...
Proper navigation lights are crucial for nighttime sailing, as they help you to see and be seen by other vessels. At a minimum, your boat should be equipped with the following lights: Bow lights: Red (port) and green (starboard) lights mounted on the bow of your boat, visible from at least one mile away. Stern light: A white light mounted on ...
Is Sailing at Night Safe? Safety is the primary concern for newcomers. We ensure all safety measures are in place, with well-trained crew adept in night navigation and emergency procedures. The sea at night is a different world, demanding respect and caution. What to do at night when sailing? Nighttime on a sailing vessel can be magical.
Know Light Patterns. When you sail at night you may encounter other boats, so it's critical that you understand the lights on other boats. ... If you want to enjoy your time on the water, make sure you have proper attire for nighttime sailing. Related Articles. 5 Reasons Why I Love Sailing Singlehanded And 5 Reasons Why I Need A Crew.
Side lights: a green light on the starboard side of the bow and a red light on the port side of the bow; Stern light: a white light at the stern; Masthead light: a white light affixed to the mast; Navigation light requirements for human-powered craft. Human-powered boats are required to display a white light that can be seen from all sides.
Cautious sail plan. Moving around on deck should be avoided whenever possible and so it makes sense to only have out sails that are well within the conditions at the time. In busy areas I also like to have quite a bit of the headsail rolled away as this improves visibility looking forward. Light spotting.
Navigation lights for kayak or canoe (human-powered vessels) at night. Navigation lights are also required for human-powered vessels (canoe, kayak) or for a sailing pleasure craft of less than 7 meters in length not under power. When underway, the operator shall, from sunset to sunrise, display, if practical, sidelights and a stern light, but if the operator cannot, he/she must have at hand, a ...
Navigation lights must be displayed on a boat if you are operating your boat at night or in poor visibility. The term "night" here refers to the period between sunset and daybreak. During the daytime, poor visibility can refer to heavy fog or even inclement weather, such as rain or snowfall. In this article, Drive a Boat Canada explains all ...
Bringing the proper clothes, bug spray, towels, sleeping items, and other equipment. Preparing your boat to lower light and sound, so it isn't distracting. Behaving safely when it comes to operation and the use of alcohol. Having an experienced skipper as a backup. Make sure when you go boating at night, you remember the safety and navigation ...
Stay on deck while night sailing. As always with pilotage, the right place to be is on deck, not least to avoid uncharted objects such as other craft, mooring buoys and fishing pot markers. Most pilotage errors occur at night rather than in the day so a thorough pilotage plan is essential. Even with a navigation station filled with electronic ...
GREEN BAY, Wis. (WBAY) - Preparations are underway Saturday afternoon for the Green Bay Yachting Club's third annual "Light Up The Fox" event. The boat parade is free and open to the public ...