
What Is A Boat With 2 Masts Called?

Two-mast sailboats hold special places in many sailors’ hearts. In addition to being dignified and majestic, a two-mast sailboat offers a perfect balance that can be easily achieved by adjusting the masts in many different ways. Let’s look at the different types of two-mast sailboats.
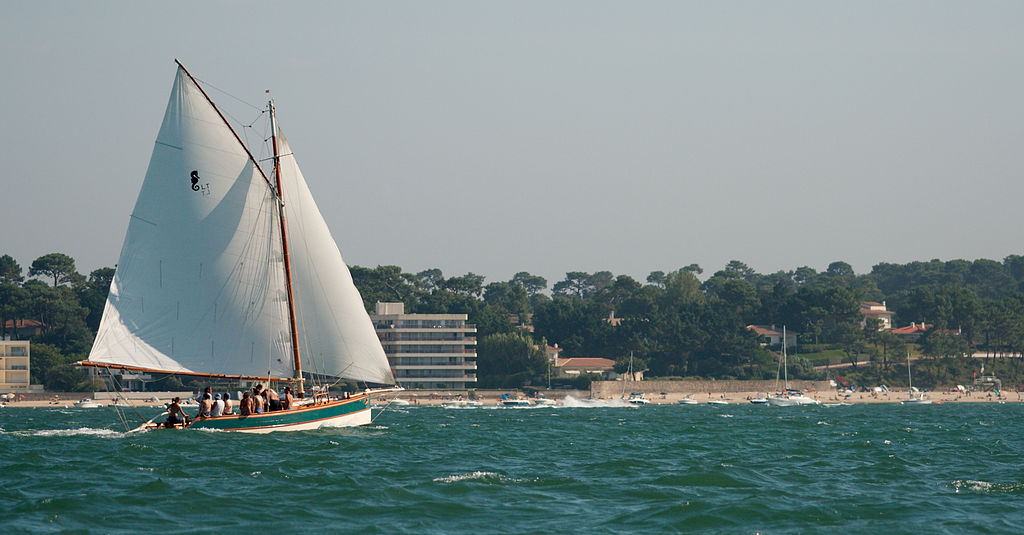
Whether you’re a sailboat fanatic or an interested observer, there’s something special about two-mast sailboats. In most cases, the first thing you’ll notice about a sailboat is the two masts. Generally, the mainmast is often taller than the aft-mast, which is often referred to as the mizzenmast. The mizzenmast is like a trusted old friend. It not only helps in stabilizing the sailboat under power but can also act as a bow thruster in certain scenarios. There are many reasons why sailors sing a lot of praises as far as two-mast sailboats are concerned. In heavier winds, you can break down the main mast and use the mizzen mast to give you a more balanced and comfortable sail even in the worst of conditions. But what is a boat with 2 masts called?
There are several sailboats with two masts. The most common ones include yawl, ketch, schooner, and brig. In most cases, the designs of the masts do vary but the main idea remains the same. They can have the extra mast either behind or in front of the mainmast. If the additional mast is in front of the mainmast, it’s known as a foremast but if the additional mast is behind (aft of) the mainmast, it’s known as a mizzenmast.
Let’s take a brief look at these two-mast sailboats.
Table of contents
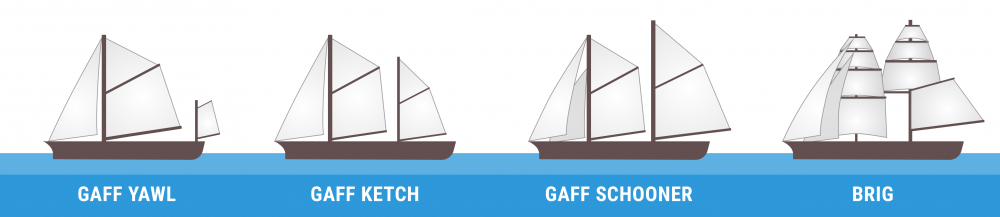
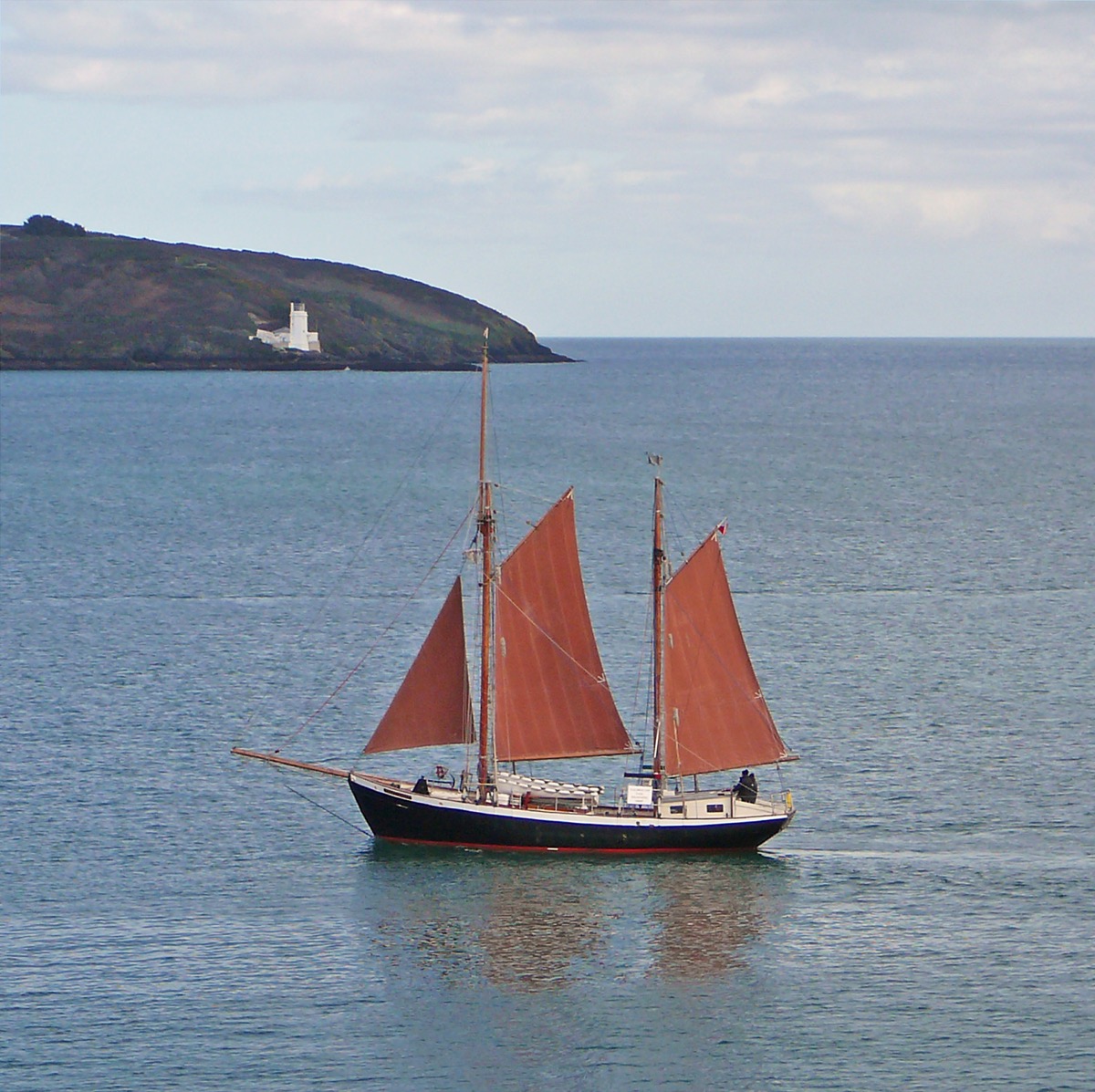
A yawl is one of the most common types of two-mast sailboats. It has two masts: a mizzenmast and the mainmast. The mizzenmast is usually much shorter than the mainmast. This makes it an oblique type of a sailboat in the sense that the mainmast is located in the front of the boat while the mizzenmast is located in the rear past or the boat.
The mizzenmast of a yawl is mainly used to increase the helm balance and is located aft of or behind the rudder.
It’s always easy to confuse a yawl with a ketch so it would only make sense to clear up before going any further. They both have two masts with the mainmast at the front while the mizzenmast is smaller. The difference between a ketch and a yawl comes down to the location of the mast. In a yawl, the mizzenmast is behind the rudder post while in a ketch, the mizzenmast if in front of the rudder post.
Again, the mizzenmast of a ketch is nearly as tall as the mainmast and is used to carry a mainsail. Its main function, however, is to drive the sailboat forward and can sufficiently sail the boat, especially in heavier winds. This is very different from the mizzenmast of a yawl, which is only used to increase the helm balance and cannot drive the boat forward. This means that the mizzenmast of a ketch is bigger than the mizzenmast of a yawl. In short, the mizzenmast on a ketch is technically a driving sail while the mizzenmast on a yawl is more of a balancing sail.
A ketch generally has an advantage over a sloop in downwind or in heavy winds. This is because it has a variety of setups than a typical sloop. The mizzenmast gives you a lot of options to depower in heavy winds and find the most perfect amount of canvas to fly. It can also help in stabilizing the sailboat under the power given that the mizzenmast is naturally in an excellent position.
In essence, a ketch has many practical benefits that can be ideal in most situations in the waters. In addition to sailing peacefully on a beam-reach, a ketch is easily manageable and can give you a lot of options in various weather conditions and situations.
When it comes to a two-mast schooner (a schooner can have two or more masts), the foremast is usually smaller than the aft most mast, which is essentially the mainmast. As such, the main characteristic of a schooner is that the masts are almost of the same height but the foremost mast is slightly smaller.
Even though a schooner is easier to sail than say a sloop (one-mast sailboat), it isn’t very fast. This is why most sailors prefer a sloop to a schooner but it’s a sight to behold, especially when under full sail. While a schooner with a square topsail is the most common, there are others with sprit rigs that run diagonally. Schooners with spritsails are not ideal in big seaways because the sprit rig cannot be lowered since it could become unmanageable. On the other hand, the sprit rig is ideal in coastal waters given that the topsail can catch a high up breeze.
Like the above-mentioned two-mast sailboats, the brig has two masts with the foremost mast squared. The mainmast can be squared, partially squared or triangular. Some brig sailboats have a lateen mainsail on the mainmast. Historically, brigs were used by pirates and were set in motion using oars. Its name is derived from the Italian word “brigantine,” which loosely translates to “pirate.” These types of sailboats were used by pirates the Mediterranean in the 16th century before they became sailboats.

The two most common types of brigs are:
Brigantine – The foremost mast is usually partially squared but the mainmast is triangular.
Hermaphrodite brig – It’s also known as the schooner brig or the half brig. The two masts are partially squared but the mainmast is gaff-rigged and topsail, which technically makes it half schooner.
When it comes to speed and maneuverability, brigs are easy to handle and maneuver and perhaps that’s why they were preferred by pirates. Again, brigs are generally larger than other two-mast sailboats or single-mast sailboats.
There you have it; there are various types of two-mast sailboats, so there’s not a single name that fits all. You can choose any of them as they’ll serve you perfectly, especially in heavy wind conditions.
Bon Voyage!
Related Articles
Daniel Wade
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Sailboat Parts
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

7 Popular Sailboats with Two Masts (With Pictures & Prices)
Sailboats can come with one, two, or even more masts. You can also have different-sized masts placed on the front, back, or middle of your vessel.
Below, I have listed popular sailboats that have two masts.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Check also: Average sailboat price examples .
Things to Know About Sailboats With Two Masts
When looking for sailboats with two masts, you should know what you are looking for. A Ketch is one type of sailboat with two masts.
Knowing this term can help you to nail down your search when looking for a boat with two masts.
These boats come in many shapes and sizes as well as many different types of designs. Generally, these types of boats have the taller mast being forward and the smaller mast near the aft.
Yawls are also boats that feature two masts.
These also come in multiple types and designs. The difference between the Ketch and the Yawl is that the Yawl has the larger mast in the aft instead of forward. They also have smaller sails and can be easier to handle.
Another type of sailing ship that features two masts is a Brigantine.
This ship has mixed sailing rigs which commonly features squared sails on the front part of the ship and triangular sails on the back of the ship.
These boats are often larger and require more people to handle them.
7 Great Used Boats with Two Masts
There are many benefits to used boats including a lower cost. You can get a larger boat for a lower cost if you choose to buy used.
When looking at used boats, you need to make sure you look at the boat and its features thoroughly to make sure everything is in great working order.
If you do not feel confident that you can properly look over a used vessel, you can even hire a marine inspector to look it over and let you know of any potential issues or needed repairs. You can use this assessment to decide what is worth it, or if the needed repairs fall into the budget.
It is much more common for a used boat to have more than one mast. This is because the newer sailboat models are creating their new designs with just one mast.
One mast ships are easier to handle and manage so new designs are trying to optimize design and ease of sailing.
Below are great used sailboats with two masts which I have arranged by price .
1. 1976 Westerly Center Cockpit Ketch

This 1976 Westerly Center Cockpit Ketch is a small 36-foot long sailboat with two masts. This is a solidly built cruising vessel that features a center cockpit ketch layout.
This boat has a small 38 horsepower engine perfectly fit to navigate its smaller size.
The interior features 1 single berth and 3 double berths all in 3 cabins. This boat also has 2 full heads onboard.
You also have a full galley with a 4 burner stove, refrigerator and freezer, stainless steel sink, and microwave oven.
This boat makes great use of limited space and offers many amenities in a much smaller frame.
Price: $37,000.00
2. 1978 Jeanneau Gin Fizz

The 1978 Jeanneau Gin Fizz is a trusted and popular two-masted design capable of crossing the Atlantic Ocean .
This boat is also very spacious for a boat that is only 38 feet in length. This model also won an award for “security, comfort, ease of handling, and ability to handle varying conditions.”
This particular used model has been well maintained and upgraded over the years.
This boat is great for family cruising, offshore passages, and even racing.
This boat features a 50 horsepower engine to help navigation.
Inside you can find 2 cabins and 1 head. You will be highly comfortable with air conditioning and other interior luxuries.
Price: $46,000.00
3. 1979 Freedom 40
The Freedom 40 is a classically designed centerboard ketch with two masts. This boat is a great sailor loaded for cruising on the wide-open blue water.
This sailboat is 40 feet in length and features accommodations for six people that include a double-v berth, another double berth, and two single berths.
There is also a full head that can be accessed both from the main salon and aft cabin.
This boat was recently painted and features newer interior fabrics, forced air heating, and much more.
You can find a dinette with separate freezer and refrigeration compartments, a stove with an oven and broiler, a double stainless steel sink, plenty of storage, and other interior features.
This boat also comes with an outboard motor with 50 horsepower and a hard bottom inflatable dinghy.
Price: $54,900.00
4. 1977 Puma 38 Ketch

The Puma 38 Ketch is a two-masted sailboat built for racing like the rest of the Puma sailing line. This brand prides itself on speed and maneuverability.
The 1977 Puma 38 is 34 feet in length with a backup diesel engine that can help you get where you need to go as well as docking into a slip. This motor features more horsepower than the average sailboat with 45 horsepower.
Features on this vessel include autopilot, electrical and manual bilge pumps, a full marine head, running hot water, and refrigerator.
This boat is made of fiberglass with teak finishes and looks well kept. You can find this boat in Spain if you are interested in purchasing it.
Price: $66,099.00
5. 1973 Morgan Out Island 41
Originally designed by Charley Morgan, the Morgan Out Island 41 is a center cockpit shoal-draft cruiser that features two masts.
This larger boat is 41 feet 3 inches in length and features many amenities.
This boat is the tri-cabin version and features interior heating, pressurized hot and cold water, a 2 burner gas oven, and a fridge.
This boat also seats up to 7 in the 3 cabins and the saloon. There are also 2 full heads on this vessel.
This boat is even equipped with an inboard motor . Inboard motors are easier when it comes to navigation including backing up, which is generally hard for sailboats to do.
Price: $68,596.00
6. 1970 Hinckley Bermuda 40

This 1970 Hinckley Bermuda 40 is a gorgeous two-masted boat painted with a mixture of desert sand and oyster white on the exterior and features a beautiful and well-kept deck.
This boat has previously had all her systems replaced and upgraded and features a 40 horsepower engine that was new in 2014.
This boat features a mahogany interior and sleeps up to 6 people in 2 cabins. You can also find a 3 burner propane stove with oven, fridge and compressor, new countertops and plenty of storage.
This boat is a stunning and highly upgraded “must-see” at a very reasonable price.
Price: $129,500.00
7. 1995 Amel Super Maramu

A newer model of sailboat is the 1995 Amel Super Maramu sailboat. This sailboat has two masts and is very long at 53 feet.
This boat features an aft deck, steps molded right into the hull, well-protected cockpit an many other features. This boat has a large 76 horsepower engine which is more than the average sailboat is equipped with.
Inside, this boat features 2 cabins and 2 heads with showers. There is also plenty of storage, air conditioning , and electric heaters. There is also a nice salon and galley with a refrigerator, dishwasher, chest freezer, microwave oven, 3 burner stove, and other appliances.
This boat is great for multiple days out on the water and is new and updated. Because of the year, this was manufactured and the features, this boat has a larger price tag than the previous models.
Price: $299,990.00
Final Thoughts:
Sailboats are a great way to enjoy a day out at sea. Most sailboat models come with sleeping arrangements and even a kitchen. This makes them ideal for trips that will take more than a day.
Having multiple masts allows you to harness the power of the wind better and can increase your speed and directional capabilities.
There are many great choices when it comes to boats with two masts, but newer models are starting to steer away from double mast designs. This does not mean that you cannot get a good boat with two masts.
Used boats can be great choices when it comes to purchasing a boat. This is even more true with large, yacht boats such as the ones listed above.
Just make sure when you buy a used sailboat you check that everything is intact and in good working order and if it is not, you have allotted space in the budget to fix what is needed.
Your new double-masted sailboat should provide you with plenty of long-lasting memories and adventures out on the water while you connect with the wind and the sea.
Click to share...

What’s a Boat with Two Masts Called: Two masted sailing boat types
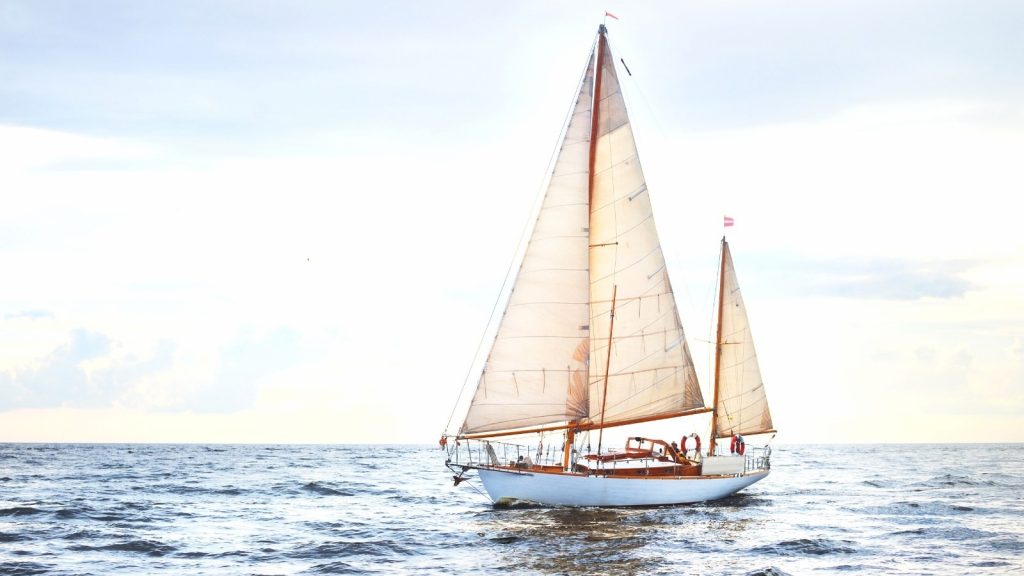

Two-masted sailing boats will always have a special place in the hearts of many sailors. Many sailors consider two-masted sailing boats to be the most attractive and graceful of all sailing vessels. They have an obvious elegance, but what do you know about these two masted sailboats? Let’s find out!
Among the most important aspects are the fact that two-masted sailing boats offer greater sail balance, engineless sailing and more heavy weather options.
Even if the two masted sailboats are not so common, the sailing world has a few of them and what is more, they represent a proof of the evolution and improvement of sailing boats over time. There are an almost endless number of ways sailors have arranged their sails on boats over the years.
Two-masted sailing boats are classified according to the size and position of their masts.
There are different two-masted sailing boat types and two of the most popular are schooners and yawls.
The origins of schooner-rigged vessels are unknown, however there is evidence of them in paintings by Dutch maritime painters dating back to the early 17th century.
Schooners were developed by Northern European countries, while yawls are believed to be descended from the fishing boats of England.
Sailboats with two masts include yawls, ketches, schooners and brigs (known as brigantines). Yawls and ketches are both types of sloops, which means they have one mast, but the difference between them is that the yawl has a second mast stepped at the bow.
Ketches and Yawls have a lower mast, unlike schooners that have a taller aft mast, which is also known as mizzen. Ketch sailing boats have something specific: the aft mast is located in front of the rudder post.
The yawl’s mizzenmast serves as a counterbalance for the jib sails, so that it doesn’t have to be hung from the forestay (the rope running from the top of the mast down to the deck). They’re usually smaller than ketches and have less rigging because they don’t carry as many sails as a sloop with two masts.
Yawls are faster sailboats than schooners because they’re lighter, more balanced and easier to sail upwind. They can also go faster because their shorter sails catch more wind. But schooners have larger payloads, which means more people or cargo — an important consideration for long trips without resupply.
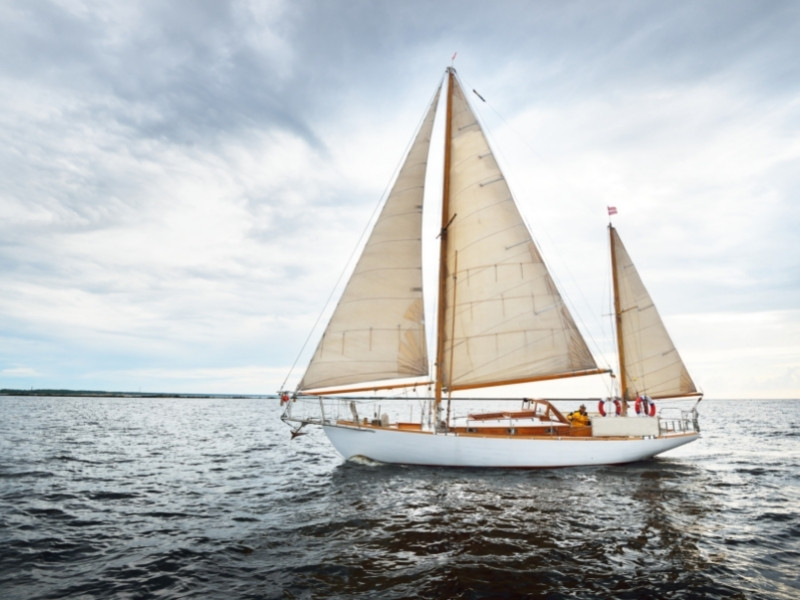

Schooners are two-masted sailing boats, but instead of having a jib sail like yawls, ketches and most sloops, schooners have a fore-and-aft spanker sail like a gaff sailboat. These two-masted sailboats have at least two masts, the foremast being slightly shorter than the main mast.
Schooners are larger than yawls, ketches and other sloops and weren’t used very much in modern times because they were more difficult to handle. They’re still used in racing competitions today.
Schooners have a longer bow portion than yawls. The mainsail is aft of the mast, and either one or two foresails are in front of it. In a schooner, these are triangular sails; in a yawl, they’re trapezoidal. Yawls have bowsprits — poles that extend beyond the bow for the jib and stay sail to be attached. Schooners have small bowsprits that can support jibs but not large sails.

The term ketch derives from the word catch, which hints to how it got its name in the 17th century. Ketches were initially intended to meet the specific requirements of offshore net fishing.
Ketch is a type of sailboat that features two masts and two sails, commonly used as a racing and cruising boat. The mainmast of this two-masted sailboat is typically taller than the mizzen mast (aft-mast). Its name derives from catch.
Taller masts allow you to use larger sails, so ketch boats are able to achieve better speeds than similar boats with only one mast. Some ketch designs feature a gaff rig, which is similar to a yawl, while others feature a yawl rig, which looks like a traditional sloop.
Ketch boats may look easy to sail but the slightest mistake can lead to disaster. You must be careful when operating this type of boat because it does not have as much stability as other boats, especially when you’re manoeuvring in tight quarters or windy conditions.
A ketch may also be a small recreational boat with only one head-sail in use. Many modern designs have moved away from sail altogether and are powered by engine, while others use both sails as well as engines depending on circumstance.

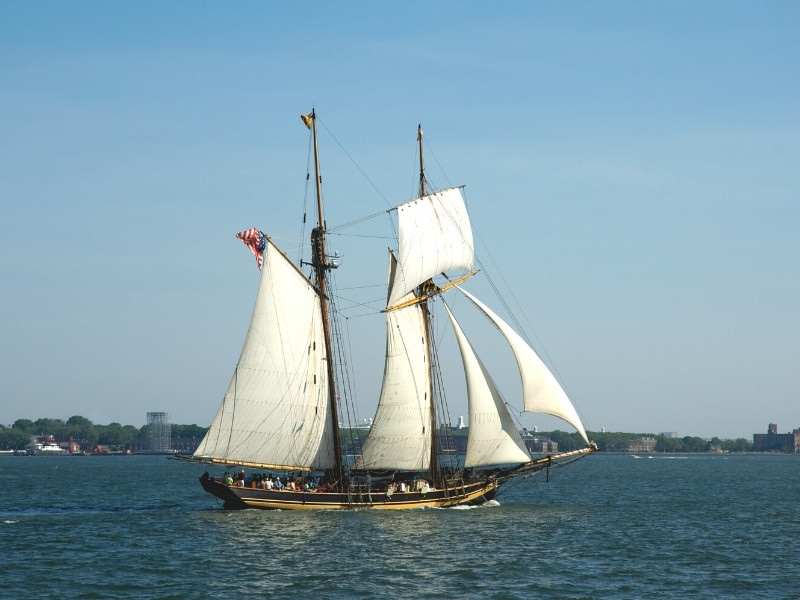
The brigantine was once a tiny ship that carried both oars and sails. It was a favorite of Mediterranean pirates.
A brigantine is a square-rigged sailing boat with two masts, with a fully square-rigged foremast and two sails on the mainmast.
The mainmast is stepped forward of the deck, making it possible to sail into the wind using a triangular headsail known as a jib. The brig’s foremast is shorter than the mainmast.
The name of this type of boat with 2 masts is derived from the Italian word “brigantino”, which means brigand.
Also, this two-masted sailing boat type was most commonly used for coastal trade and pirate hunting. The brigantine had an advantage over other ships of the time because it could sail against the wind using both sails, making it easier to travel against strong winds.
Faster and easier to manoeuvre than a sloop or schooner, it was used for piracy and espionage.

FAQ: Two-Masted Sailboats
What do you call a two-masted sailboat.
Two-masted sailboats are of several types: yawls, schooners, ketches or brigantines.
Why do some sailboats have two masts?
The vast majority of sailboats feature a mainsail and a jib. These two-masted sailboats provide several advantages in terms of speed and maneuverability. These two masts may be configured in a variety of ways.
The foresail directs air beyond the back of the mainsail, generating greater power from the wind. In order to help menouvering, the foresail can be backed. So, adding sails makes things simpler for bigger boats, making them easier to handle in heavy winds.
What is the difference between a ketch and a yawl sailboat?
Because they are lighter, more balanced, and easier to sail upwind, yawls are faster sailboats than schooners. They can also go at a faster speed since their shorter sails collect more wind. Schooners, on the other hand, have higher cargoes, which means more people or freight – a crucial consideration for extended journeys without replenishing.
What is a one masted sailboat?
It's a sailing boat having a single mast roughly one-third the length's aft of the bow. A sailboat with a single mast usually has one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail behind the mast.
What is a two-masted square rigger?
It's a brig with two square-rigged masts. A gaff-rigged fore-and-aft sail also called a "mizzen" is used in addition to jibs and staysails (stays'ls) before the foremast and staysails between the masts.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- The Enchanting World of Two-Masted Sailing Ships: A Comprehensive Guide
Two-masted sailboats, with their elegant profiles slicing through the waves, serve as a bridge between the past and present, combining traditional sailing heritage with contemporary performance. These vessels, marked by their dual masts—the foremast and the mainmast—embody a blend of artistry and engineering, appealing to a wide array of sailing enthusiasts.
History and Evolution: From Ancient Origins to Technological Advancements
The lineage of two-masted sailboats stretches back to ancient maritime civilizations, where the imperative of ocean exploration spurred the development of advanced sailing technologies. These early innovations laid the groundwork for the evolution of sailboats, which adapted over the centuries to meet the changing demands of navigation, trade, and warfare. The design and functionality of two-masted sailboats have been refined through technological advancements, making them as much a symbol of historical progress as they are of nautical tradition.
Design and Features: Anatomy and Types of Two-Masted Sailboats
Understanding the design of a two-masted sailboat is key to appreciating its capabilities. The complex arrangement of hull, masts, sails, rigging, and keel is essential for the boat's performance at sea. These components work in harmony to harness the power of the wind, enabling the vessel to navigate with precision and grace. The variety within this category, including schooners, ketches, yawls, and brigs, highlights the adaptability of two-masted sailboats to different sailing needs, from leisurely coastal cruising to high-stakes ocean racing.
Read our top notch articles on topics such as sailing, sailing tips and destinations in our Magazine .
Check out our latest sailing content:
Two-masted sailboats in use today: recreational and competitive sailing.
Today, two-masted sailboats flourish in both recreational and competitive arenas. For leisure sailors, these vessels offer a unique combination of challenge and tranquility, allowing for intimate experiences with the sea. The versatility of two-masted sailboats makes them ideal for a range of activities, from day sailing to extended voyages. In the competitive realm, these sailboats demonstrate their enduring relevance and performance, participating in regattas and races that test the skill and strategy of their crews.
Maintenance and Upkeep: Ensuring Longevity and Performance
The beauty and functionality of two-masted sailboats are preserved through meticulous maintenance and thoughtful care. Routine inspections and maintenance tasks are crucial for keeping these vessels seaworthy, highlighting the importance of attention to detail in preserving their condition. Beyond the immediate upkeep, long-term care strategies are essential for ensuring that these iconic vessels continue to grace the world's waterways, serving as living links to the rich maritime heritage they embody.
Famous Two-Masted Ships: Icons of the Seas
Throughout history, several two-masted ships have etched their names into the annals of nautical lore, becoming icons of exploration, power, and adventure. Ships like the HMS Beagle, renowned for carrying Charles Darwin on his epic voyage that contributed to the development of evolutionary theory, and the schooner Bluenose, a racing legend and fishing vessel that symbolized Canadian grit and maritime prowess, are prime examples. These famous ships not only highlight the critical role of two-masted vessels in exploration and competition but also celebrate their timeless beauty and enduring spirit.
In essence, two-masted sailboats encapsulate the spirit of sailing, merging the allure of history with the thrill of modern-day navigation. They stand as a testament to human creativity and the ceaseless quest for harmony with the elements, inviting each new generation of sailors to partake in a journey that transcends time and tides.
So what are you waiting for? Take a look at our range of charter boats and head to some of our favourite sailing destinations.
Interested in exploring the world of two-masted sailing ships? Contact me to book your yacht experience today!

Denisa Kliner Nguyenová

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge
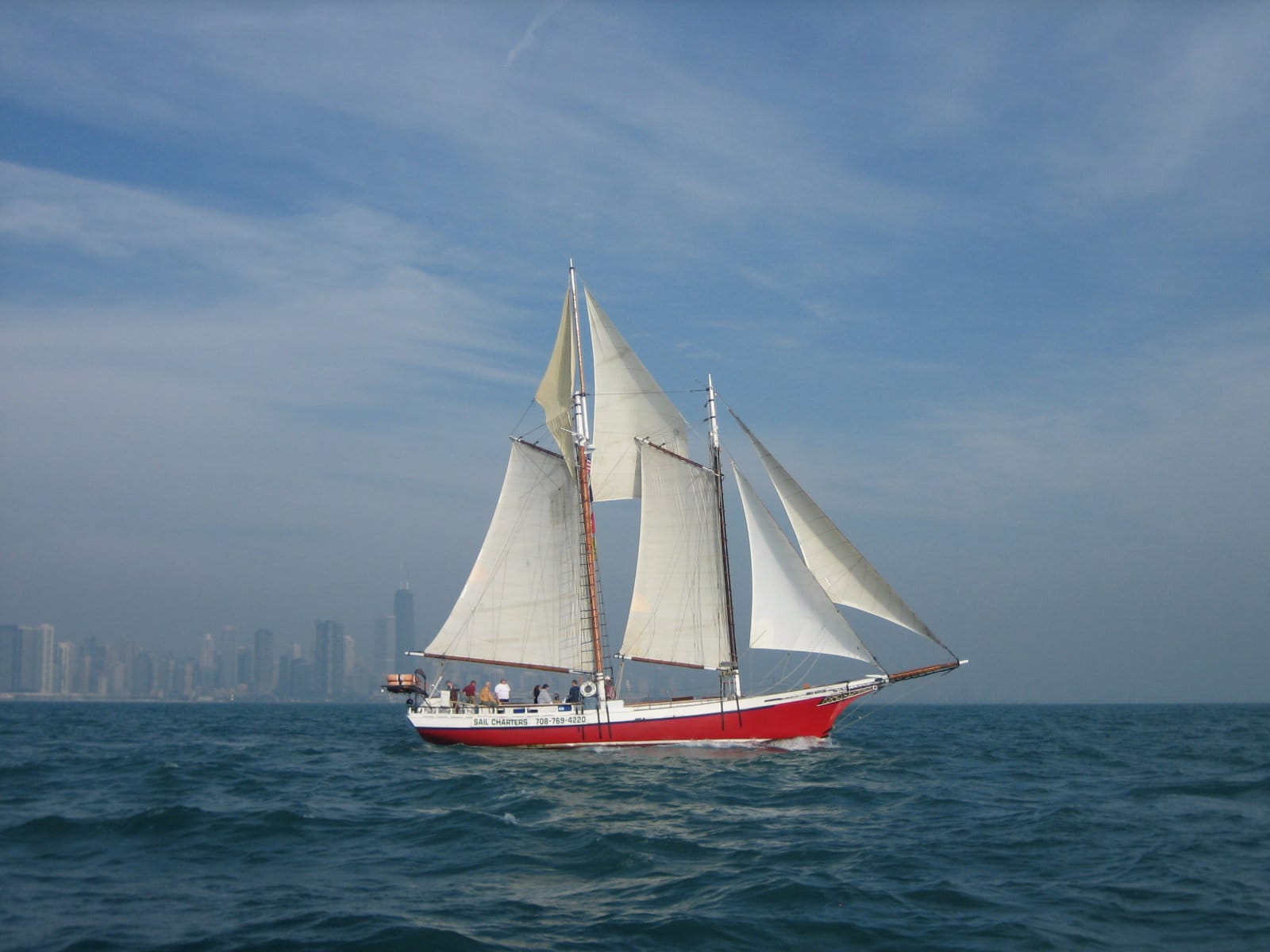

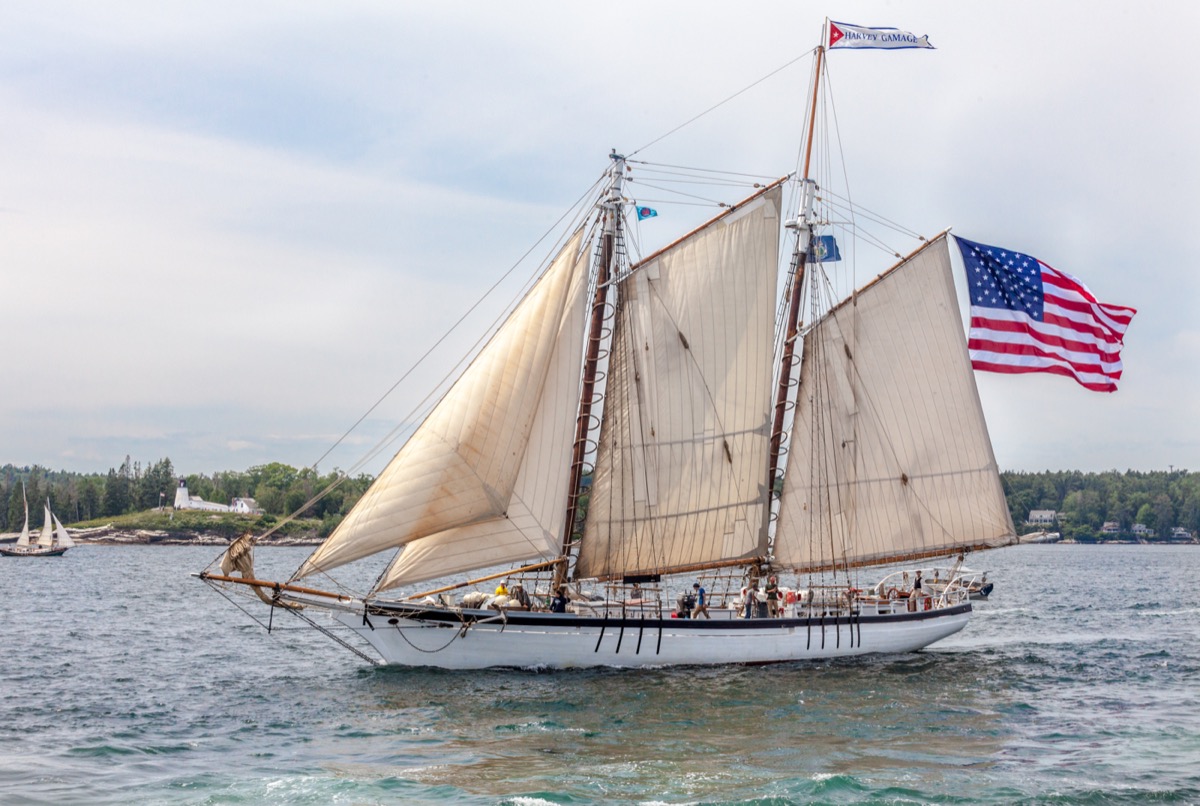
What’s in a Rig – The Schooner
By: Pat Reynolds Sailboat Rigs , Sailboats
What’s in a Rig # 7– The Schooner
The schooner is another split rig plan, like the ketch and yawl, but really fell out of favor after having a very dominant place in sailing history for quite a long time. Early in the 18 th century on into the 19 th they became widely popular for their speed, versatility, and upwind prowess, which by today’s standards is not good, but at the time was surely better than the larger unwieldy ships of the day.
By definition, a schooner is a sailboat with at least two masts, with the forward mast (foremast) being a bit shorter than the main mast. Although a schooner can have more than two masts, most were just two. During the time of their popularity this smaller and better upwind set up allowed for a more efficient and manageable sailboat. It was the preferred choice of pirates, privateers, slaveship captains and others.
Although schooners filled a need at the time, they were eventually all but replaced with sloops and yawls that were even better upwind and easier to manage. The schooner’s two large sails weren’t all that efficient and there was a lot of sail to deal with. Perhaps yawls and ketches are still around mainly for that reason – the second sail is pretty manageable – a schooner, on the other hand, was (is) a lot of work and a lot to maintain.
In the other What’s in a Rig articles we made a case (or a partial case) for the practicalities of each particular rig, but the schooner doesn’t have any shining advantages over what came after it. Perhaps their contribution to modern sailing is to illustrate how it was once done. They are an extremely important element in the evolution of sailing and,for that matter, world history.
From the times of swarthy pirates to the racing legend America that ushered in a modern age, schooners ruled the oceans, so give them their just due. Maybe next time you see one, give a nod and say, “ thanks schooner, if not for you I probably wouldn’t be sailing this bitching J-boat right now. ”
What's in a Rig Series:

Related Posts:

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login
Understanding the Two-Masted Sailboat
By Matt Claiborne
Two-Masted Boats with Fore-and-Aft Rigged Sails
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat. The rear mast, called the mizzen mast, is shorter than the forward main mast. The mizzen mast is mounted forward of the rudder post.
A yawl is similar to a ketch, but the rear mizzen mast is moved farther aft, behind the rudder post. This makes the mizzen on a yawl seem like an afterthought, almost like it’s attached to the railing.
If a two mast boat has masts of equal height or the forward mast is the shorter of the two, it is a schooner. They can have as many masts as the design called for.
Benefits of Two Masted Sailboats
Easy to balance steering forces
More sail plan options for heavy winds
Lower sheet loads mean smaller and less expensive
Lighter loads on smaller sails for easier handling
Shorter overall mast height for bridge clearance
Mizzen can be used as a riding sail at anchor
2 Masted Ship Examples with Square Rigged Sails
A brig is a double mast sailboat with both masts square rigged. In addition, it has fore-and-aft staysails and jibs and a mizzen sail on the aft mast–which is usually gaff-rigged.
A brigantine is a ship with two masts, with the foremast square-rigged and the aft mainmast fore-and-aft rigged.
The Two-Masted Sailboat
Boat maintenance.
What Is A Boat With 2 Masts Called?
Sailboats have held and air of mystique and romance ever since the early explores sailed the globe.
However, the early trade ships were somewhat restricted in their ability to sail into, or against, the wind. As a result, the ships that discovered the new world were slaves to the directions the trade winds were blowing.
Today, thanks to advances in hull design, sail orientation and mast placement, there are numerous sailboat designs that use multiple sail configurations that can travel around the world in any direction at any time of year.
Over the years the types of sailboats have been reduced to a few well-performing designs. These designs are divided into the two main classifications of one-masted boats and those with two or more masts with each mast being capable of supporting one or more sails.

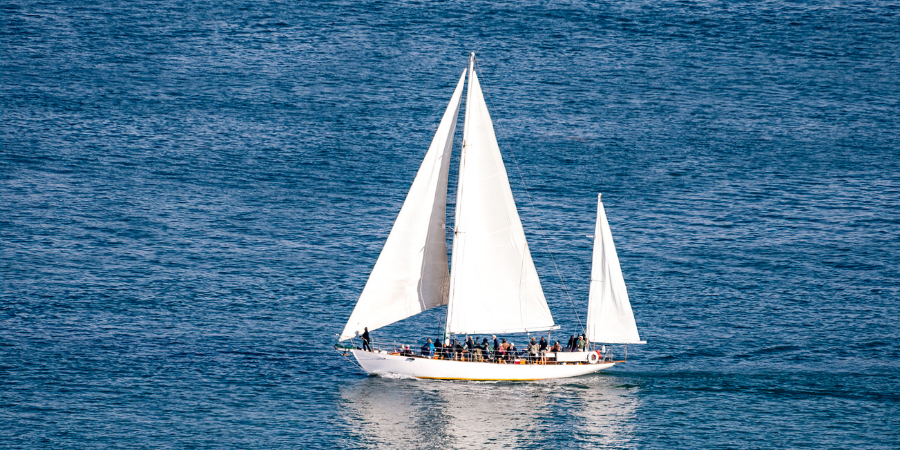
The sloop is the most common type of sailboat and has just one mast, placed roughly at midship, with up to three headsails attached to the mast by guy lines. Boats with 2 masts or more are the ketch, yawl, brigantine, brig and the schooner , with the schooners having two, three, or in rare cases, four masts.
Many sailors like the ketch-rigged design for its off-shore performance, comfort and overall balance. This design has a main and mizzen sail, with the mainsail set in approximately the same position as on a sloop, The mizzen is a smaller mast sail set towards the rear of the boat.
The concept behind the two-sail setup on the ketch-rigged sailboat is that it provides two smaller sails that provide more overall sail area than the single sail design.

In theory the smaller sails are easier to work with in heavy off-shore winds, making the boat much easier to sail in storms. Because of the smaller and easier-to-handle sails, the design is a good choice for long distance short-handed sailing.
The mizzen sail also acts as sort of a “rudder” in helping to keep the boat sailing in the proper direction because of the downward force the mizzen applies to the rear of the boat.
Comfort is another strong selling point of this design. Whereas most sailboats are designed with the cockpit at the stern of the boat, this sailboat has a center cockpit design to allow for the placement of the mizzen sail aft.
Having the cockpit in the middle of the boat allows for more headroom below deck at the rear of the boat and a larger aft cabin. Additionally, unlike an aft cockpit that usually has the rear open to the ocean, a center cockpit is fully enclosed. This offers protection from the elements while at sea and makes for a much nicer sitting area.
The ketch-rigged sailboat is a time-proven rig that has made untold circumnavigations of the globe. For sailors who like the two-mast design, this sailboat is a hard choice to beat.
The yawl is also equipped with a main and a mizzen mast. However, a yawl typically has a smaller mizzen with the mast set aft of the rudder post.
There are as many arguments about whether the yawl is a practical off-shore design as there are species of fish in the ocean. While there are some that site the sail plan of the yawl as more aesthetic than functional, there are many long-time professional sailors who swear by the yawl design.

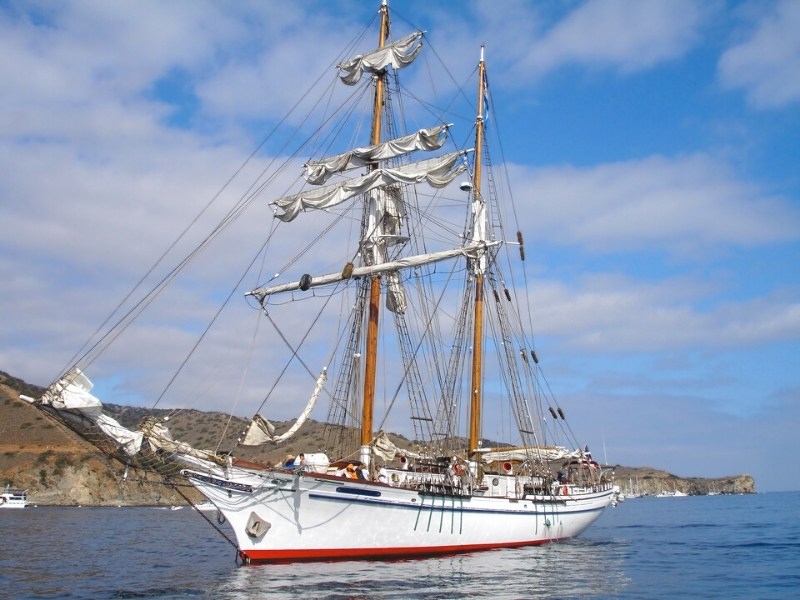
In theory, at least, the rear mast works as a rudder similarly to the ketch-rigged sailboat. The arguments typically start over the size and placement of the mizzen mast.
Some claim that placing the mizzen further back aids in helping to steer the boat. The other side of the argument is the reduced sail size makes it less efficient.
There is also the point that some sailors feel the mizzen being placed further back aids in heaving, or changing direction, and helps with steadying the boat at anchor.
Still, most sailors familiar with both the ketch and yawl say that the mizzen on the yawl is not a match for that of the ketch-rigged sailboat.
Brigantine and the Brig
Of similar, but not identical design, the brigantine and brig fall into the category of “clipper” or merchant ships.

Both are two-masted boats with the brigantine having square sails on the foremost mast and gaff sails on the mainmast. Here note that the smaller foremast is set forward of mast for the main sail.
Gaff sails are a four-cornered sail design attached to horizontal pole that hangs from the mast. Because of the smaller design, gaffs sails are more easily handled. In contrast, the brig uses square sails on both masts.
Both ships handle both coastal waters and ocean crossings as the square sails are well suited for sailing the trade wind routes.
A schooner is another boat with 2 masts, but can also have more. Like the brig and brigantine, a two-masted schooner has a foremast and an aft mast, the latter essentially being the mainmast.
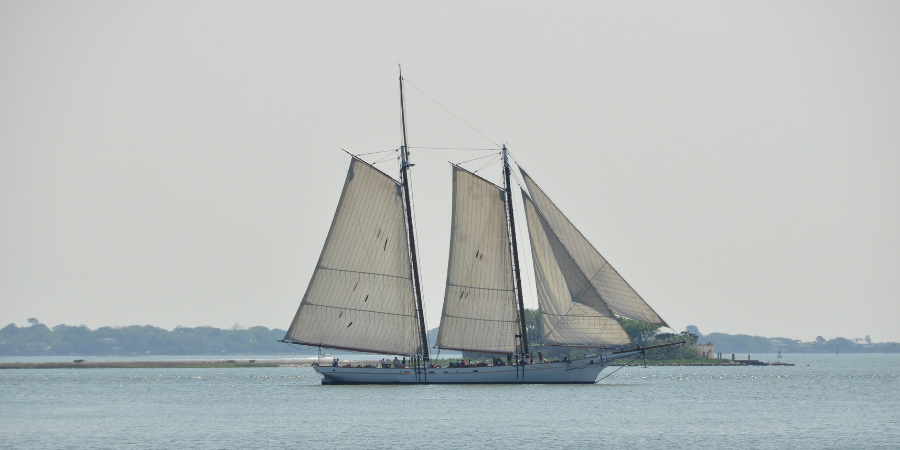

The main characteristic of the schooner is the masts are almost the same size, with the foremost mast sometimes being slightly shorter. The schooner is equipped with gaff sails on all masts, making it better equipped to handle strong seas.
This makes the schooner very versatile and well suited to crossing the ocean on the trade-wind routes as well as sailing coastal waters with varying wind directions.
Closing Thoughts
Because of the versatile design, many pleasure sailboats during the 19th century were schooner-rigged.
While a square topsail is the most common schooner sail plan, some have sprit rigged topsails that run diagonally across the mast. However, sprit rigging is inefficient in adverse weather as the sails are not easily lowered.
Conversely, sprit rigging excels in coastal waters where the sails can more readily catch the light winds that tend to blow higher up.
While a schooner is easy to sail, can handle various wind and water conditions and is probably the most magnificent sight on the sea under full sail, the draw back of the schooner is it is definitely not the fastest sailboat design.

Two-Mast Sailboat Types
Numerous sailors have a soft spot for two-mast sailboats, and there really is something unique in two-mast sails, irrespective of whether you are a sailboat enthusiast or just an intrigued passerby.
The two masts are typically the first feature you observe on such a sailboat. The mainmast, or foremast will usually be larger than the rear mast, also known as the mizzenmast.
But aside from being elegant and impressive, a two-mast sailboat provides perfect balance, which can be best obtained by making adjustments to the masts in a variety of ways.
The mizzenmast acts as that shoulder you can rely on as it assists with the sailboat’s stability while it is moving, and it can also function as a propulsion system in certain situations.
So, let’s take a look below at various kinds of two-mast sailboats and their advantages!
What Do You Call A Sailboat With Two Masts?
Several sailboats have two masts (see also ‘ Sailboat Mast: Everything You Need To Know ‘), the four most popular of which we will explore in a bit. In these sailboats, the styles of their masts differ in most instances, but the basic concept stays the same.
All these sailboats come with an extra mast at the rear or the front of the foremast. If that supplemental mast is in front of the foremast, it is called a foremast; if it is behind it, it is called a mizzenmast.
Among the most popular two-mast sailing vessels is the yawl. It is equipped with a mizzenmast and a foremast. Typically, the mizzenmast will be relatively short, particularly when compared to the foremast.
This renders it an angled sailboat, seeing that the foremast is situated at the front of the boat and the mizzenmast is situated at the back. A yawl’s mizzenmast is situated toward the back of the boat steering mechanism and is primarily used to boost helm stability.
It’s very easy to mix up a yawl and a ketch, so it’s best to clear that up before proceeding. They both are two-mast sailboats, with the foremast at the front and the mizzenmast behind it.
The spot of the mast is what distinguishes a ketch from a yawl. The mizzenmast is placed behind the boat steering mechanism post in a yawl and in front of it in a ketch.
A ketch’s mizzenmast is approximately the same height as the foremast, and it is employed to hold the mainsail. Its primary purpose, though, is to propel the boat as well as sail it adequately, especially in stronger wind.
That very function contrasts with a yawl’s mizzenmast, which is only utilized to help with balancing the steering wheel and cannot propel the boat forward.
This indicates that a ketch’s mizzenmast is larger than a yawl’s mizzenmast. In summary, a ketch’s mizzenmast is a moving sail, whereas a yawl’s mizzenmast serves as a balancing one.
In downwind or wind gusts, a ketch is at a favorable position when compared to a sloop. This is due to the fact that it has more setup options than a standard sloop.
The rear mast allows the sailor to adjust in strong winds and choose the most appropriate percentage of canvas to move with.
Provided that the mizzenmast is typically in an ideal position, it may also aid in the stabilization of the sailboat under force.
Essentially, a ketch comes with numerous practical advantages that make it ideal for most scenarios on the water.
A ketch, other than cruising serenely on a beam reach, is completely controllable and can provide a wide range of possibilities in a variety of weather circumstances and situations.
A schooner can even have three masts, but the one with two typically has a fairly small mainmast and a bigger mizzenmast, which in essence becomes the mainmast.
As a result, the main feature of a schooner is that its masts are both tall and with little to no difference, with the rear mast, in some cases, being a bit taller.
A schooner is slower than a sloop, despite being simpler to navigate. That is why so many seafarers choose to sail with a sloop than with a schooner, although it’s still an impressive sight, and even more so when fully sailing.
Even though schooners with square-shaped sail is what most people often get, several other schooners available are equipped with diagonal sprit rigs.
Schooners that have spritsails are unsuitable for large sea routes as, when the sprit rig gets lowered, it becomes impossible to manage. The sprit rig, on the contrary, is perfect in coastal areas because the topsail can hold a high gust of wind.
The brig, same as all the previously mentioned sailing ships, is a two-mast sailboat, with the foremast being of a square shape.
The foremast may come in the shape of a square, part square, or triangle in design. The foremast of certain brigs has a lateen mainsail (see also ‘ The Definition And History Of The Lateen (Triangular) Sail ‘).
These sailboats have been heretofore employed by pirates and launched by oars. Its name originates from the Italian term “brigantine,” which roughly translates to “pirate.” Before becoming sailboats, such kinds of sailboats were employed by pirates in the 1500s.
The two most prevalent brig varieties are:
- Brigantine – The main mast is triangular, while the front mast is partly squared.
- Hermaphrodite brig – This brig is equipped with two slightly squared masts, with the mainmast being gaff-rigged and topsail, something that makes it a half schooner. That is why it is also referred to as the schooner brig or the half brig.
Brigs are simple to operate and navigate in terms of speed and drivability, which may be why pirates favored them, and they are usually bigger than the rest of the two-mast or single-mast sailboats.
The Benefits Of A Two-Masted Sailboat
But why might someone prefer a two-masted sailboat more than a single-masted one?
At first glance, perhaps it will look like a one-masted sloop is easier to control. However, having more masts and a wider range of sails to pick from has its benefits.

A Two-Masted Sailboat Has Greater Sail Area Division
When a sail area is split over a larger number of sails, the area for every sail becomes smaller and easier to navigate.
This is especially useful when moving with fewer passengers on board and in strong weather conditions.
A Two-Masted Sailboat Provides More Rough Weather Choices
If a cruiser encounters higher-than-expected winds, having more sails, and thus more alternatives, can be extremely beneficial.
Most ketch-rigged boats, for instance, can rest nicely in rising winds and waves with only the mizzen being used to hold the boat’s bow facing up into the wind, a practice called “heaving to.”
This tends to mean that the staff does not have to be on deck and can remain safely hidden below since the sail works on its own.
A Two-Masted Sailboat Provides More Sail Balance
Seafarers must be knowledgeable of sail balance if they want to maneuver a boat proficiently.
This entails ensuring that the sails are drawn in such a way that the sailboat can float in a horizontal line without having to utilize the rudder excessively in order to right the route.
A Two-Masted Sailboat Allows For Engine-Free Sailing
If you want the enjoyment of cruising without relying on an engine, or if your engine won’t work, knowing that you have a mizzen sail could be extremely advantageous.
The mizzen can be employed to float smoothly and in perfect control when trying to catch or deciding to leave a mooring ball.
The same is true for anchoring while sailing. This is definitely not an uncommon case scenario; we have all had to do something similar at least once in our lives.
A Two-Masted Sailboat Provides An Anchor Riding Sail
Even as you are sailing across the globe, you will inevitably come across an anchorage that is just not perfectly easy and serene.
The smallest wave that can create some kind of shuddering can make people onboard feel nervous and become dissatisfied with their sailing experience.
A two-mast sailboat will be in an advantageous position in this situation as the mizzen can be lifted and fastened in firmly to counteract the boat’s side-to-side moving.
It may also be counterbalanced by attempting to make use of the wind to direct the boat’s bow into the waves, resulting in a way steadier sailboat and a satisfied crew.
A Two-Masted Sailboat Is Nearly Impossible To Be Completely Dismasted
A two-masted sailboat has an extra benefit: the mizzen, while too small to push the sailboat at high speeds, can most likely get you back safe in case the mainmast breaks or is torn apart in extreme situations.
The Bottom Line
There are dozens of reasons why seafarers chant paeans to these sailboats. Even in windy conditions, you can break down the mainmast and employ the mizzen mast to provide a more aligned and pleasant voyage.
There are different kinds of two-mast sailboats, thus there is no single term that can fit them all.
The only thing that can group them is their two-mast feature, so if you decide to sail in one of them, it is up to your preference to choose which one will take you on your next adventure!
Related Posts:

- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
The Different Types of Sailboats
If you’re a sailboat fanatic like me, all types of sailboats will attract your attention. Some more so than others admittedly, but all will have something about them that catches your eye.
If you’re not a fanatic (not yet, that is) but just an interested observer, then the first thing you’ll notice about a sailboat will be how many masts it has and the configuration of its sails - in other words, its 'rig'.
This observation alone will enable you to identify the five main types of sailboats — sloops, cutters, ketches, yawls and schooners - all of which are described here.
But apart from the various rig types, you can describe types of sailboats from a different viewpoint - sailing dinghies, dayboats, motorsailors, monohulls, catamarans and trimarans.
Let's make a start with the various rig types...
A single-masted sailboat with just two sails — a foresail (aka headsail or jib) and a mainsail — is a sloop, the purest type of sailboat.
The sloop rig can also be described as a Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig or Marconi rig.
Read more about sloops...

Examples of Sloops

If a sloop has an additional sail between the headsail and the mainsail, then it's no longer a sloop - it's a cutter.
Some cutters - like the one shown here - have the foresail set forward on a bowsprit, with the inner forestay permanently rigged to the stemhead where the foresail otherwise would be, or to a central chainplate further aft on the foredeck.
Read more about cutters...
Examples of Cutters

The following boats may look like cutters with their double headsails, but they're not cutters at all...

To find out why, click here...
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat, a main mast forward and a shorter mizzen mast aft.
But not all two-masted sailboats are ketches — they might be yawls (see below).
A ketch may also sport a staysail, with or without a bowsprit, in which case it would be known as a cutter-rigged or staysail ketch.
Read more about ketches...
Examples of Ketches

Note that the Ocean 71 and the Irwin 52 are cutter-rigged, and are traditionally referred to as Staysail Ketches .
Cat Ketches
Cat-ketches are recognised by the lack of any standing rigging to support their pair of unstayed masts.
And yes, if the after mast is taller than the foremast then it's called a cat- schooner sailboat.
Read more about cat-ketches...

Yawls have their origins as old-time sail fishing boats, where the small mizzen sail was trimmed to keep the vessel steady when hauling the nets.
Much like a ketch, the difference being that the yawl has the mizzen mast positioned aft of the rudder post whereas the ketch has its mizzen mast ahead of the rudder post.
You’ll not be surprised to learn that a yawl with a staysail is known as cutter-rigged yawl.

A schooner is a two-or-more masted sailboat, in which the aft-most mast - the mainmast - is the same height or taller than the foremast.
The one shown here is gaff cutter rigged, with a topsail set on the mainmast.
Many sailors agree that of all the different types of sailboats, a schooner under full sail is one of the most beautiful sights afloat.

Gaffed-rigged sailboats, or 'gaffers', have their mainsail supported by a spar - the 'gaff' - which is hauled up mast by a separate halyard.
Often these types of sailboats are rigged with a topsail, as shown here and in the gaff schooner above, which really adds some grunt in light airs.
All this comes at a price of course, both in terms of material cost and weight aloft, which is why very few modern yachts are fitted with gaff rigs these days.
All artwork on this page is by Andrew Simpson

Examples of the Various Types of Sailboats...

Other Types of Sailboats
The seven sailboat rig variations shown here are the most popular types of modern cruising boat rigs, but there are other rig versions which were once found on commercial, fishing, and naval sailing vessels.
They include:
- Full square-rigged sailing vessels
- Barkentines
- Brigantines
And you can see examples of them here ...
In this article I've said that ketches, yawls and schooners with two headsails can be called cutter rigged. This is a commonly used description but strictly speaking, there's only one rig that can accurately be called a cutter - and that's a single-masted sailboat with two headsails. My thanks to 'Old Salt' for drawing my attention to this!
Recent Articles
Amel Kirk 36 Sailboat Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Sep 07, 24 03:38 PM
Pearson 33 for sale
Sep 04, 24 03:29 PM
Apla 42 Sailboat Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Aug 30, 24 02:51 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com
17 Sailboat Types Explained: How To Recognize Them
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.
Every time I'm around a large number of sailboats, I look around in awe (especially with the bigger ones). I recognize some, but with most of them, I'll have to ask the owner. When they answer, I try to hide my ignorance. The words don't make any sense!
So here's a complete list with pictures of the most common sailboat types today. For each of them, I'll explain exactly where the name comes from, and how you can recognize it easily.

So here's my list of popular sailboat types, explained:
Bermuda sloop, sailing hydrofoil, dutch barge, chinese junk, square-rigged tall ship, in conclusion, how to recognize any sailboat.
Before we get started, I wanted to quickly explain what you should look for when you try to identify a sailboat.
The type of sailboat is always determined by one of these four things:
- The type of hull
- The type of keel
- The number of masts
- And the type of sails and rig
The hull is the boat's body. There are basically three hull types: monohull, catamaran, and trimaran. Simply said: do I see one hull, two hulls (catamaran) or three hulls (trimaran)? Most sailboats are monohulls.
Next, there is the keel type. The keel is the underwater part of the hull. Mostly, you won't be able to see that, because it's underwater. So we'll leave that for now.
The sail plan
The last factor is the number of masts and the sail plan. The sail plan, simply put, is the number of sails, the type of sails, and how the sails are mounted to the masts (also called rigging ).
Sailboat are mostly named after the sail plan, but occasionally, a sail type is thrown in there as well.
So now we know what to pay attention to, let's go and check out some sailboats!

Dinghies are the smallest and most simple sailboats around.
They are your typical training sailboats. Small boats with an open hull, with just one mast and one sail. Perfect for learning the ways of the wind.
On average, they are between 6 and 20 ft long. Mostly sailed single-handed (solo). There's no special rigging, just the mainsail. The mainsail is commonly a Bermuda (triangular) mainsail. Dinghies have a simple rudder stick and no special equipment or rigging.
Dinghies are great for learning how to sail. The smaller the boat, the better you feel the impact of your trim and actions.
How to recognize a sailing dinghy:
- short (8ft)
- one Bermuda sail
- open hull design
- rudder stick
Common places to spot them: lakes, near docks

If you'd ask a kid to draw a sailboat, she'll most probably draw this one. The Bermuda Sloop is the most popular and most common sailboat type today. You'll definitely recognize this one.
How to recognize a Bermuda Sloop:
- triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail)
- a foresail (also called the jib)
- fore-and-aft rigged
- medium-sized (12 - 50 ft)
Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind.
Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop. Even if the sails are another shape or rigged in another way. For example, here's a gaff-rigged sloop (more on the gaff rig later):

If you want to learn all about sail rigs, check out my full Guide to Understanding Sail Rig Types here. It has good infographics and explains it in more detail
The Bermuda sloop has a lot of advantages over other sailboat types (which is why it's so popular):
- the Bermuda rig is very maneuverable and pretty fast in almost all conditions
- it's really versatile
- you can sail it by yourself without any problems
- it's a simple setup
Common places to spot a sloop: everywhere. Smaller sloops are more common for inland waters, rivers, and lakes. Medium-sized and large sloops are very popular cruising boats.

Cutters have one mast but three or more sails. Most cutters are Bermuda rigged, which means they look a lot like sloops.
How to recognize a cutter:
- looks like a sloop
- two or more headsails instead of one
- commonly one mast
- sometimes an extra mast with mainsail
Cutters have more sail area, which makes them faster, but also harder to sail single-handed. There's also more strain on the mast and rigging.
Common places to spot a cutter: everywhere. Cutters are very popular for cruising.
They mostly have a Bermuda rig, which means triangular sails. But there are also gaff cutters and naval cutters, and some have two masts.
Here's an example of a two-masted naval cutter with an extra gaff mainsail and top gaff:

The Hydrofoil is a pretty new sailboat design. It's a racing sailboat with thin wing foils under the hull. These lift up the hull, out of the water, reducing the displacement to nearly zero. The foils create downforce and keep it from lifting off entirely.
This makes the hydrofoil extremely fast and also impressive.
The hydrofoil refers to the keel type. There are both monohull and multihull hydrofoils.
How to recognize a hydrofoil:
- it flies above the waterline and has small fins
Common places to spot a hydrofoil: at racing events

Famous catamaran: La Vagabonde from Sailing La Vagabonde
A catamaran is a type of cruising and racing multihull sailboat with two hulls. The hulls are always the same size.
Most catamarans have a standard Bermuda rig. The catamaran refers to the hull, so it can have any number of masts, sails, sail types and rig type.
How to recognize a catamaran:
- any boat with two hulls is called a catamaran
Common places to spot catamarans: coastal waters, The Caribbean, shallow reefs
The advantages of a catamaran: Catamarans heel less than monohulls and are more buoyant. Because of the double hull, they don't need as deep a keel to be stable. They have a smaller displacement, making them faster. They also have a very shallow draft. That's why catamarans are so popular in the Caribbean, where there's lots of shallow water.
Catamarans are nearly impossible to capsize:
"Compared with a monohull, a cruising catamaran sailboat has a high initial resistance to heeling and capsize—a fifty-footer requires four times the force to initiate a capsize than an equivalent monohull." Source: Wikipedia

How to recognize a trimaran:
- any boat with three hulls is called a trimaran
Trimarans have three hulls, so it's a multi-hull design. It's mostly a regular monohull with two smaller hulls or floaters on the sides. Some trimarans can be trailered by winching in the auxiliary hulls, like this:

This makes them very suitable for long-term cruising, but also for regular docking. This is great for crowded areas and small berths, like in the Mediterranean. It sure is more cost-effective than the catamaran (but you also don't have the extra storage and living space!).
Common places to spot Trimarans: mostly popular for long-term cruising, you'll find the trimaran in coastal areas.

Gaffer refers to gaff-rigged, which is the way the sails are rigged. A gaff rig is a rectangular sail with a top pole, or 'spar', which attaches it to the mast. This pole is called the 'gaff'. To hoist the mainsail, you hoist this top spar with a separate halyard. Most gaffers carry additional gaff topsails as well.
Gaff rigs are a bit less versatile than sloops. Because of the gaff, they can have a larger sail area. So they will perform better with downwind points of sail. Upwind, however, they handle less well.
How to recognize a gaffer:
- sail is rectangular
- mainsail has a top pole (or spar)
Since a gaffer refers to the rig type, and not the mast configuration or keel type, all sailboats with this kind of rigging can be called 'gaffers'.
Common places to spot a gaffer: Gaffers are popular inland sailboats. It's a more traditional rig, being used recreationally.
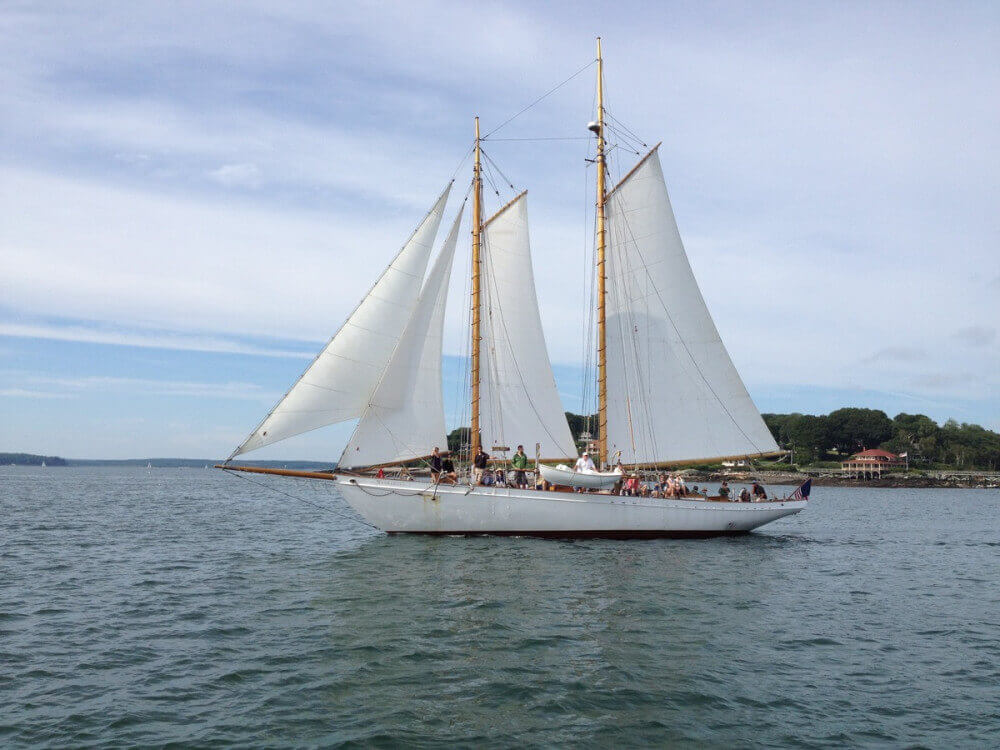

Schooners used to be extremely popular before sloops took over. Schooners are easy to sail but slower than sloops. They handle better than sloops in all comfortable (cruising) points of sail, except for upwind.
How to recognize a schooner:
- mostly two masts
- smaller mast in front
- taller mast in the back
- fore-and-aft rigged sails
- gaff-rigged mainsails (spar on top of the sail)
Common places to spot a schooner: coastal marinas, bays

How to recognize a ketch:
- medium-sized (30 ft and up)
- smaller mast in back
- taller mast in front
- both masts have a mainsail
The ketch refers to the sail plan (mast configuration and type of rig). Ketches actually handle really well. The back mast (mizzenmast) powers the hull, giving the skipper more control. Because of the extra mainsail, the ketch has shorter masts. This means less stress on masts and rigging, and less heel.
Common places to spot a ketch: larger marinas, coastal regions

How to recognize a yawl:
- main mast in front
- much smaller mast in the back
- back mast doesn't carry a mainsail
The aft mast is called a mizzenmast. Most ketches are gaff-rigged, so they have a spar at the top of the sail. They sometimes carry gaff topsails. They are harder to sail than sloops.
The yawl refers to the sail plan (mast configuration and type of rig).
Common places to spot a yawl: they are not as popular as sloops, and most yawls are vintage sailboat models. You'll find most being used as daysailers on lakes and in bays.

Dutch Barges are very traditional cargo ships for inland waters. My hometown is literally littered with a very well-known type of barge, the Skutsje. This is a Frisian design with leeboards.
Skutsjes don't have a keel but use leeboards for stability instead, which are the 'swords' or boards on the side of the hull.
How to recognize a Dutch Barge:
- most barges have one or two masts
- large, wooden masts
- leeboards (wooden wings on the side of the hull)
- mostly gaff-rigged sails (pole on top of the sail, attached to mast)
- a ducktail transom

The clipper is one of the latest sailboat designs before steam-powered vessels took over. The cutter has a large cargo area for transporting cargo. But they also needed to be fast to compete with steam vessels. It's a large, yet surprisingly fast sailboat model, and is known for its good handling.
This made them good for trade, especially transporting valuable goods like tea or spices.
How to recognize a Clipper:
- mostly three masts
- square-rigged sails
- narrow but long, steel hull
Common places to spot a clipper: inland waters, used as houseboats, but coastal waters as well. There are a lot of clippers on the Frisian Lakes and Waddenzee in The Netherlands (where I live).
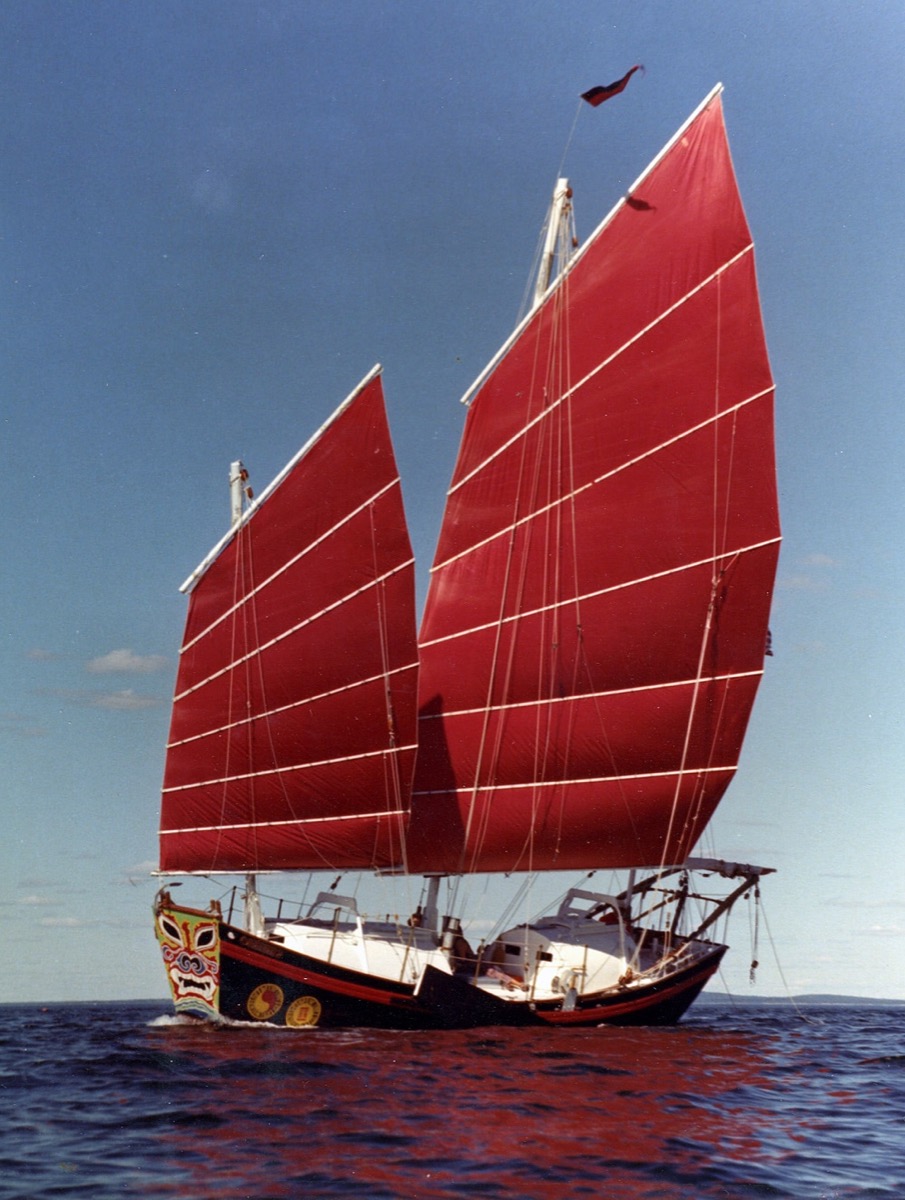

This particular junk is Satu, from the Chesapeake Bay Area.
The Chinese Junk is an ancient type of sailboat. Junks were used to sail to Indonesia and India from the start of the Middle Ages onward (500 AD). The word junk supposedly comes from the Chinese word 'jung', meaning 'floating house'.
How to recognize a Chinese junk:
- medium-sized (30 - 50 ft)
- large, flat sails with full-length battens
- stern (back of the hull) opens up in a high deck
- mostly two masts (sometimes one)
- with two mainsails, sails are traditionally maroon
- lug-rigged sails
The junk has a large sail area. The full-length battens make sure the sails stay flat. It's one of the flattest sails around, which makes it good for downwind courses. This also comes at a cost: the junk doesn't sail as well upwind.

The cat rig is a sail plan with most commonly just one mast and one sail, the mainsail.
Most sailing dinghies are cats, but there are also larger boats with this type of sail plan. The picture above is a great example.
How to recognize a cat rig:
- smaller boats
- mostly one mast
- one sail per mast
- no standing rigging
Cat-rigged refers to the rigging, not the mast configuration or sail type. So you can have cats with a Bermuda sail (called a Bermuda Cat) or gaff-rigged sail (called a Gaff Cat), and so on. There are also Cat Ketches and Cat Schooners, for example. These have two masts.
The important thing to know is: cats have one sail per mast and no standing rigging .
Most typical place to spot Cats: lakes and inland waters

Famous brig: HMS Beagle (Charles Darwin's ship)
A brig was a very popular type of small warship of the U.S. navy during the 19th century. They were used in the American Revolution and other wars with the United Kingdom. They carry 10-18 guns and are relatively fast and maneuverable. They required less crew than a square-rigged ship.
How to recognize a brig:
- square-rigged foremast
- mainmast square-rigged or square-rigged and gaff-rigged
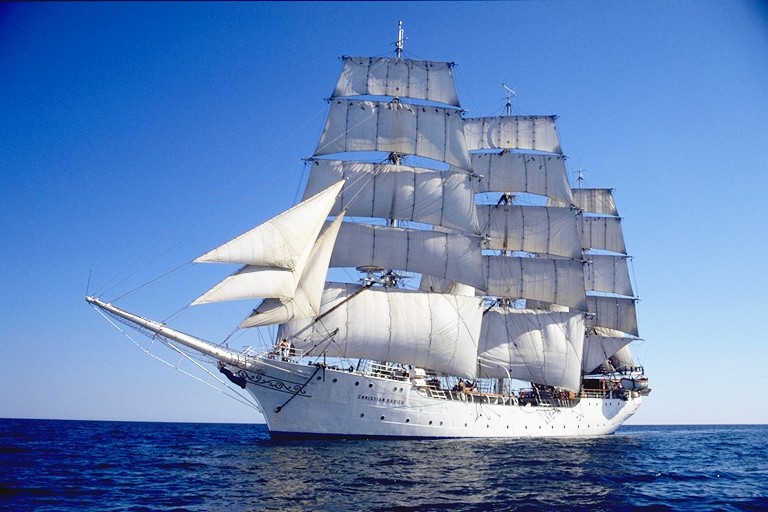

How to recognize a tall ship:
- three or four masts
- square sails with a pole across the top
- multiple square sails on each mast
- a lot of lines and rigging
Square-rigged ships, or tall ships, are what we think of when we think of pirate ships. Now, most pirate ships weren't actually tall ships, but they come from around the same period. They used to be built from wood, but more modern tall ships are nearly always steel.
Tall ships have three or four masts and square sails which are square-rigged. That means they are attached to the masts with yards.
We have the tall ship races every four years, where dozens of tall ships meet and race just offshore.
Most common place to spot Tall Ships: Museums, special events, open ocean
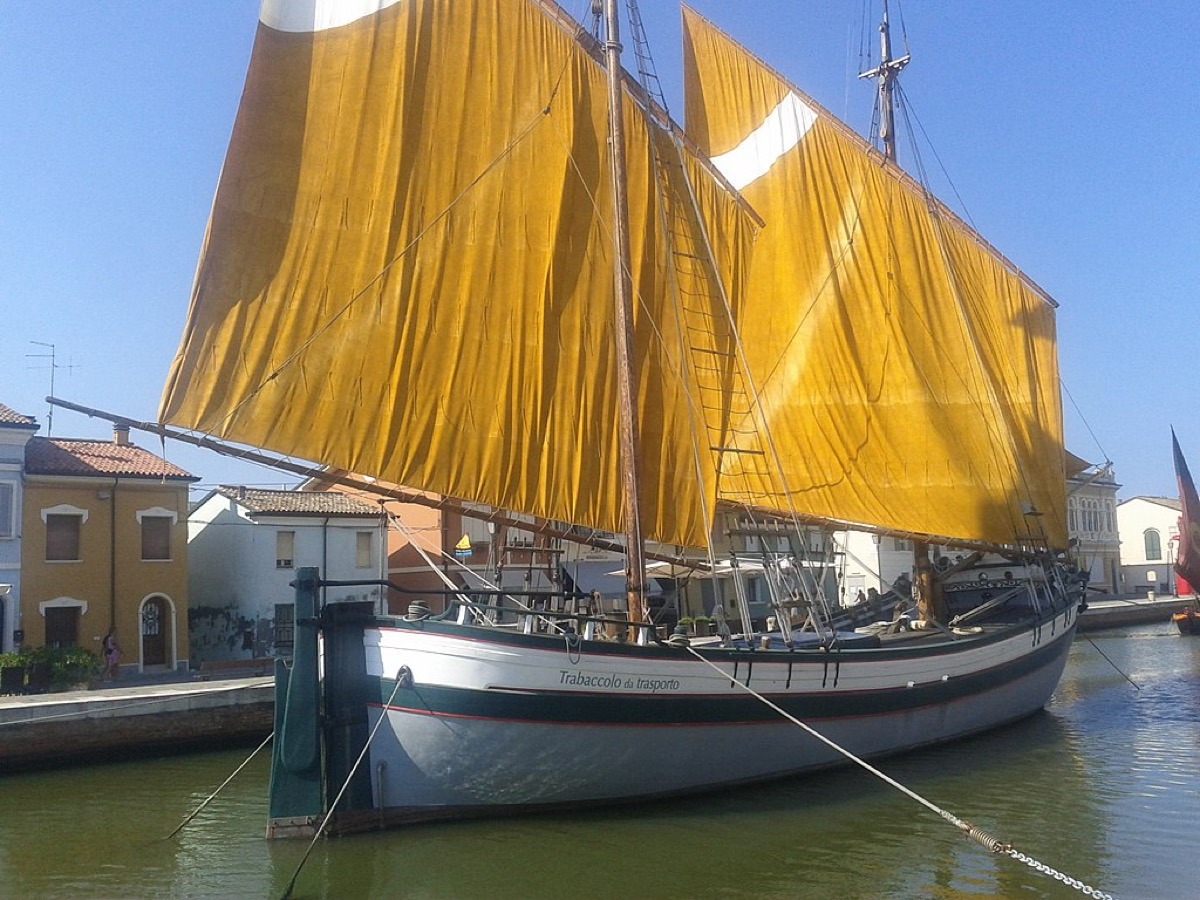

This is a bonus type since it is not very common anymore. As far as I know, there's only one left.
The Trabaccolo is a small cargo ship used in the Adriatic Sea. It has lug sails. A lug rig is a rectangular sail, but on a long pole or yard that runs fore-and-aft. It was a popular Venetian sailboat used for trade.
The name comes from the Italian word trabacca , which means tent, referring to the sails.
How to recognize a Trabaccolo:
- wide and short hull
- sails look like a tent
Most common place to spot Trabaccolo's: the Marine Museum of Cesenatico has a fully restored Trabaccolo.
So, there you have it. Now you know what to look for, and how to recognize the most common sailboat types easily. Next time you encounter a magnificent sailboat, you'll know what it's called - or where to find out quickly.

I loved this article. I had no idea there were so many kinds of sailboats.
i have a large sailing boat about 28ft. that im having a difficult time identifying. it was my fathers & unfortunately hes passed away now. any helpful information would be appreciated.
Jorge Eusali Castro Archbold
I find a saleboat boat but i can find the módem…os registré out off bru’x, and the saleboat name is TADCOZ, can you tell me who to go about this matter in getting info.thank con voz your time…
Leave a comment
You may also like, guide to understanding sail rig types (with pictures).
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)

What Is A Sailboat Mast?
A sailboat mast is one of the most defining features of a sailboat (along with the sails of course!) You can immediately tell that a boat is a sailing boat when you spot the tall mast sticking out of the hull.
But why do sailboats need a mast? Having lived on a sailboat for years now I’ve never really questioned the need for a mast. It’s such an integral part of the boat that I just sort of forget it’s there!
When our friends recently lost their mast due to a rigging failure it got me thinking – why do sailboats need a mast and what function (aside from holding up the sails) do they actually play. It turns out, quite a lot!
We’re going to dive into the fascinating world of sailboat masts, exploring different rigs, mast materials, and the different functions that masts play. It’s important stuff if you want to go sailing, and a lot of it I should have known sooner!

As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We also earn from other affiliate programs. This means we may receive a small commission on products purchased through our links at no extra cost to you.
Table of Contents
Why do sailboats need a mast, parts of the mast, what materials are masts made from, single mast rigs, sailboats with two masts, sailboats with three masts, how to look after your mast.

A sailboat mast is a vertical, upright structure that supports the sails of a sailboat. It is a crucial component of the boat’s rigging system and plays a key role in harnessing the power of the wind to propel the vessel. Typically located in the center of the boat, the mast extends upward from the deck or hull.
The height of the mast varies depending on the size and type of the sailboat, directly impacting the sail area and overall performance of the boat.
Together with the boom (a horizontal spar attached to the bottom of the mast), the mast allows sailors to control the shape and orientation of the sails, optimizing their efficiency in different wind conditions.
The design and configuration of the mast can vary depending on the type of sailboat, such as a sloop, cutter, ketch, or schooner.
Sailboats require a mast primarily to support the sails.
It holds the sails in an elevated position, allowing them to catch the wind effectively. Without a mast, the sails would lack the means to be raised and positioned to harness the power of the wind.
There are a few other important jobs that the mast plays:
Control and Manipulation of Sails: The mast, along with the boom (a horizontal spar attached to the mast’s lower end), enables sailors to control and manipulate the sails.
By adjusting the angle and tension of the sails through the mast, sailors can optimize their performance according to wind conditions and desired boat speed.
This control allows for maneuverability and efficient use of wind power.
Structural Integrity: The mast contributes to the overall structural integrity of the sailboat. It helps distribute the loads and forces exerted by the sails, rigging, and masthead components throughout the boat’s hull and keel.
The mast’s design and construction ensure stability and strength, allowing the boat to withstand the forces generated by the wind.
Attachment Points for Rigging: The mast provides attachment points for various rigging components, including halyards (lines used to raise and lower the sails), stays (wires or rods that support the mast in different directions), and shrouds (wires that provide lateral support to the mast).
These rigging elements are essential for properly tensioning the sails and maintaining the mast’s stability.
Height and Visibility: The mast’s height contributes to the sailboat’s visibility, allowing other vessels to spot it more easily, particularly when sailing in congested waters. The mast’s presence also serves as a visual reference for determining the boat’s position, orientation, and distance from potential hazards.
While the mast’s primary purpose is to support the sails and enable control over their position, it also plays a significant role in maintaining the structural integrity of the sailboat and enhancing its visibility on the water.
Basically, the mast is pretty darn important!

Along with a million other confusing sailboat terms , the mast has lots of different parts too. A sailboat mast consists of several distinct parts, each serving a specific function. Here are the different parts commonly found on a sailboat mast:
- Masthead: The masthead is the topmost section of the mast. It often includes attachment points for various components such as halyards (lines used to raise and lower the sails), the forestay (the wire or rod that supports the front of the mast), and other rigging elements. The masthead may also house instruments like wind vanes or antennas.
- Spreaders: Spreaders are horizontal bars attached to the mast, typically positioned at specific intervals along its length. They help support the rigging wires and prevent excessive sideways bending of the mast. The position and angle of the spreaders contribute to the proper alignment and tension of the rigging.
- Shrouds: Shrouds are the wires or cables that provide lateral support to the mast. They connect the mast to the sides of the boat, helping to stabilize the mast and distribute the loads generated by the sails. Shrouds are typically tensioned using turnbuckles or other adjustable fittings.
- Backstay: The backstay is a cable or wire that provides support to the rear of the mast. It helps counterbalance the forces exerted by the forestay and the mainsail, preventing the mast from excessively bending forward. Adjustable backstays allow for tuning the mast’s rigidity based on wind conditions and sail trim.
- Halyard Sheaves: Halyard sheaves are small wheels or pulleys located at the masthead or lower down the mast. They guide halyards, which are lines used to raise and lower the sails. Halyard sheaves minimize friction, allowing smooth and efficient hoisting or lowering of the sails.
- Gooseneck: The gooseneck is a fitting that connects the boom to the mast. It allows the boom to pivot or rotate horizontally, enabling control over the angle and position of the mainsail. The gooseneck may include a pin or other locking mechanism to secure the boom to the mast.
- Mast Step: The mast step is the base or fitting where the mast rests and is secured to the deck or hull of the sailboat. It provides stability and distributes the loads from the mast to the boat’s structure.
These are some of the primary parts found on a sailboat mast. The specific configuration and additional components may vary depending on the sailboat’s design, rigging system, and intended use.

I was surprised to learn that sailboat masts are commonly made from several different materials, each offering its own advantages in terms of strength, weight, and flexibility.
The choice of material depends on various factors, including the type and size of the sailboat, desired performance characteristics, and budget.
Here are some of the materials used for sailboat mast construction:
Aluminum is a popular choice for sailboat masts due to its favorable combination of strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum masts are relatively easy to manufacture, making them cost-effective. They offer good stiffness, enabling efficient power transfer from the sails to the boat.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber has gained significant popularity in sailboat mast construction, especially in high-performance and racing sailboats. You’ll see black carbon fibre masts on fancy sailboats!
Carbon fiber masts are exceptionally lightweight, providing excellent stiffness-to-weight ratios. This allows for enhanced responsiveness, improved performance, and reduced heeling (tilting) of the boat.
Carbon fiber masts can be precisely engineered to optimize flex patterns and provide targeted strength where needed.
Traditional sailboats, particularly those with a classic or vintage design, may have masts made from wood. Wood offers an aesthetically pleasing and traditional look.
Wooden masts can be constructed using solid wood or laminated techniques, which involve layering thin strips of wood for added strength and stability. Wood masts require regular maintenance, including varnishing and sealing to protect against moisture.
In some cases, steel may be used for sailboat masts, especially in larger vessels or those designed for specific purposes, such as offshore cruising or heavy-duty applications.
Steel masts offer robustness and durability, but they are heavier compared to other materials. They require adequate corrosion protection to prevent rusting.
Composite Materials
Sailboat masts can also be constructed using composite materials, such as fiberglass or fiberglass-reinforced plastics. These materials provide a balance between cost, weight, and strength. Fiberglass masts can be an option for recreational sailboats or those on a tighter budget.
It’s worth noting that advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques continually evolve, introducing new possibilities for sailboat mast construction.
The choice of mast material should consider factors such as boat type, intended use, performance requirements, and personal preferences, balanced with considerations of cost and maintenance.
Different Types Of Masts

There are several different types of masts used in sailboat designs, each with its own characteristics and purposes.
We’ve included how the masts are fixed on the boat. This one is an important one when buying a sailboat as you might have a preference over how your mast is attached to the hull or deck.
We’ve also included different rigs, as some boats have just a single mast and other sailboats will have two or more masts. Again, you might have a preference as to which rig set up you prefer so it’s worth knowing the pros and cons of each.
Keel-stepped Mast
A keel-stepped mast is one that extends down through the deck and is secured to the boat’s keel or structural framework. Keel-stepped masts offer stability and strength, as they transfer the loads directly to the boat’s foundation.
They are commonly found in larger sailboats and offshore cruising vessels. We loved knowing our deck was secured to one of the strongest parts of the boat.
It does come with some problems though, like the fact it can leak and start raining in the boat! A decent mast boot will stop this.
Deck-stepped Mast
A deck-stepped mast rests on a step or fitting on the deck, rather than extending down through it. Deck-stepped masts are typically used in smaller sailboats and are more straightforward to install, maintain, and unstep.
They are often lighter and less expensive than keel-stepped masts but may sacrifice some stability and rigidity.
Fractional Rig
A fractional rig features a mast where the forestay is attached below the masthead, typically at a point less than halfway up the mast’s height. This design allows for a larger headsail and a smaller mainsail.
Fractional rigs are popular on modern cruising and racing sailboats as they offer versatility, easy sail control, and improved performance in various wind conditions.
Masthead Rig
In a masthead rig, the forestay attaches at the top of the masthead. This design is commonly found in traditional sailboats. Masthead rigs typically feature larger headsails and smaller mainsails. They are known for their simplicity, easy balance, and suitability for cruising and downwind sailing.
There are various different rig set ups that just have one single mast. We’ll look at a few of the most popular types, but be aware that there are quite a few variations out there these days! It can get a little complicated!
The sloop rig is one of the most popular and widely used single mast rigs. It consists of a single mast with a mainsail and a headsail. The headsail, typically a jib or genoa, is attached to the forestay at the bow of the boat, while the mainsail is attached to the mast and boom.
Sloops offer simplicity, versatility, and ease of handling, making them suitable for a wide range of sailboats, from small day-sailers to larger cruising vessels.
A cutter rig utilizes two jibs : a smaller headsail attached to the forestay and a larger headsail called a staysail attached to an inner stay or a removable stay.
The mainsail is usually smaller in a cutter rig. This rig provides versatility and options for different sail combinations, making it suitable for offshore cruising and handling various wind conditions.
We absolutely loved our cutter rig as it gave so much flexibility, especially in heavy weather. A downside is that tacking is a little harder, as you have to pull the genoa past the stay sail.
Sailboats with two masts tend to be seen on older boats, but they are still popular and quite common, especially with long-distance sailors looking for versatility.
The yawl rig features two masts, with a shorter mizzen mast positioned aft of the main mast and rudder stock. The mizzen mast is usually shorter than the main mast.
Yawls offer versatility, improved balance, and increased maneuverability, making them suitable for offshore cruising and long-distance sailing.
A ketch rig has two masts: a taller main mast located near the boat’s center and a shorter mizzen mast positioned aft of the main mast but forward of the rudder stock. The mizzen mast is typically shorter than the main mast.
Ketch rigs provide additional sail area and options for sail combinations, offering good balance and flexibility for cruising and long-distance sailing. A lot of long-term cruisers love ketch rigs, though they tend to be found on older boats.
The downside is that you’ll have two masts with accompanying rigging to maintain, which isn’t necessarily a small job.
Sailboats with three masts or more are rare. They tend to be seen only on very large, expensive sailing yachts due to the additional expense of maintaining three masts, rigging and additional sails.
They aren’t great for single-handed crews but they do look very impressive and can power bigger vessels.
Schooner Rig
A schooner rig features two or more masts, with the aft mast (known as the mizzen mast) being taller than the forward mast(s).
Schooners are known for their multiple headsails and often have a gaff-rigged or square-rigged configuration on one or both masts. Schooner rigs offer impressive sail area, versatility, and classic aesthetics.
Schooner rigs are much rarer than the rigs mentioned above so it’s unlikely you’ll find one on a cruising vessel.
These are just a few examples of the different types of masts used in sailboat designs. Each rig type has its own advantages and considerations in terms of sail control, performance, balance, and intended use.
The choice of mast and rig depends on factors such as boat size, purpose, sailing conditions, and personal preferences.

We didn’t know the first thing about looking after our mast when we first moved aboard and we made it our mission to find out. When you’re sailing frequently then the last thing you want is to experience a mast coming down mid-passage!
Taking proper care of your sailboat mast is important to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Here are some tips on how to look after your mast:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of your mast to check for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Look for cracks, dents, loose fittings, or any other issues that may compromise the mast’s integrity.
- Cleaning: Keep your mast clean by regularly washing it with fresh water. Remove dirt, salt, and other contaminants that can accelerate corrosion. Use a mild detergent or boat-specific cleaner, and rinse thoroughly.
- Corrosion Prevention: Protect your mast from corrosion by applying a suitable corrosion inhibitor or protective coating. Pay particular attention to areas where fittings, rigging, or other components come into contact with the mast.
- Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts such as sheaves, shackles, and slides with a marine-grade lubricant. This helps prevent friction and ensures smooth operation. Be cautious not to over-lubricate, as excess lubricant can attract dirt and debris.
- Rigging Maintenance: Inspect your rigging regularly for signs of wear, such as broken strands, fraying, or excessive stretching. Replace any worn or damaged rigging promptly to avoid potential mast damage.
- UV Protection: The sun’s UV rays can degrade and weaken the mast over time. Protect your mast from UV damage by applying a UV-resistant coating or using mast covers when the boat is not in use.
- Storage Considerations: If you need to store your boat for an extended period, consider removing the mast and storing it horizontally or in a mast-up position, depending on the boat design. Store the mast in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area to prevent moisture buildup and potential damage.
- Professional Inspections: Periodically have your mast inspected by a professional rigger or boatyard to assess its condition and identify any potential issues that may require attention. They can provide expert advice on maintenance and repair.
Remember, if you are unsure about any maintenance or repair tasks, it’s always recommended to consult with a professional rigger or boatyard to ensure proper care and safety of your mast.
We learned so much from having our rigging inspected, so we highly recommend you do this if you’re at all unsure.
Conclusion: What Is A Sailboat Mast?
In conclusion, a sailboat mast is a crucial component that plays a vital role in the performance, control, and integrity of a sailboat. It’s a good idea to learn about sailboats before you head out on a sail – unlike us!
The mast serves as a vertical structure that supports the sails, allowing them to capture the power of the wind effectively. The mast enables sailors to control and manipulate the position of the sails, optimizing performance based on wind conditions.
Additionally, the mast contributes to the overall structural integrity of the boat, distributing loads and forces throughout the hull and keel. Various rigging components, such as halyards, shrouds, and spreaders, are attached to the mast, providing support and enabling precise sail control.
By understanding the importance of the mast and properly caring for it through regular inspections, cleaning, corrosion prevention, lubrication, and rigging maintenance, sailors can ensure their mast’s longevity and optimal performance.
A well-maintained sailboat mast contributes to a safe, enjoyable, and successful sailing experience.
- How much do new sails cost?
- How long do new sails last?
- Storm sails
Similar Posts

22 Sailing Movies You Must Watch In 2024

How Long Does It Take To Sail Across The Atlantic 2024?

Greece’s Top 10 Anchorages

The Best Books On Sailing For Beginners

Is Sailing Hard To Learn?

Sailing Your Sailboat In A Storm: The Ultimate Guide

Types of Sailboats by Type of Rig
16 December 2015
To have a better idea of which types of sailboats would best suit your needs, your Allied Yachting broker can advise you on the various options available on the market for new or second-hand vessels as well as new construction. In the meantime, here is a summarized guide to the different categories of sailing yachts by type of rig , whether they are monohull (single hull) or multihull , as they’re called in the Mediterranean.
Sailboats by rig type: hulls, masts

Single masted sailboat with monohull
The most common monohull modern sailing yacht is the sloop, which features one mast and two sails, thus sloops are single-masted sailboats. If they have just two sails — a foresail and a headsail — then they’re a Bermudan sloop, the purest type of sailboat. This simple configuration is very efficient for sailing into the wind.
Sailing sloops with moderate rigs are probably the most popular of all cruising sailboats. Just a single-masted sailboat with two sails (a foresail or headsail, and a mainsail) and the minimum of rigging and sail control lines they are relatively simple to operate and less expensive than rigs with multiple masts.
Sloops are adapted for cruising as well as racing, depending on the height and size of their rig.
The cutter sailing yacht is also a monohull similar to a sloop with a single mast and mainsail but generally carries the mast further aft to allow for a jib and staysail to be attached to the head stay and inner forestay, respectively. Once a common racing configuration, today it gives versatility to cruising boats, especially in allowing a small staysail to be flown from the inner stay in high winds.
Thus, a cutter-rig sailboat has an additional sail (the staysail) set on its own stay between the foresail and the headsail.
Cutters are mostly adapted for cruising, but capable of good performance while racing as well.
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat, the main-mast forward and a shorter mizzen mast aft.
But not all two-masted sailboats are ketches — they might be yawls.
A ketch may also carry a staysail, with or without a bowsprit, in which case it would be known as a cutter-rigged ketch.
Ketches are also monohulls, but there is a second shorter mast astern of the mainmast, but forward of the rudder post. The second sailboat mast is called the mizzen mast and its sail is called the mizzen sail.
Yawls have their origins as old-time sail fishing boats, where the small mizzen sail was trimmed to keep the vessel steady when hauling the nets.
Similar to a ketch, the difference being that the yawl has the mizzen mast positioned aft of the rudder post whereas the ketch has its mizzen mast ahead of the rudder post.
Thus, a yawl is also a monohull, similar to a ketch, with a shorter mizzen mast carried astern the rudderpost more for balancing the helm than propulsion.
Schooners are generally the largest monohull sailing yachts.

Monohull two masts sailing boat
A schooner has a mainmast taller than its foremast, distinguishing it from a ketch or a yawl. A schooner can have more than two masts, with the foremast always lower than the foremost main. Traditional topsail schooners have topmasts allowing triangular topsails sails to be flown above their gaff sails; many modern schooners are Bermuda rigged.
A schooner is a two-(or more) masted sailboat, in which the aft-most mast – the mainmast – is the same height or taller than the foremast. Many sailors agree that of all the different types of sailboats, a schooner under full sail is one of the most beautiful sights afloat.
Gaffed-rigged sailboats, or “gaffers”, have their mainsail supported by a spar – the “gaff” – which is hauled up the mast by a separate halyard. Often these types of sailboats are rigged with a topsail. The gaff rig is no longer seen on modern production yachts.
A catamaran (‘cat’ for short) is a multihull yacht consisting of two parallel hulls of equal size.
A catamaran is geometry-stabilized, that is, it derives its stability from its wide beam, rather than having a ballasted keel like a monohull. Being ballast-free and lighter than a monohull, a catamaran can have a very shallow draught. The two hulls will be much finer than a monohull’s, allowing reduced drag and faster speeds in some conditions, although the high wetted surface area is detrimental in lower wind speeds, but allows much more accommodations, living and entertaining space in stability and comfort.

Two parallel hulls sailing catamaran
The speed and stability of these catamarans have made them a popular pleasure craft in Europe, most high-quality catamarans are built in France, but careful since their wide beams aren’t easy (or cheap) to berth in the French Riviera.
Racing catamarans technology has made them today’s leading racing sailboats of the world, like in the latest editions of America’s cup or other renowned transoceanic races.
Please surf through our website listings of sailing catamarans .
OTHER MULTIHULLS
Even harder to berth in the Mediterranean, and most commonly designed for around-the-globe racing rather than cruising, the trimarans have also been gaining some popularity in the western hemisphere, especially by naval designers with futuristic projects.
A trimaran is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or ‘floats’) which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams.
MOTORSAILER
A motorsailer or “motorsailor”, is a type of sailing vessel, typically a pleasure yacht, that derives propulsion from its sails and engine(s) in equal measure.
While the sailing yacht appeals primarily to the purist sailing enthusiast, the motorsailer is more suited for long-distance cruising, as a home for ‘live-aboard’ yachtsmen. The special features of the motorsailer (large engine, smaller sails, etc.) mean that, while it may not be the fastest boat under sail, the vessel is easily handled by a small crew. As such, it can be ideal for retired people who might not be entirely physically able to handle large sail areas. In heavy weather, the motorsailer’s large engine allows it to punch into a headwind when necessary to make landfall, without endless tacking to windward.
The Turkish word gulet is a loanword from the French goélette, meaning ‘schooner’.
A gulet is a traditional design of a two-masted (more common) or even three-masted wooden sailing vessel from the southwestern coast of Turkey, particularly built in the coastal towns of Bodrum and Marmaris; although similar vessels can be found all around the eastern Mediterranean. For considerations of crew economy, Diesel power is commonly used on these vessels, similar to a motorsailer. Today, this type of vessel, varying in size from 14 to 45 meters, is very popular and affordable for tourist charters in Turkey, the Aegean, Greece and up to Croatia in the Adriatic.
Please surf through our website listings of cruising sailing yachts by type of rig.
OUR YACHT LISTINGS:
- New Yachts for Sale
- Pre-owned Yachts for Sale
- Yachts for Charter
You might also like

Yachting Consultants
Sale-Charter-Brokerage-Management
Headquarters:
34 Rue Caffarelli 06000 Nice, France
Front Office:
Boulevard de La Croisette – Port Canto 06400 Cannes, France
T.: +33 493 43 82 83 Email: [email protected] Website: www.alliedyachting.com


COMMENTS
Yawl. A yawl is one of the most common types of two-mast sailboats. It has two masts: a mizzenmast and the mainmast. The mizzenmast is usually much shorter than the mainmast. This makes it an oblique type of a sailboat in the sense that the mainmast is located in the front of the boat while the mizzenmast is located in the rear past or the boat.
The Hinckley Bermuda 40 is a classic sailboat that has been around since the 1960s. This boat is known for its beautiful lines, excellent handling, and comfortable interior. The Bermuda 40 is a yawl-rigged sailboat, which means it has two masts, a mainmast, and a smaller mast called a mizzenmast.
1. 1976 Westerly Center Cockpit Ketch. This 1976 Westerly Center Cockpit Ketch is a small 36-foot long sailboat with two masts. This is a solidly built cruising vessel that features a center cockpit ketch layout. This boat has a small 38 horsepower engine perfectly fit to navigate its smaller size.
Ketch is a type of sailboat that features two masts and two sails, commonly used as a racing and cruising boat. The mainmast of this two-masted sailboat is typically taller than the mizzen mast (aft-mast). Its name derives from catch. Taller masts allow you to use larger sails, so ketch boats are able to achieve better speeds than similar boats ...
Schooners are powered by the sails and a rudder, as are most sailboats. The specific rig setup of a schooner calls for two masts, with rigging options available for multiple sails, depending on the amount of wind power needed. Some setups will only rely on 2 or 3, while others may have as many as six or seven sails between the two masts.
Five Ocean-Going Sailboats With Two Masts. Some of the most reputable boat builders in the world favor ketch and yawl rigs. Some popular sailboats with two masts used nowadays include the Nicholson 38, the Bayfield 40, the Amel Super Maramu, the Hinckley Bermuda 40, and the Bowman 46. Let's look at each model.
Two-masted sailboats, with their elegant profiles slicing through the waves, serve as a bridge between the past and present, combining traditional sailing heritage with contemporary performance. These vessels, marked by their dual masts—the foremast and the mainmast—embody a blend of artistry and engineering, appealing to a wide array of ...
By definition, a schooner is a sailboat with at least two masts, with the forward mast (foremast) being a bit shorter than the main mast. Although a schooner can have more than two masts, most were just two. During the time of their popularity this smaller and better upwind set up allowed for a more efficient and manageable sailboat. It was the ...
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat. The rear mast, called the mizzen mast, is shorter than the forward main mast. The mizzen mast is mounted forward of the rudder post. Read more. Yawl. 02. A yawl is similar to a ketch, but the rear mizzen mast is moved farther aft, behind the rudder post. This makes the mizzen on a yawl seem like an afterthought ...
Learn about the different sailboat designs that have two or more masts, such as ketch, yawl, brigantine, brig and schooner. Compare their features, advantages and disadvantages for off-shore and coastal sailing.
The two-masted rigs are: Lugger - two masts (mizzen), with lugsail (a cross between gaff rig and lateen rig) on both masts. Yawl - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast is much taller than mizzen. Mizzen without a mainsail. Ketch - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts.
These are two-masted vessels that include a mizzenmast and a larger main mast, with a sloop-like jib. Ketches are typically over 40 feet in length, simply due to a need for significant power in a manageable size. ... Once the boat has been constructed, the masts will be added to the final design and then the ketch rigs can be strung up on the ...
A yawl is a type of boat. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or sailplan), to the hull type or to the use which the vessel is put. As a rig, a yawl is a two masted, fore and aft rigged sailing vessel with the mizzen mast positioned abaft (behind) the rudder stock, or in some
2. Yawl. A yawl is one of the typical two-masted sailing boats. It has two masts: a mizzen mast and the main mast. The mizzen mast is usually much shorter than the main mast. So, it is a leaning sailboat where the main mast is in the front part of the boat while the mizzen mast is in the back part.
Among the most popular two-mast sailing vessels is the yawl. It is equipped with a mizzenmast and a foremast. Typically, the mizzenmast will be relatively short, particularly when compared to the foremast. This renders it an angled sailboat, seeing that the foremast is situated at the front of the boat and the mizzenmast is situated at the back.
A schooner is a two-or-more masted sailboat, in which the aft-most mast - the mainmast - is the same height or taller than the foremast. The one shown here is gaff cutter rigged, with a topsail set on the mainmast. Many sailors agree that of all the different types of sailboats, a schooner under full sail is one of the most beautiful sights afloat.
Brigantine. A brigantine is a two-masted sailing vessel with a fully square-rigged foremast and at least two sails on the main mast: a square topsail and a gaff sail mainsail (behind the mast). [1] The main mast is the second and taller of the two masts. Older usages are looser; in addition to the rigorous definition above (attested from 1695 ...
Although the most popular sailboat types and styles are monohull sloop (one mast) and a monohull ketch (two masts) it is possible to have a mutli-masted catamaran. There are also other two mast variations such as the yawl, the junk rig, and the schooner, although they are not as widely used.
Mast configurations and sail combinations are another way of categorizing sailboats. These are just a few of the most common types. Sloop The most common type of sailboat is a sloop. A sloop has one mast and two sails, a mainsail and a headsail. Depending on the size and shape of the headsail, it may be called a jib, genoa or spinnaker.
one mast. triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail) a foresail (also called the jib) fore-and-aft rigged. medium-sized (12 - 50 ft) Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind. Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop.
A sailboat mast is a vertical, upright structure that supports the sails of a sailboat. It is a crucial component of the boat's rigging system and plays a key role in harnessing the power of the wind to propel the vessel. Typically located in the center of the boat, the mast extends upward from the deck or hull.
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat, the main-mast forward and a shorter mizzen mast aft. But not all two-masted sailboats are ketches — they might be yawls. A ketch may also carry a staysail, with or without a bowsprit, in which case it would be known as a cutter-rigged ketch. Ketches are also monohulls, but there is a second shorter mast ...