
5 upcoming futuristic yachts that billionaires across the world are excited for

You may also like

Superyacht Regina d’Italia, home to reality TV royalty, the Kardashians, during the Kourtney-Travis wedding, is an absolute queen of the high seas. The bathrooms have gold fittings studded with rubies and the furniture is dotted with leopard skin.

Hiding for months, the $119 million superyacht yacht ‘Graceful’ has changed its name to ‘Killer Whale’. The 270 feet vessel on its way to St Petersburg has a wine cave, a wellness area and a pool that transforms into a dance floor.

Longer than a football field, Feadship’s new Project 710 is one of the greenest superyachts ever built.

FarmVille’s billionaire creator, Mark Pincus, has treated himself to a stunning $70 million superyacht. Aptly named ‘Come Together,’ from the pool to the cinema to the sun deck, everything on the 197-foot-long vessel is designed specifically to be enjoyed with the full family.

Unveiled Ilma, the breathtaking new addition to the Ritz-Carlton Yacht Collection. This 790-foot vessel offers 224 lavish suites, a luxurious spa, multiple gourmet restaurants, a humidor, and a kid’s program for an unforgettable vacation experience.

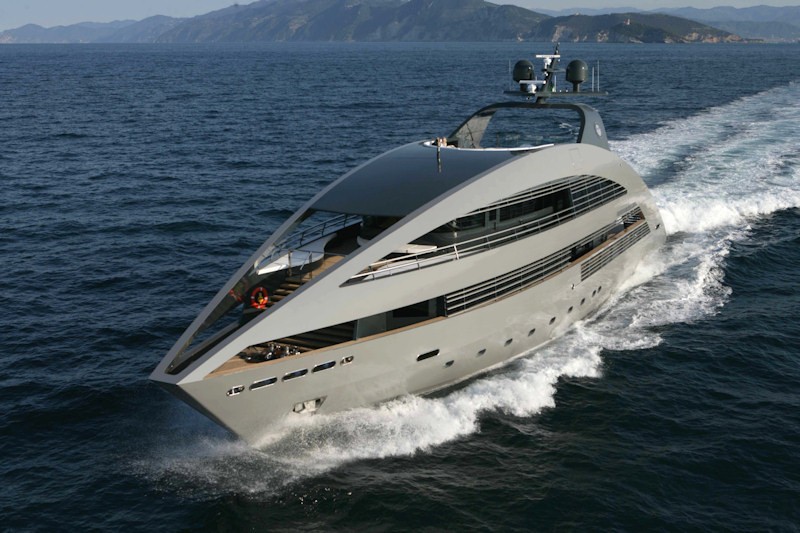
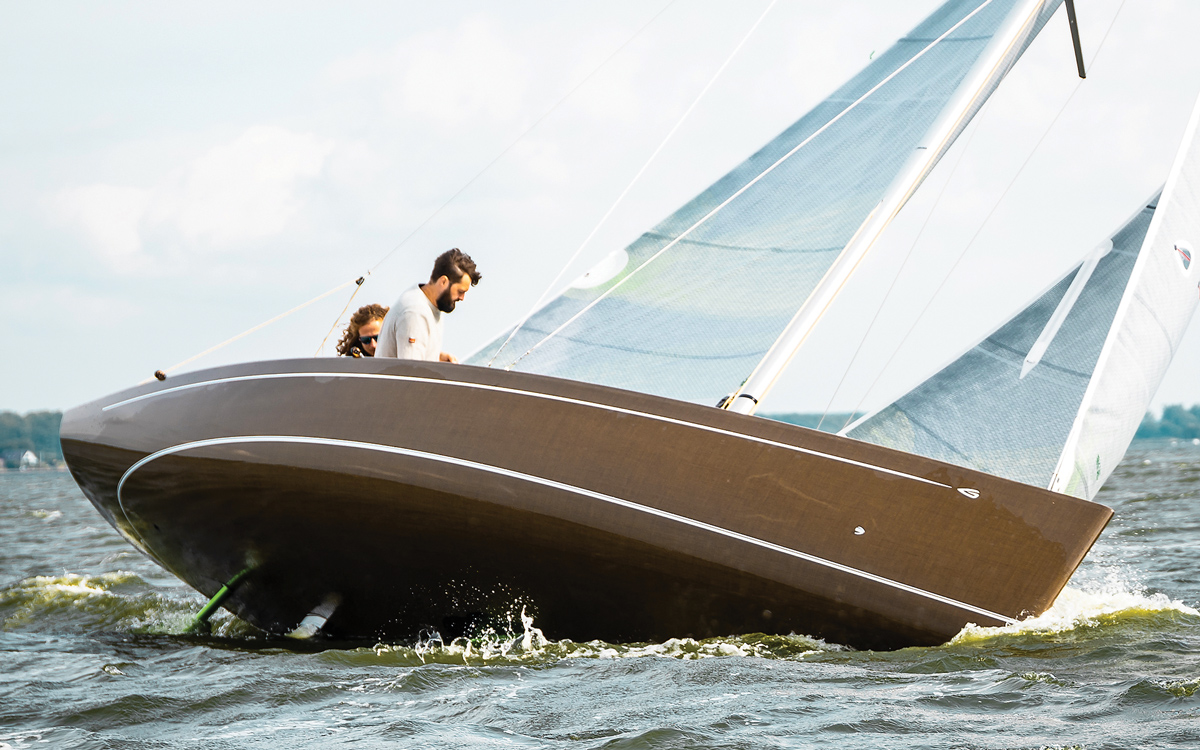
This 295 feet luxury yacht is inspired by a hammerhead shark

Heesen’s most powerful superyacht Yet, Ultra G, is great for the sea-faring billionaire and his beast.

Jeff Bezos and Lauren Sanchez have sailed so much aboard their Koru megayacht that the $500 million vessel and its support ship had to be taken to one of Europe’s largest shipyards for maintenance.

First of its kind: The world’s largest sailing superyacht to get an IMAX theatre

- Subscribe Now
- Digital Editions

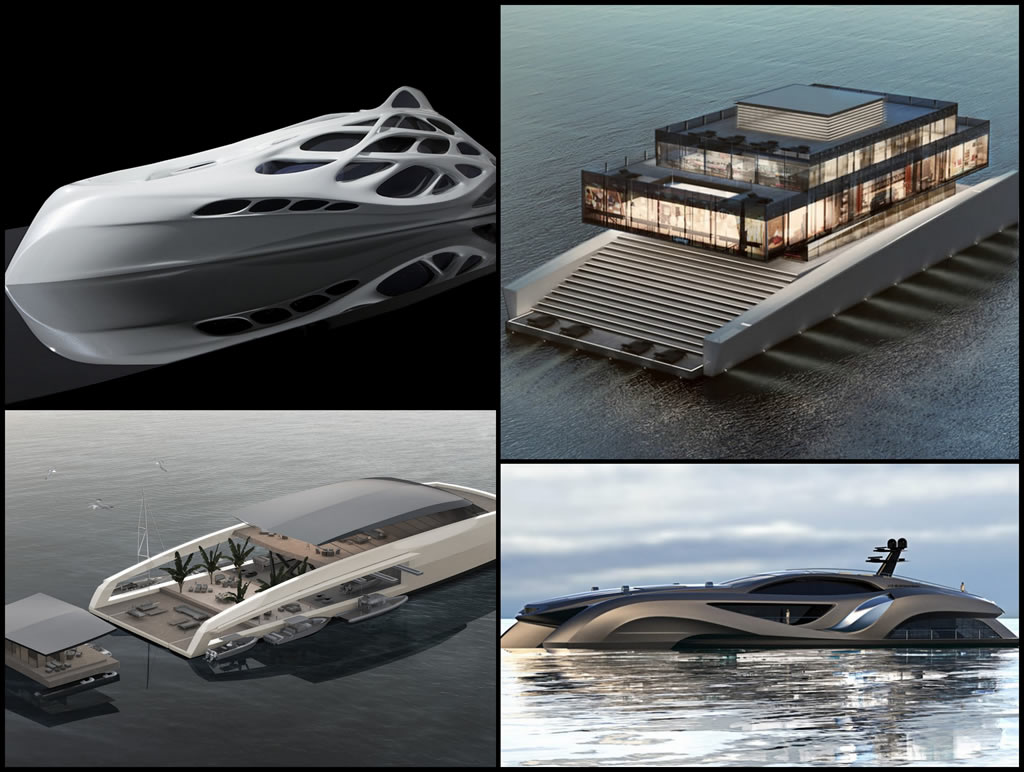
Welcome to the future: 5 futuristic yachts being built today
- Top stories
The future of the motor boat has never looked so exciting but what form will it take? We take a closer look at five craft of tomorrow you can buy today
The 2019 Boot Düsseldorf show was awash with exciting new boats , brands and concept craft all claiming to represent the future of boating. Some were touting hybrid or pure electric drivetrains; others were offering radical new hull shapes, while yet another promised a completely fresh approach to its interior layout.
The one thing they all agreed on is that the market for motor boats is ripe for change, with customers looking not just for the next new model but for a genuinely fresh approach to the whole boating experience.
Having scanned the halls, here is our pick of the five most interesting new craft heading to a marina near you in the months ahead.
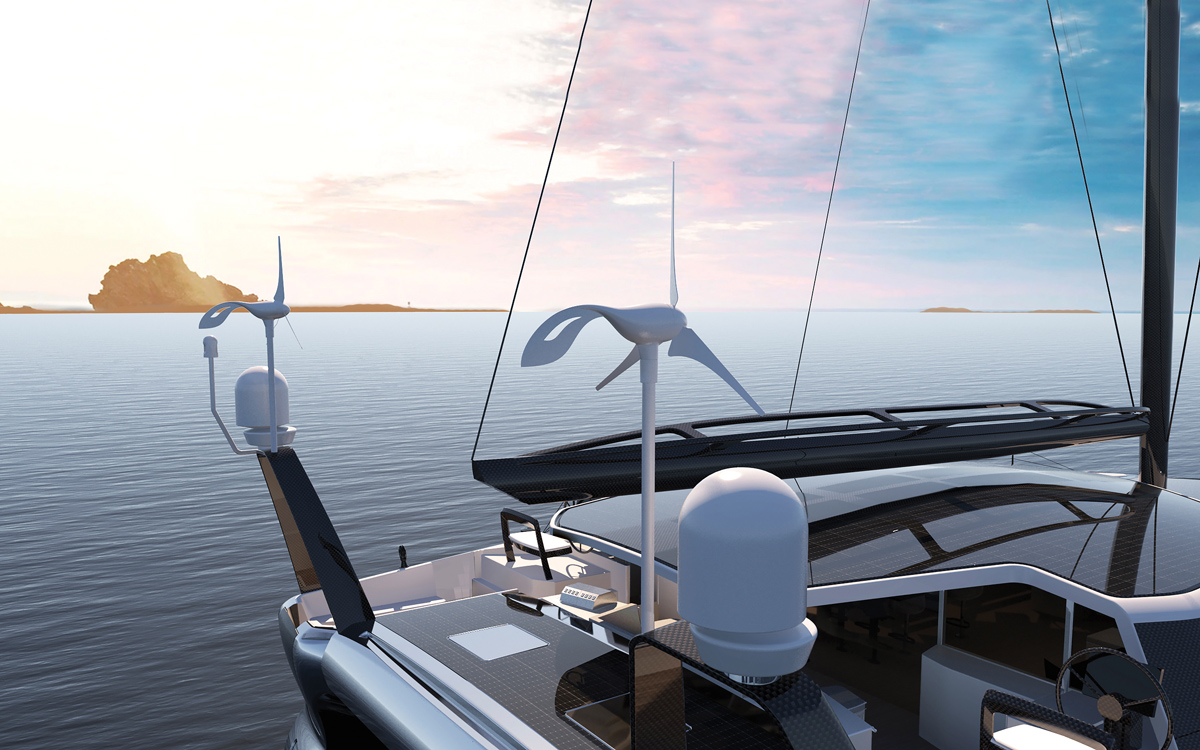
Solar Impact

The folding hard top, coachroof and hinged side-deck shades are covered in 300m² of solar panelling
Solar Impact is a 78ft ocean-going solar-powered motor yacht based on an aluminium SWATH hull. The result of a five-year research project by Swiss start-up SolarImpact Yacht AG, it claims to offer unrivalled luxury and refinement with cutting-edge aesthetics in a sustainable package.
What makes it special?
Its SWATH (Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull) design consists of two torpedo-shaped tubes housing the electric motors and batteries, which travel a few feet under the water, avoiding the waves which make life uncomfortable for conventional ‘surface’ craft. The accommodation is raised above the waterline on slender blades to minimise drag and frontal area.
Power comes from twin 500kW electric motors fed by an 800kWh battery pack which is kept topped by 300m 2 of solar cells mounted on the coachroof, hard top and folding wings. A pair of exceptionally compact 70kVA rotary-engined generators help extend the range during cloudy conditions. This is claimed to give a top speed of 22 knots for short periods with 10 hours battery life at slower cruising speeds and an indefinite range at 5 knots in calm sunny conditions.

The open-plan living areas are designed to feel like a luxury waterside apartment
Accommodation consists of a large open-plan saloon and galley on the main deck with a master suite forward and four twin or double cabins below, each with their own ensuite bathrooms, plus a further small cabin for crew.
When can I have one?
The first one is already in build at Schaaf Yachtbau in Germany with a projected launch date of February 2020. The price for this futuristic craft is €7.2million ex VAT.
X Shore is the closest thing yet to a Tesla for the sea according to its founder, the Swedish tech magnate Konrad Bergström. Having made his fortune in premium headphones and speakers, he has now turned his attention to creating an all-electric boat brand that offers proper performance and range in a stylish, sustainable and environmentally friendly package.
The design features a tall bow for a dry ride matched with a modular cockpit for flexible seating options. The hull has a deep step amidships with a single exposed shaft taking the drive from the electric motor in the bow to the propeller, which is set in a stern tunnel to keep the drive angle as close to horizontal as possible.
A unique gearbox using magnetic teeth that never actually touch the cogs reduces friction for maximum efficiency. The result is a claimed top speed of 40 knots and a range of 60nm at 25 knots or 100nm at displacement speed. Charging takes 8-12 hours depending on the source and the battery is good for 5,000 cycles.

A touchscreen helm and multi-function wheel replace the usual gauges and switches, while a cork dial supplants the throttle
It’s not just the drivetrain that’s innovative. The helm station features a rotary dial instead of a throttle lever, the seats are mounted on sliding rails and the steering uses fly-by-wire technology. Even the decks are made of sustainably sourced cork instead of teak. Front and rear bow thrusters make light work of manoeuvres.
There are two models available, the Eelex 8000 (pictured above and launched last year) and the smaller Eelex 6500 shown at Düsseldorf, deliveries of which begin later this year. Prices start from €249,000 ex VAT.
The Cetera 60 is a fresh take on a liveaboard cruising yacht with an innovative ‘multispace’ layout that prioritises space and comfort over performance. A joint venture between Guida Design & Engineering and the Fiart shipyard, it is claimed to have 30m² more living space than a conventional 60ft flybridge.
The starting point is a broad 18ft beam with a blunt rounded bow that barely tapers at either end on a hull designed for efficient cruising at 20 knots and a top speed of 23 knots. Twin IPS600 engines allow for a short engineroom and tender garage leaving space ahead for a full-length (but restricted height) technical deck with separate compartments for fuel and water tanks as well as electrics and batteries for the planned hybrid version.
All three sleeping cabins and bathrooms are on the lower main deck off a central corridor that leads from the water-level beach club area through to the forward cockpit. The saloon/study is forward and a couple of steps up, giving a clear view ahead as well as access to the spacious bow cockpit.

The innovative layout puts the cabins on the main deck and the galley and dining area in a ‘convertible’ enclosed fly deck
An internal staircase leads up to the large open-plan dining area, galley and helm on the enclosed upper deck, although drop- down windows and twin sunroofs open it up to the elements when required.
Hull no 1 is already in build and due to be launched at the Cannes Yachting Festival in September. Modular construction using simple box-shaped cabins keeps the starting price to €1million ex tax.

The self-righting aluminium hull is designed to be tough but easily driven by conventional diesel or electric hybrid power
Arksen isn’t just a new breed of explorer yacht, it’s also a new approach to ownership that combines off-the-grid boating with a socially responsible attitude. All its boats are fitted with monitoring systems that continuously relay information about global water quality, and owners pledge to donate 10% of their vessel’s sea time to projects supported by the Arksen foundation, such as scientific research or film-making.
It’s the brainchild of entrepreneur and experienced sailor Jasper Smith, who spotted a gap in the market for a range of three adventure yachts from 70ft to 100ft that he claims are tougher, smarter and more efficient than the competition.
Designed by Humphreys Yacht Design and built by the Wight Shipyard Company in Cowes, they feature self-righting, aluminium hulls that can slip through the water at 7 knots using minimal power or push on to 14 knots when needed. Hybrid propulsion is optional but even with diesels the 85 has a range of 6,000nm from its 16,000-litre tanks. Fins, gyros and flopper stoppers maintain stability while solar panels generate up to 4.2kw of power.

Even the entry-level Arksen 70 has an ice-capable hull and multiple solar panels
All Arksen Yachts are designed to be semi-autonomous so that in the future Arksen Mission Control will be able to deliver your yacht to any given destination. It also plans to offer curated adventures to remote corners of the globe. Interiors by Design Unlimited are said to be stylish but also easily reconfigured from leisure to research or commercial use.
Arksen has sufficient funding to build the first boat on spec but is already discussing orders with potential buyers. Prices start at £4.5million ex VAT for the Arksen 70 rising to £8.5m for the Arksen 100. 1% of its annual sales will be donated to environmental causes.

The helm is just as clean and elegant as the design of the long, slender hull
The Q30 is perhaps the closest thing yet to the gentleman’s launch of the future. Designed and built in Finland with a long, slender 9.3m hull and a modern, minimalist Scandinavian aesthetic, it uses a proven Oceanvolt electric drive system to slip silently along.
Rather than attempt to create a high-performance electric sportsboat with all the limitations of speed and range that implies, Q-Yachts has focused on building an elegant, efficient and useable day boat for rivers, harbours and coastal waters.
With a cruising speed of 9 knots, a fast cruise of 14 knots and a claimed range of 42nm and 22nm respectively (double that if you opt for the 60kWh battery pack), it’s perfect for day trips. And because the entire drivetrain is supplied by Oceanvolt, it should work seamlessly together.

Charging from 5% to 95% takes 13 hours and the batteries are rated for 500 cycles with minimal loss. As Q-Yachts points out if you discharged it fully 50 times a year (the equivalent of 2,000nm/220 hours at 9 knots) the batteries should last at least 10 years and retain 80% of their capacity. You can also fit a 2kW petrol range extender if required. A cuddy cabin with a vee-berth and under-seat toilet makes overnighting possible and the whole boat is trailable.
The first boats have already been delivered and crucially for British customers, Wessex Boats (the UK importer for Targa and Marex ) is representing them in the UK. The boat comes with a two-year warranty and prices start at €183,000 ex VAT and delivery.

Oceanco unveils 105 metre expedition yacht Esquel
Netherlands based superyacht builder Oceano unveiled plans for Esquel, a daringly styled superyacht, at the Dubai International Boat Show

Sunseeker and MTU go hybrid
Sunseeker will launch its first hybrid production boat in 2020
New Boats at Southampton Boat Show: Windy 29 Huracán
New boats at cannes boat show: azimut seadeck 7, new boats at cannes boat show: ferretti infynito 80, latest videos, watch: beneteau swift trawler 54 sea trial – £1.4m cruiser is the ultimate home, watch: parker sorrento sea trial: 50-knot cruiser with a killer aft cabin, watch: virtue v10 sea trial: €272k weekender, how to mark your anchor chain: 6 top tips from our expert.
Futuristic Yacht Designs That Will Leave You Breathless
Ever since people developed a sense of imagination and a taste for time (as a concept), they started imagining the future in all its guises and forms. Whether it was about their own lives or how the world would be in a few years or centuries. There's this famous quote from Einstein which goes: "Logic will get you from A to B. Imagination will take you everywhere." Beautifully said by the genius - he knew that the essential component to anything new and innovative involved imagination and, of course, inspiration.

EarthRace Biodiesel Powerboat

MV Brigitte Bardot

The Code X Yacht
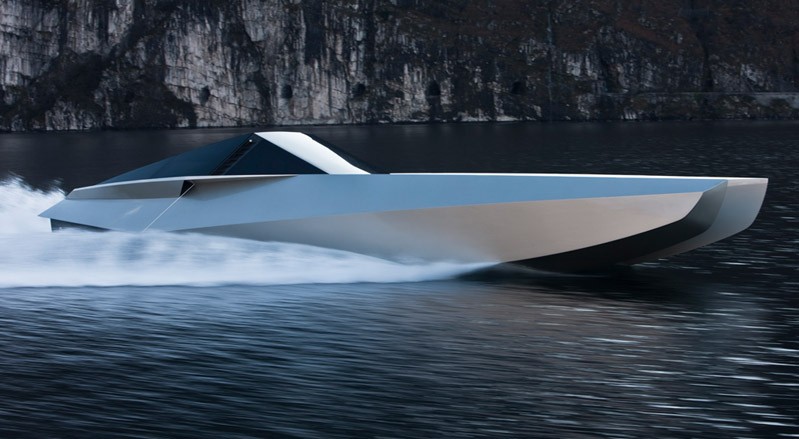

The Wallypower 118 Super Yacht

Bugatti Veyron Sang Bleu (concept)
Ocean Emerald

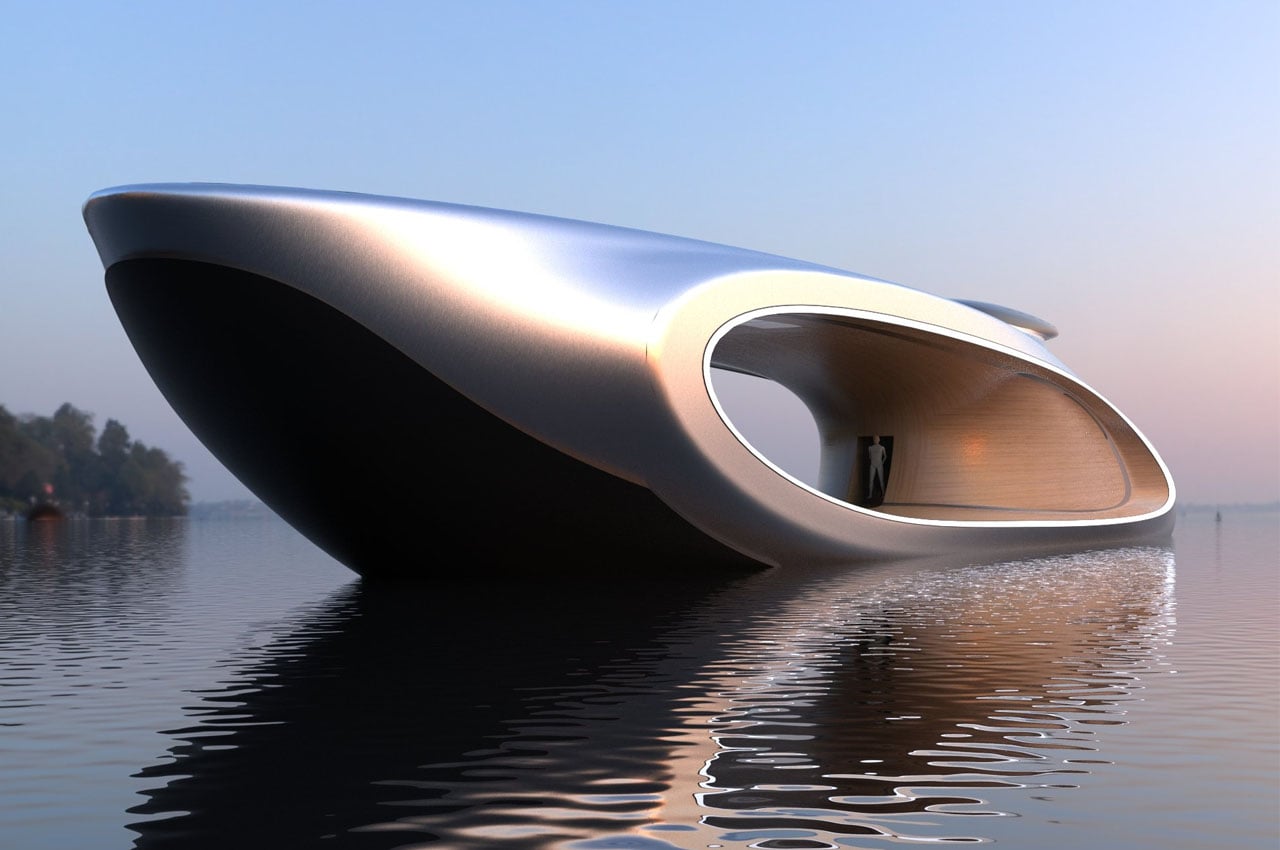
Oculus (concept)

Valkyrie Trimaran Yacht (concept)


Sleek and futuristic yachts designed to revolutionize the luxury automotive world
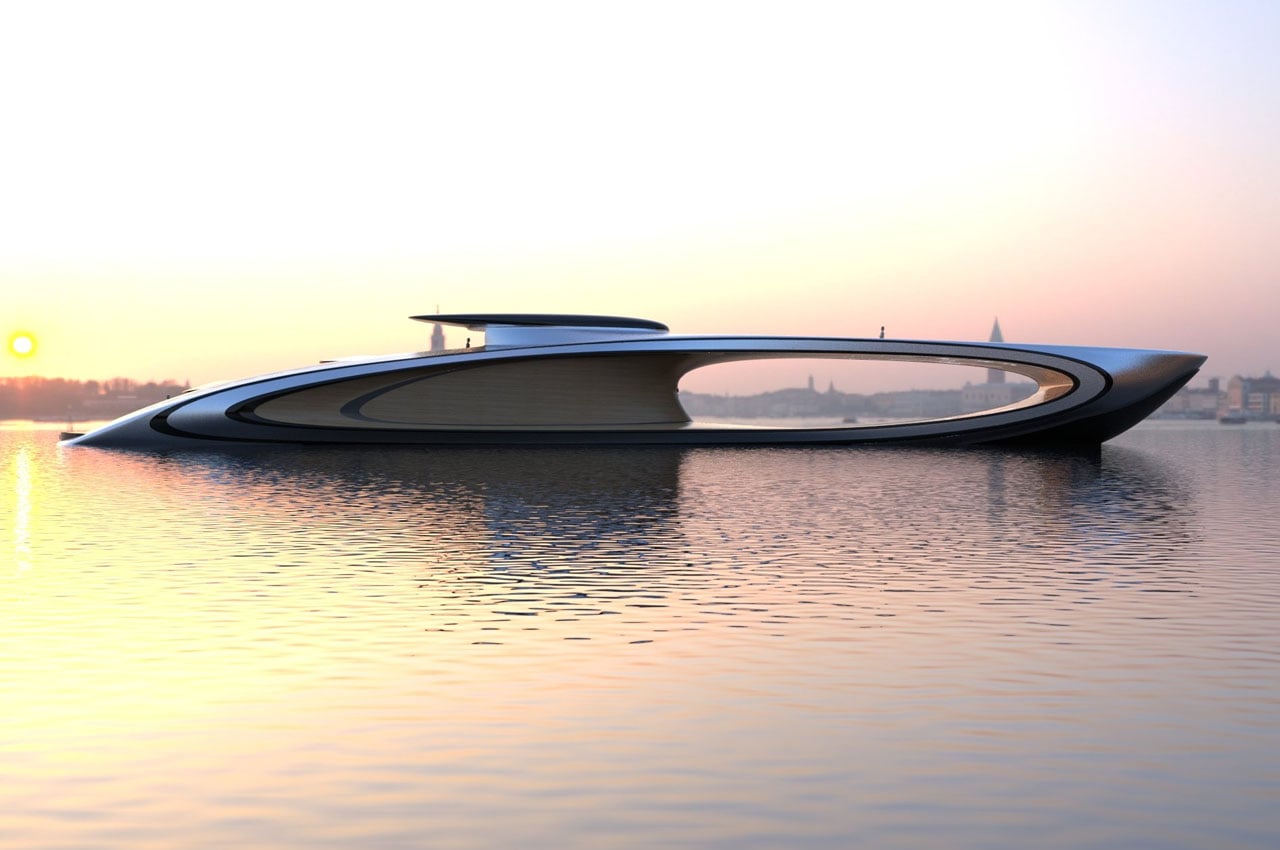

Though I’ve never been on a yacht , one thing is pretty clear – they’re cool as hell! These luxurious vessels are taking over water bodies, and are slowly becoming a preferred means to travel from one destination to another. How exciting would it be to explore beautiful locations in these exotic vehicles? I mean you now have yachts that function as solar-powered floating villas, while some are even inspired by sportscars! The yacht experience has been elevated to a whole ‘nother ball game. And, we’ve curated a collection of the best yachts we’ve come across! From a conceptual swan-shaped yacht to a superyacht with a gaping void in the middle – this collection of automotive designs will leave you completely impressed, and itching to get aboard one!
1. The Shape

Christened “The Shape” this superyacht breaks all the fundamental rules of sailing and yacht design that we’ve seen so far. It has a gaping hole right in the middle (just like the ones in modern skyscrapers) that serves as the sun deck and a never-before-seen unique visual attraction. How it will address the turbulent seas when the weather is hostile, is a question for another day! The beastly concept is 69 meters long and having a draft of 3.90 meters yacht offers a living area of 35 meters past the void. It has three decks hidden in the colossal structure – the first floor having the suites, the second one being the shared living space, and the command center on the third.
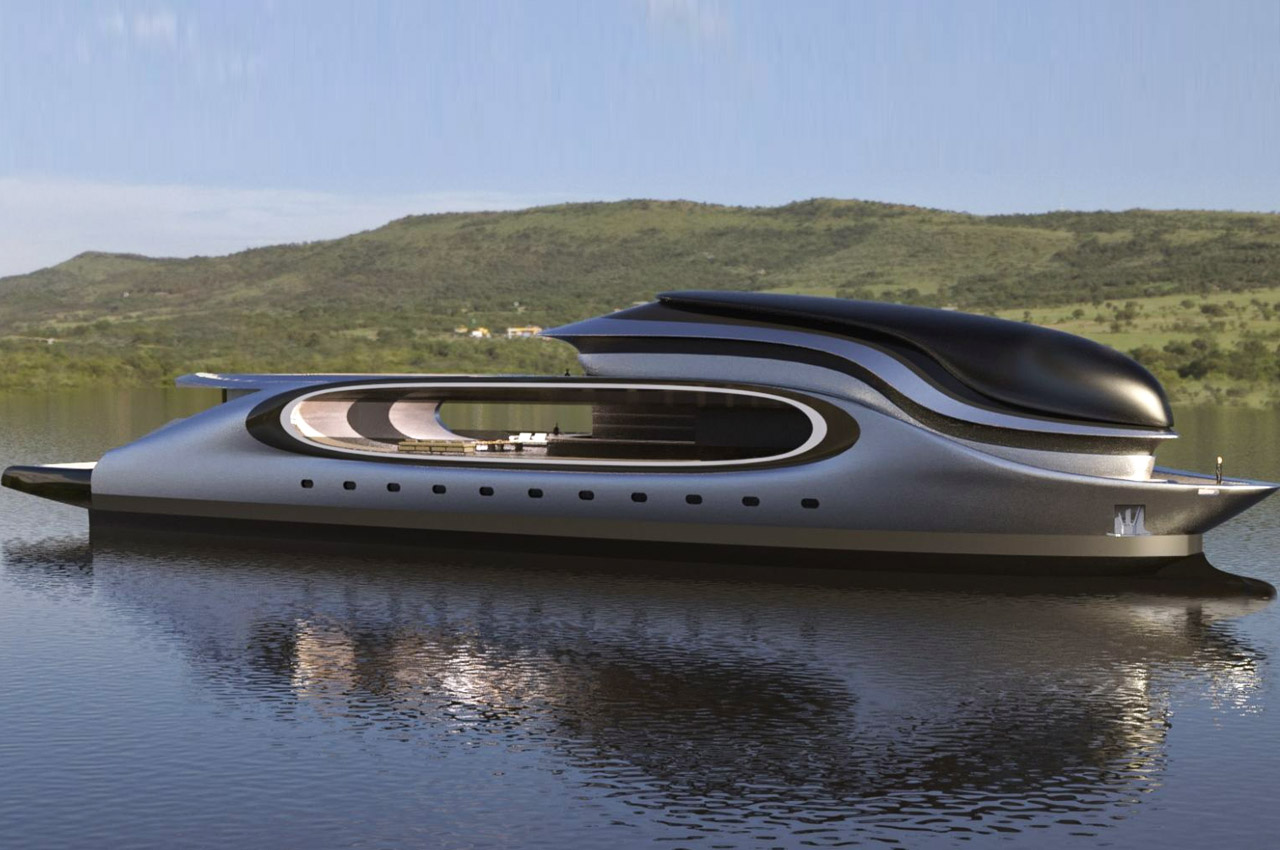

The silhouette of the Xenomorph head from the Alien franchise is an apparent relatable element, and the traces of Avanguardia yacht are also evident. So, has the Italy-based design house finally hit saturation with its thinking cap on? Most definitely not, as the 279-foot Icaria vessel hones massive deck space for two helicopters to park and a full-fledged tender garage to house a couple of watercraft, accessible via two foldable doors. The superyacht has an imposing bow followed by a large glass bridge. Icaria is more tailored for explorers who like to tread out into the rough waters. For times when adventure seekers need to relax in the warmth of the sun, there is the gorgeous deck right by the hollowed-out area the designers refer to as “hole deck.”
3. Avanguardia
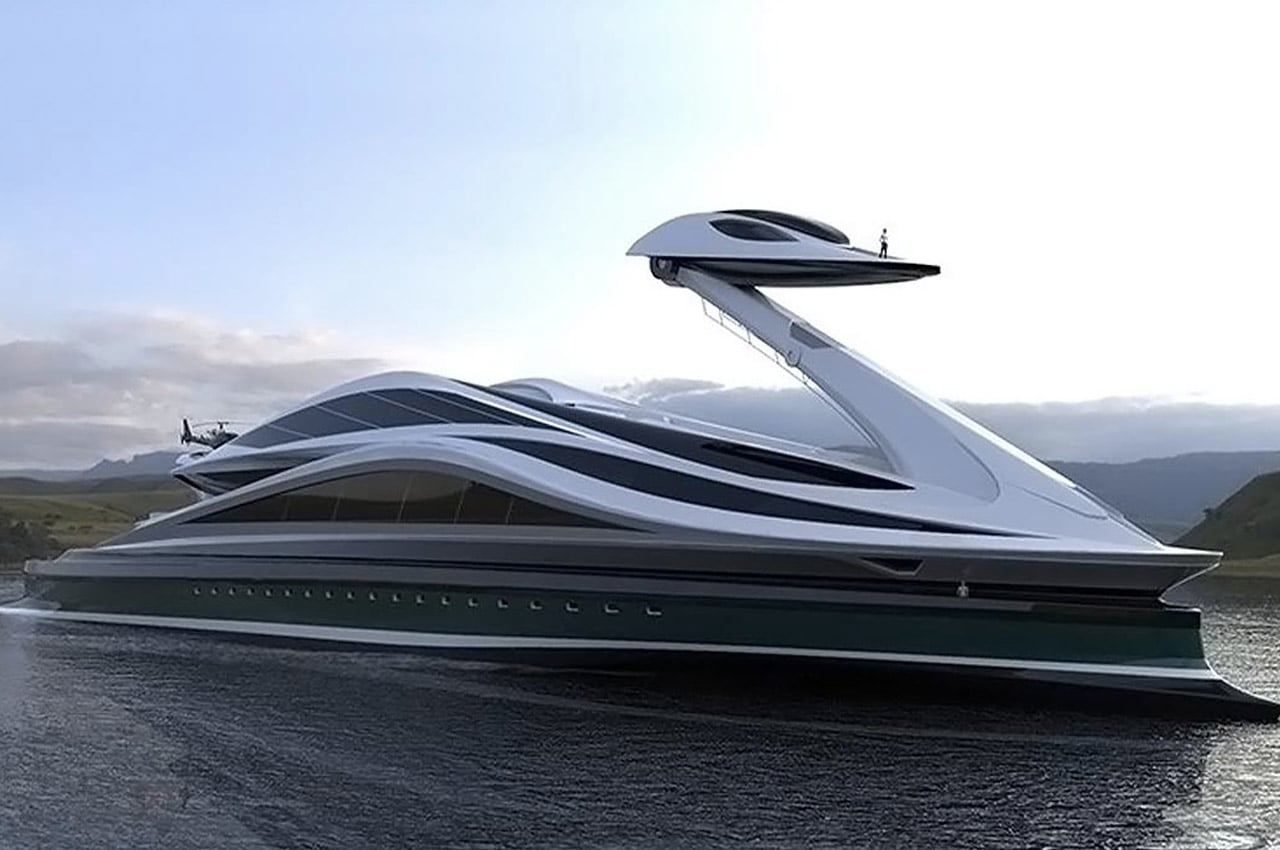

Pierpaolo Lazzarini of Lazzarini Design Studio is known for his unique and extraordinary watercraft creations and this swan-shaped concept yacht called ‘Avanguardia’ tops the list. The name means ‘vanguard’ and it comes from the position of its control tower which is perched like a swan’s head. Can you guess which 1970’s Japanese manga unintentionally inspired this? Avanguardia is subdivided into 5 decks and can fit up to 60 passengers. The ‘swan head’ is the control tower that is used to maneuver this 137-meter long, almost outrageous, yacht. Another interesting feature about the control tower is that it can detach from the ‘neck’ and transform itself into an auxiliary 16-meter boat. When in motion, the mobile control tower can adjust Avanguardia’s position by lowering itself right into the center of the yacht.
4. Lazzarini GTM Concept
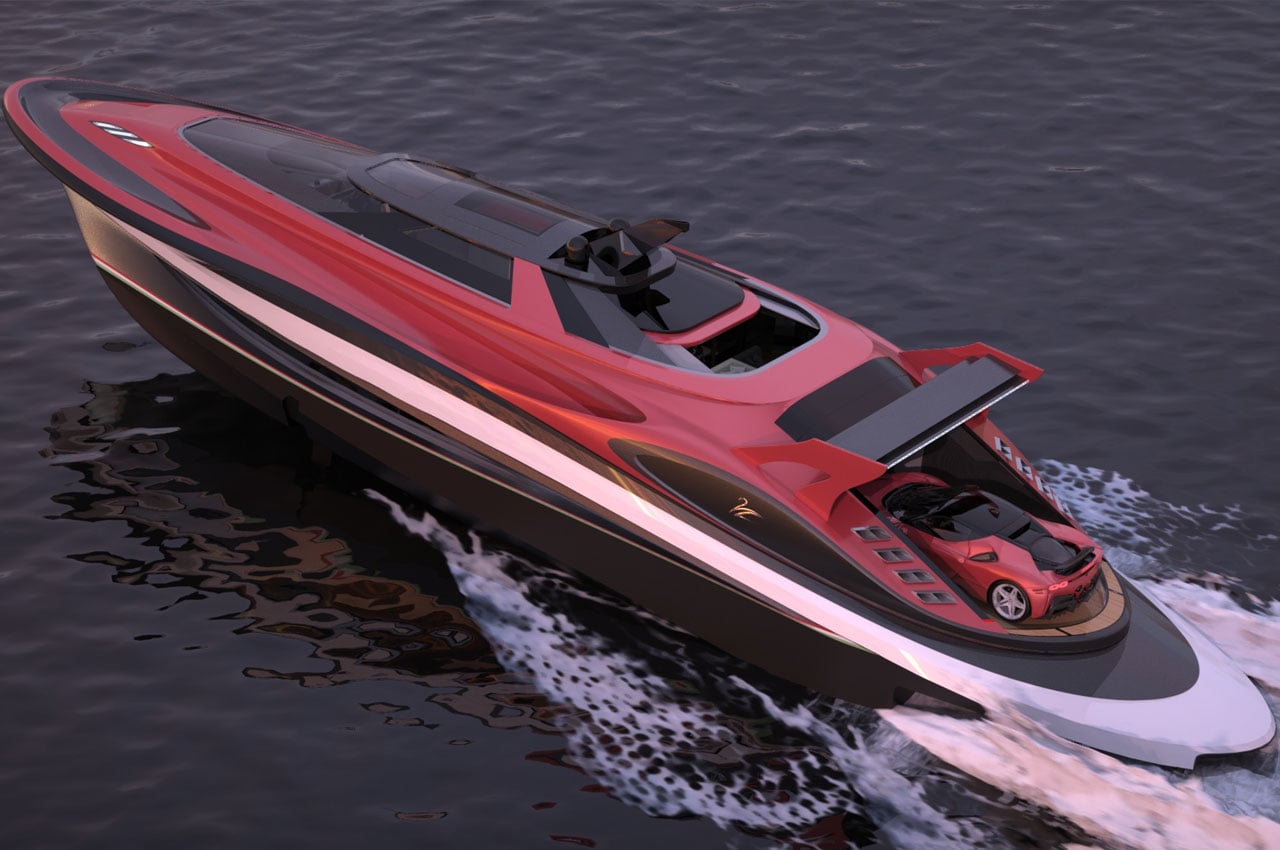

Delivering to the desirous a notion of how a Ferrari would look like on the water, the Lazzarini GTM doesn’t give out the car it may be based on but does replete the Prancing Horse DNA without a doubt. The two companies have not collaborated on the design, so you cannot earmark this one as official, but the concept has a design worth seeing the light of the day someday. Beyond the inspired look, the Gran Turismo Mediterranea is an 88-foot, sporty yacht, made using the Ferrari-favored carbon fiber. Undeniably Ferrari for the seas, this design renders appear with a Ferrari badge on the front, gullwing doors and a cabin that welcomes the owner and crew into a sportscar-esque cockpit that ensure you don’t feel any difference from the Italian stallion’s driver seat to the pilot seat of this hyper yacht.
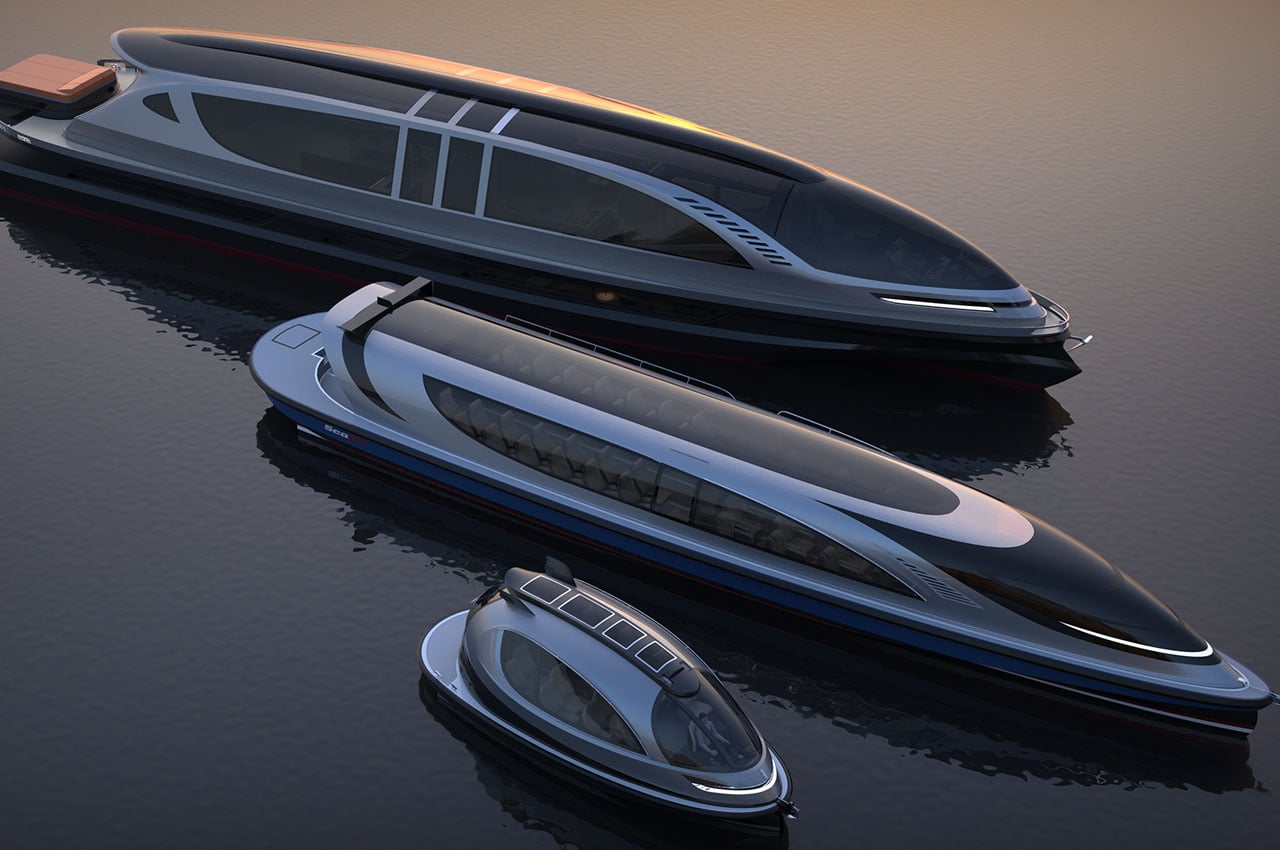

The concept christened SeaJet is a hyper-fast transportation yacht that’s encapsulated in a sense of style and luxury – affluent travelers will take a keen interest in it. This watercraft would be stored in a superyacht and is designed to haul around 50 passengers from one location to the other for short travels. Much like the Xenos hyper yacht and the Jet Capsule, this one being 23 meters in length is bigger than the Jet Capsule and smaller than Xenos- suggesting a fleet of hyper watercraft in the making for a profound travel experience on the seas.
6. The Tecnomar
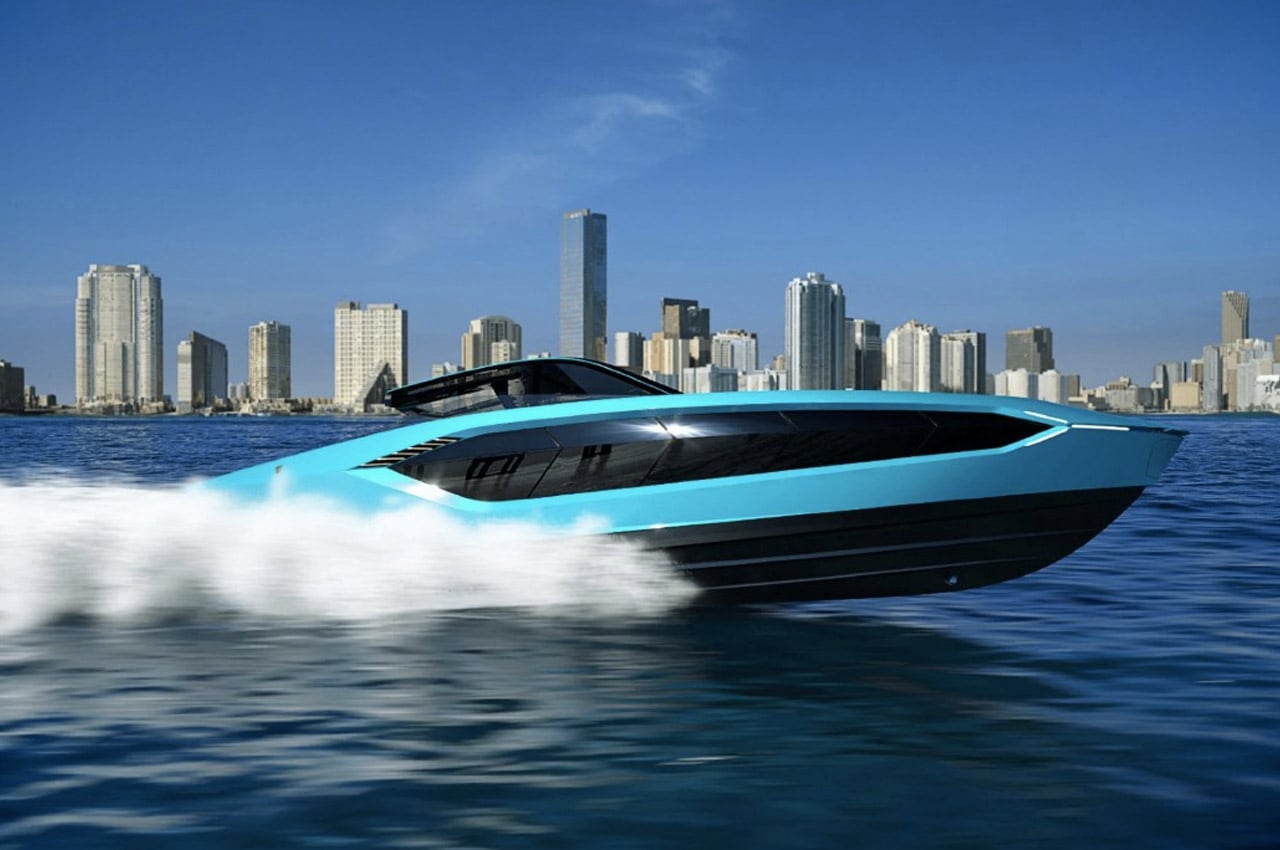

The Tecnomar pulls inspiration directly from the Lamborghini Sián FKP 37’s design details (the two even feature together in the video). Outwardly, it’s pretty easy to draw parallels between a car and yacht, simply because they both need to be incredibly aerodynamic and streamlined, but the Tecnomar manages to do so much more to look the part (apart from the angular bodywork, of course). Take for instance the Y-shaped headlights, a detail that’s directly taken from Lamborghini’s playbook (remember the Terzo Millennio), or the zig-zag stepping on the rear of the yacht that’s inspired by the rear profile of the Aventador.
7. Arkup 75
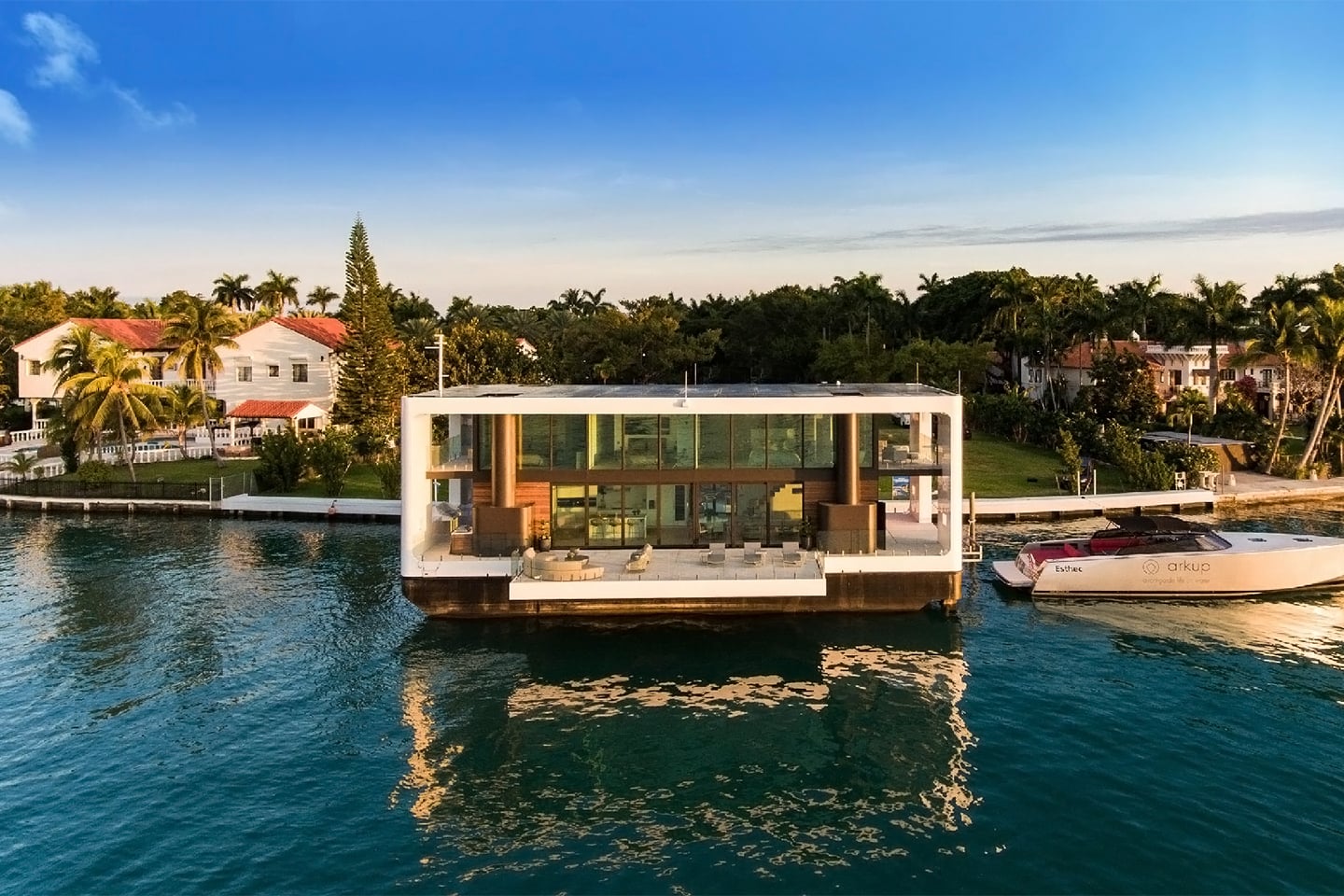

Arkup 75 lets you live in comfort and luxury in total autonomy – enjoy life between the sea, the sky, and the city. The 75 feet long yacht has a total living space of 4,350 sqft! It is truly floating architecture and modern interior goals at its finest. Arkup is a game-changer for the hospitality market when it comes to self-sustainable, blue developments. floating and overwater eco-resorts a reality with the versatility to scale, configure, even relocate. “We are revolutionizing life on the water. We leverage Arkup products and expertise for fast deployment, modular, floating communities that you scale according to market demands,” says the team.
8. Drakkar S
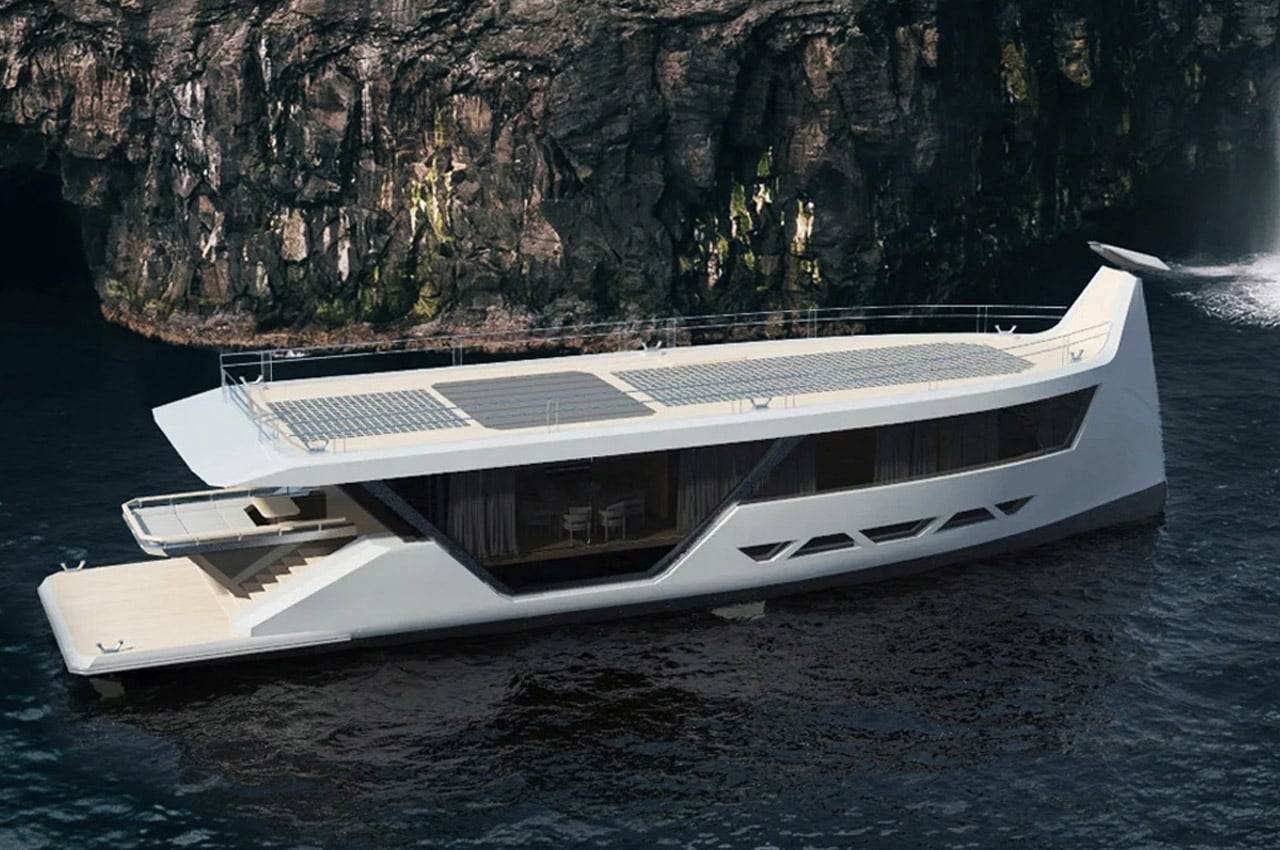

The designer has created the blueprint of the 85-foot superyacht dubbed Drakkar S inspired by the ye olde Viking longships, which’s perfect for newbie sailors who would rather prefer the autonomous luxury of a vessel. To make self-propelling possible, Drakkar S is infused with advanced autopilot and artificial intelligence systems for smart navigation – detecting any underwater obstacles or even estimating the ideal distance for mooring. Even more so, it can be controlled with a smartphone app – that just sets the tone for a future Apple yacht in Silver or even the Space Grey colors.
9. Estrella
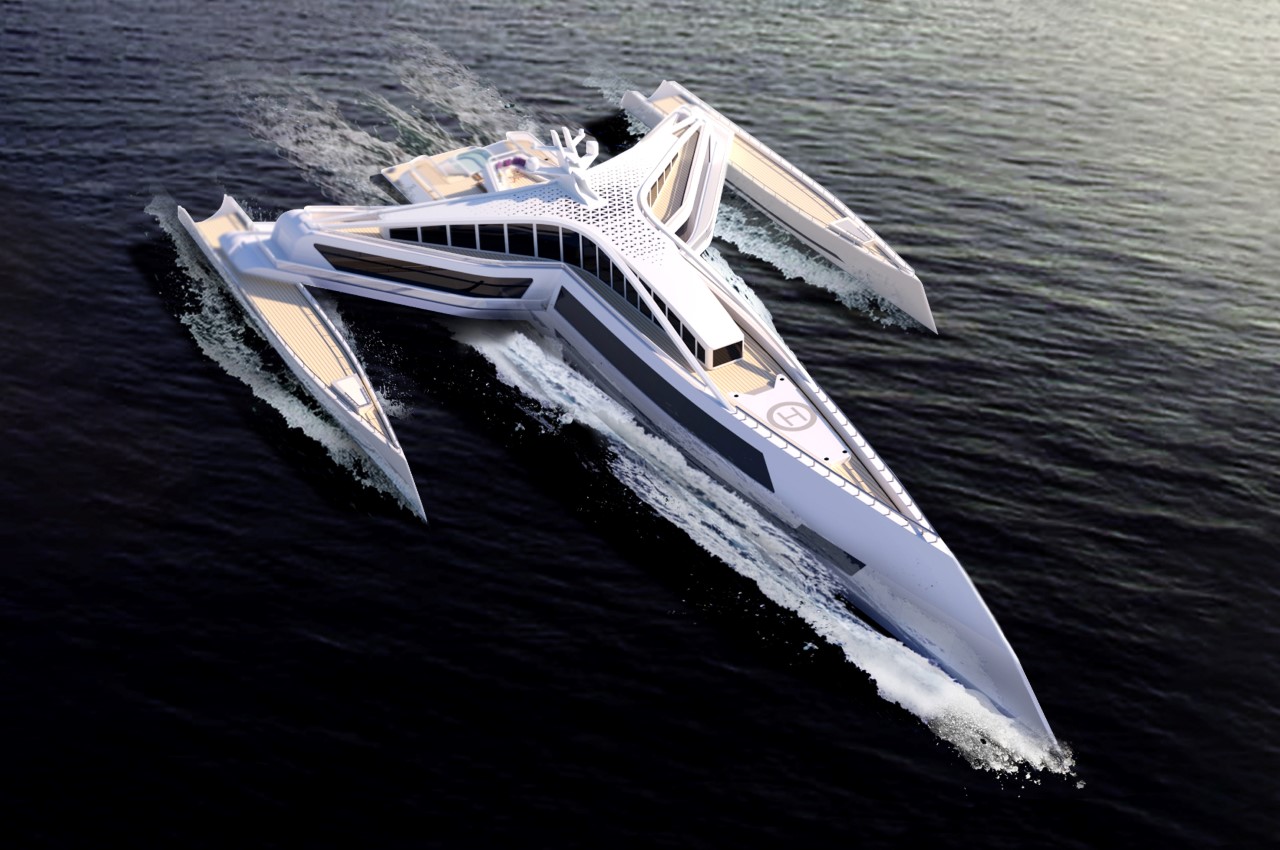

There are over 5,000 superyachts currently on this planet, however, none of them look as impactful as the Estrella . Designed by South Kore-based Yeojin Jung, Estrella hopes to break the mold of ‘boring’ practical superyacht design with something that’s a cross between feasible and outlandishly luxurious. Envisioned to look like the jewel of the seas, Estrella comes made for UHNWIs (or Ultra High Net Worth Individuals, as my sorry self just learned), and sports a split-hull design that divides the yacht into the main component, and two floater components on either side, reminiscent of a seaplane.
10. The Earth 300
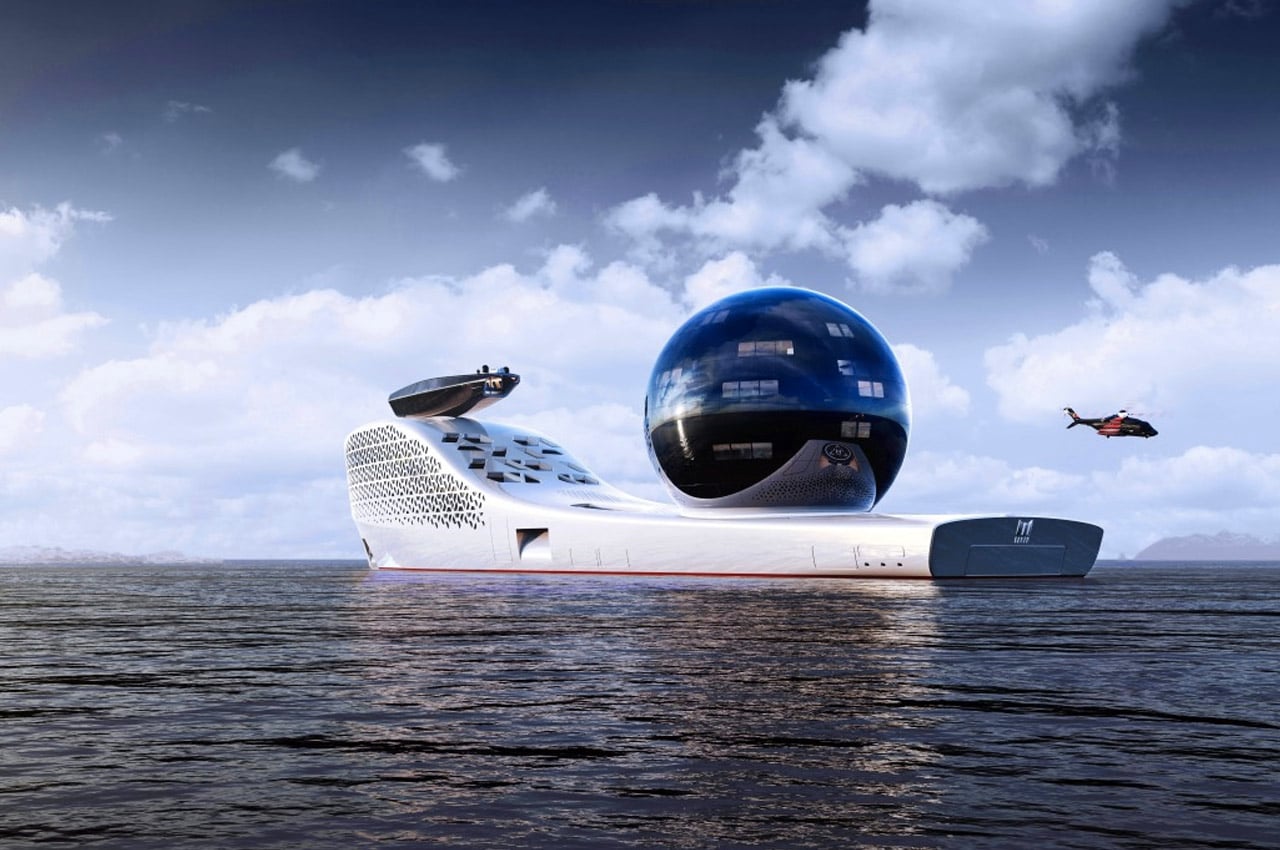

Designed to be 300 meters in length and capped with a 13-story-high ‘science sphere’ on top, the Earth 300 was conceptualized by naval architect Iván Salas Jefferson (founder of Iddes Yachts) as the torchbearer of global science, allowing us as a species “to expand our knowledge and understanding of the universe, both above and below the ocean’s surface.” It comes equipped with 22 state-of-the-art laboratories for research, a cantilevered observation deck, and has space for 160 scientists (along with dozens of other experts and student researchers), 164 crew members operating the vessel, and finally 40 additional slots for ‘VIP guests’. However, here’s the most impressive part of the Earth 300 vessel… it runs entirely on ‘clean’ nuclear energy.
Related Posts

Discover 10 Minimalist Must-Haves for a Stylish Labor Day
Labor Day is here, and it’s time to chill out, fire up the grill, and make the most of the holiday weekend. Whether you’re planning…

Heal your gut and Calm your mind with this pair of innovative wearable devices
Our health is the single most important investment we can make, but most people tend to take it for granted or are at a loss…
MINI Spaceman reinvents the legendary hatchback’s iconic status
The current generation MINI Cooper is a prime example of powerful engineering, compact size and superior handling. That classic British styling in a nimble package…

This concept Porsche was designed to be the last car you’d ever need to buy
The brief behind Ilya Zakharov’s Porsche Exclusive GT is simple. Make the car less of an impulse buy and more of a consciously purchased product…

Explore the unexplored in the adventure-driven, all-terrain ALD09 camping trailer
Arguably, the traditional image of camping and outdoor exploration is in a relay of evolution, and Georgia-based ROC Trailers is sharing the baton. To that…

This futuristic e-bike comes with a sleek design featuring hubless wheels and a fingerprint lock!
As this world takes to bicycling again (the pandemic has seen a surge in bicycle-use), the guys at Beno Inc want to finally get e-bikes…

- Charter & Brokerage
- Yacht Design & New Builds
- Tenders & Toys
- Superyacht Events Calendar
- Career & Training
- Departments
- Superyacht Crew Finances
- Sustainability
- Shipyards and Marinas
- Health & Wellbeing
- Polar Region
- Our Services
- Meet the Team
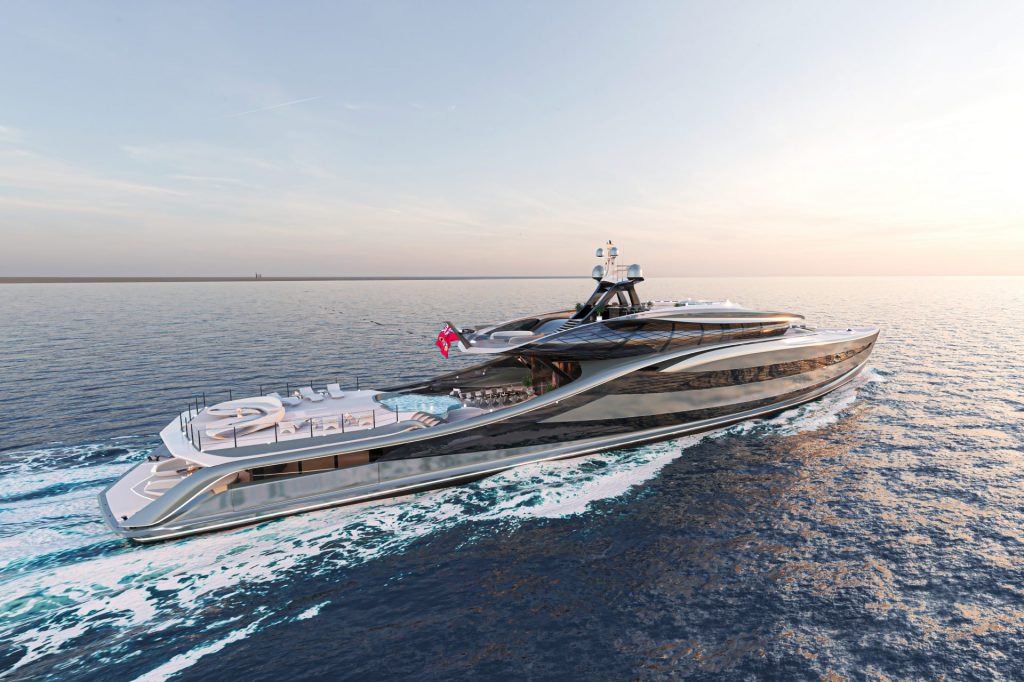
THE YACHT WITH A FUTURISTIC NATURE
.png)
For Dutch design studio Vripack , inspiration is all around; from a three-jointed bird’s wing to the powerful thrust of a shark’s tail. When the studio set about designing its latest concept, the 66m fossil-free Futura, the focus was to capture wildlife’s innate ability to freely propel through air and water.
“That’s the beauty of naval architecture,” says co-creative director Marnix Hoekstra. “First and foremost, you should mimic nature in the sense that you use as little energy as possible when crossing through the waves. We were driven by that goal from the outset.”
With sustainability at the fore, Futura is slender, efficient and supremely sleek – just a third of the height of a comparable 66m yacht. Her flowing, curvaceous lines denote an elegant femininity that draws from a collection of shapes found in nature. An aerial view of the cocoon-like superstructure reveals a streamlined bow and a rounded middle, like the silhouette of a whale. Made out of glass, the superstructure is also exceptionally lightweight thanks to Vripack’s engineering ingenuity that uses rhombus-shaped framing. The result is a cross-hatched diamond effect, much like fish scales.

“The superstructure, with its egg shape sliced onto a beautiful slender hull, is a concept that has been maturing in our minds for over a decade. Used with a biometric way of structuring, the result is lighter than traditional shipbuilding methods and something that is aesthetically beautiful, too,” says Hoekstra. “Additionally, the diamond shape has always been used by luxury brands, such as Louis Vuitton and Dior, so people subconsciously associate it with prestige.”
Organic shapes continue throughout the ergonomic flow of the interior. Designed as a ‘split and merge’ concept, Futura moves away from a traditional deck setup and uses human interaction as its source of inspiration. The result is a loft style, split mezzanine configuration that intertwines and interconnects – outside as well as in, upstairs as well as down, all through diagonal side-lines. And of course, the large expanse of glass used throughout introduces Vripack’s signature ‘shadow versus light’ aspect of interior design.
Modular furniture means each space is versatile and adaptable. An enormous 30-person dining table makes a bold invite to entertain, as does a DJ booth setup in the upper deck observation area, while a helipad, large shapely swimming pool and whirlpool tick all the boxes.
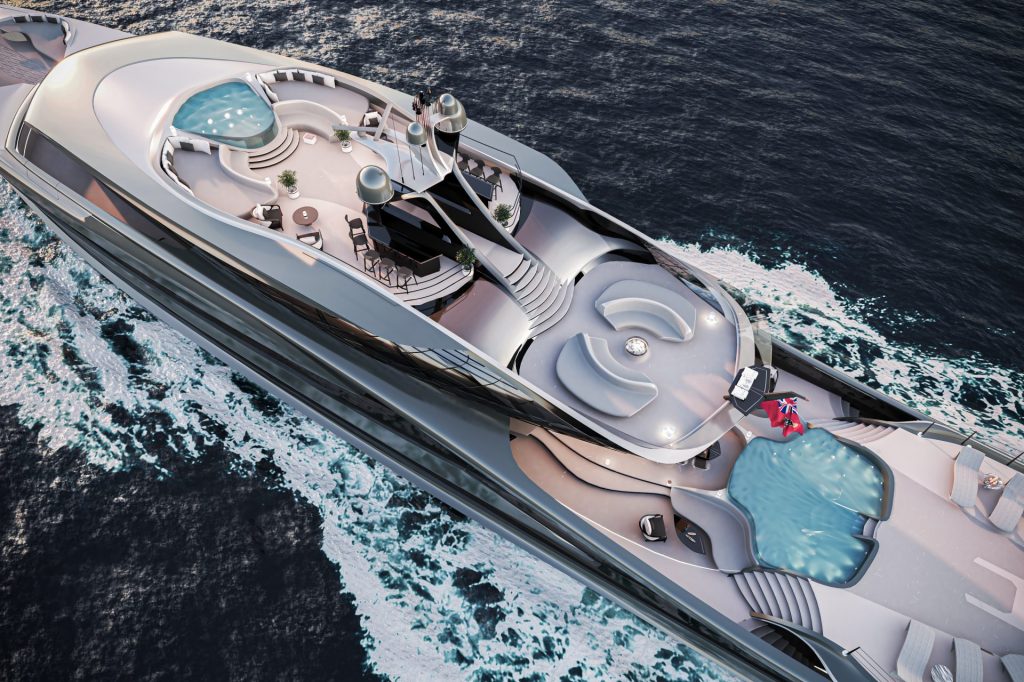

“The statement piece is a big crystal palace of glass, which is set neatly on top of the hull so you can see everything on the boat,” explains co-creative director Bart Bouwhuis. “In practice, this means that everybody on Futura can be doing their own thing, but you’ve still got this consciousness of where your family and friends are,” and because it was designed using virtual reality, adds Hoekstra, “we were able to combine an interior that is without compromise for the owner blended with an exterior that focuses on sustainability.”
Capable of holding 100,000 litres of fuel, Futura is an electric/diesel hybrid with a difference. Designed to run solely on ‘blue diesel’ if desired – a type of Finnish biofuel made from waste food currently being used in the trucking industry – it also possesses revolutionary bio-based batteries made from salt, sand, water and plants. Charged by an enormous kite on an electric winch that can be released at the touch of a button (an innovative means of harvesting energy formulated by Vripack in-house), the battery bank itself is 100% biodegradable.
“What Futura offers owners is choice,” says Hoekstra. “By approaching sustainability as a design challenge, we’re not waiting for owners to request this technology, we’re presenting them with a concept based on sustainable solutions that currently exist. The answers are out there, the supply is out there, owners just need to want it.”
With a portfolio that now represents over 7000 designs, Vripack has been able to evolve its processes to be as efficient and as effective as possible.
Julia Zaltzman
Related articles, he’s running (again). let’s look at donald trump’s superyacht history, it’s been a long ride but oceanco’s alfa nero finally has an owner, zeitgeist: the 86m futuristic-looking superyacht concept from kurt merki jr, “love from above”: ayss’ drone video competition for superyacht crew.

Popular Posts
- How Do Flag States Protect Yacht Crew?
- The Real Cost of Owning a Superyacht
- Superyacht Turnaround: 5 Tips And Hacks For Crew
- Environmental Officers
- Boundless Benefits Of Content Marketing In The Superyacht Industry
Superyacht Content
Social media influencer and digital brand expert.
Superyacht Content brings you the latest in social news for the superyacht industry.
Keep up to date with us across our social channels, and don’t forget to hit that share button!
- Superyacht News
- Superyacht Jobs
- Superyacht Marketing
Join our Newsletter
- Your Name First Last
- Your Email *
Copyright © 2023 Superyacht Content | Website Design by Zonkey
Privacy | Credits | Get in Touch
WallyWhy150 : un yacht futuriste aux larges espaces

WallyWhy150 - Le modèle réduit d'un superyacht futuriste | @abysyachting
Présenté en Première Mondiale lors du Venice Boat Show 2023, le WallyWhy150 est le dernier modèle de la ligne à semi-déplacement du chantier naval Wally, une marque du Groupe Ferretti. Lancé deux ans après le succès du fameux WallyWhy200, ce nouveau bateau est considéré comme son « petit frère », même s'il représente bien plus.
Le WallyWhy150 présente une évolution majeure. Ce yacht de luxe futuriste développe des idées pionnières dans la gamme, tout en embellissant les caractéristiques principales qui font la renommée de la marque. Avec un volume total de 150GT, il offre l'expérience unique d'être comme sur un yacht plus grand. Luca Bassani, Chef Designer et CEO de Wally, est reparti d’une page blanche, afin de créer une œuvre unique et mémorable. Découvrez un yacht futuriste de la gamme « SPACESHIP ».
WALLYWHY150 : Un yacht qui reprend les codes d'un superyacht futuriste
Pour Luca Bassani : « Concevoir un bateau identique au WallyWhy200, mais avec trois mètres de moins n’a pas grand intérêt ». Le WallyWhy150 est donc un yacht qui réexploite l’espace , avec une attention portée tout particulièrement aux zones extérieures. Le but étant de maximiser le plaisir à bord, en étendant les zones de loisir. L’espace de vie du propriétaire a également été redéfini.
Ce yacht de moins de 24 mètres offre des espaces que l’on ne trouve normalement que sur les yachts encore plus grands. En effet, les concepteurs ont puisé à travers une large gamme d’éléments, comme l’ajout de grandes baies vitrées du sol au plafond, afin d’inonder de lumière naturelle l’espace modulaire du salon principal. Pour cette taille, c’est aussi le premier yacht de la gamme à disposer d’une suite propriétaire, à l’avant .
Le WallyWhy150 est un bateau puissant . Il est équipé de 3 moteurs Volvo Penta IPS1200 de série de 1000 CV (IPS1350 en option), qui propulse une coque rapide et planante jusqu’à 23 nœuds, et de 2 stabilisateurs Seakeeper. Une disposition, qui lui assure ainsi un grand confort en navigation. Son autonomie est d’environ 4.000 miles (plus de 6.400km) à 20 nœuds, avec la motorisation la plus puissante.

Coque rapide et planante

forme signature en V, avec Master Cabin à l'avant

ZONES DE LOISIRS ÉTENDUES POUR PLUS DE PLAISIR

3 moteurs volvo penta de 1000 CV
Un design extérieur avec des caractéristiques uniques
Le WallyWhy150 a été conçu par le Wally-Ferretti Group Engineering pour le design extérieur, ainsi que le Studio A. Vallicelli & C , pour l'intérieur. Il est l’expression d’un nouveau style de yacht, désormais reconnaissable comme une forme signature des yachts Wally, notamment avec l'ajout d'un imposant T-top . La forme iconique de la coque en V lui donne également l'avantage, par rapport à ses concurrents, de maximiser son volume à bord.
Sur le flybridge, la terrasse est épurée et fonctionnelle. Une banquette en U est bien abritée par l'imposant T-top en carbone, et peut accueillir jusqu'à 8 personnes et 3 bains de soleil. Le T-top est l'u ne des pièces maîtresses sur ce modèle, dessiné bien avant la proue, et contribue à définir l'identité du WallyWhy150. La couleur vert foncé métallisé de la coque est un clin d'œil au WallyPower118, pour leurs similitudes à l'avant.
Le pont arrière, en contact direct avec l’eau, a entièrement été dessiné et reprend les codes d’un WallyTender. Le Beach Club est immense et entièrement équipé pour les repas, avec bar et plusieurs réfrigérateurs. Le poste de pilotage est accessible via à un petit escalier, légèrement déplacé en contrebas, de manière à ne pas gêner la vue.

Beach Club immense et entièrement équipé

T-TOP EN CARBONE AVEC BANQUETTE EN U
Un aménagement intérieur magistral, avec trompe-l’œil
Le CEO a souhaité un bateau qui soit pragmatique, où la circulation puisse se faire de manière fluide et naturelle , afin de rejoindre la mer le plus simplement possible. Pour cela, tout sur le WallyWhy150 est de plain-pied. De la plateforme de bain, en passant par le solarium et la salle à manger, jusqu’aux marches menant au salon, à mi-hauteur.
Sur le pont principal, la hauteur sous barrots atteint les 2,5 mètres pour la partie basse, chose peu commune pour un yacht de cette taille. L’espace reste modulable, avec un salon qui se sépare de la table à manger par des marches disposées de chaque côté. Cette conception permet au salon de se fondre parfaitement avec le cockpit, offrant une vue directe sur la mer.
Le plafond incurvé et en 3 dimensions donne l'effet d'être sous un dôme. Pour cette taille, c'est aussi le seul modèle à disposer d'une Master Cabin pleine largeur à l’avant, qui offre une vue à 270 degrés sur la mer . Un large lit est orienté également vers l’avant, pour un effet « amphithéâtre sur la mer ». L’accès se fait à tribord, le long d’un couloir entièrement vitré, ce qui donne l’impression d’être comme sur un balcon extérieur.

MARCHES DISPOSÉES DE CHAQUE CÔTÉ, qui SÉPARENT LE SALON DE LA SALLE À MANGER

Salon qui se fond avec le cockpit grâce à sa surélévation

Ambiance cosy et chaleureuse à bord

CONCEPTION DE PLAIN-PIED POUR UNE CIRCULATION FLUIDE ET NATURELLE jusqu'à la mer

Master Cabin avec vue à 270 degrés sur la mer

Accès avec un couloir entièrement vitré
Profitez d’un yacht polyvalent et adapté pour toute la famille, les couples ou les invités en charter. Le WallyWhy150 peut accueillir jusqu’à 8 invités dans 4 cabines généreuses. Deux grandes cabines peuvent loger jusqu’à 4 membres d’équipage. L’ambiance à bord est des plus cosy, avec des couleurs chaleureuses, de nombreux rangements et de larges penderies le long du mur. Soyez connecté à la mer, peu importe la pièce où vous vous trouvez. Pour en découvrir plus, retrouvez la fiche technique du WallyWhy150 .
Nos derniers articles

Retour Monaco Private Preview 2024
Découvrez quelques images du Monaco Private Preview 2024 du Groupe Ferretti, avec ABYS Yachting, Importateur Exclusif France. Des yachts de luxe incroyables...
Lire la suite

Cannes Yachting Festival 2024 : les yachts exposés
Ferretti Yachts, Pershing, Custom Line... Visitez en VIP avec ABYS Yachting. Voici tous les yachts exposés du Groupe Ferretti au Cannes Yachting Festival 2024.

Cannes Yachting Festival 2024
Vivez le Cannes Yachting Festival 2024 avec ABYS Yachting ! Sept premières spectaculaires vous attendent. Préparez votre visite avec notre équipe dévouée.
Trouvons ensemble votre yacht !
Nos experts yachting vous accompagnent pour trouver le bien correspondant à vos attentes.

Distributeur exclusif
Recevoir la newsletter

The global authority in superyachting
- NEWSLETTERS
- Yachts Home
- The Superyacht Directory
- Yacht Reports
- Brokerage News
- The largest yachts in the world
- The Register
- Yacht Advice
- Yacht Design
- 12m to 24m yachts
- Monaco Yacht Show
- Builder Directory
- Designer Directory
- Interior Design Directory
- Naval Architect Directory
- Yachts for sale home
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Explorer yachts
- Classic yachts
- Sale Broker Directory
- Charter Home
- Yachts for Charter
- Charter Destinations
- Charter Broker Directory
- Destinations Home
- Mediterranean
- South Pacific
- Rest of the World
- Boat Life Home
- Owners' Experiences
- Conservation and Philanthropy
- Interiors Suppliers
- Owners' Club
- Captains' Club
- BOAT Showcase
- Boat Presents
- Events Home
- World Superyacht Awards
- Superyacht Design Festival
- Design and Innovation Awards
- Young Designer of the Year Award
- Artistry and Craft Awards
- Explorer Yachts Summit
- Ocean Talks
- The Ocean Awards
- BOAT Connect
- Between the bays
- Golf Invitational
- BOATPro Home
- Superyacht Insight
- Global Order Book
- Premium Content
- Product Features
- Testimonials
- Pricing Plan
- Tenders & Equipment
Futureyachts
With new technologies and cutting-edge materials, the yachting industry is evolving rapidly to meet the needs of modern yacht owners, but what does the future hold for superyacht design? Discover the latest trends and read our in-depth interviews with yachting’s key influencers and disruptors.
From our partners
Sponsored listings, yachts for sale, latest yacht design features.

Yachts Conceptuels et Futuristes : Les Projets les Plus Audacieux


Une Nouvelle Ère de Conception Nautique
L'industrie nautique est en pleine révolution. Les designers et architectes navals repoussent constamment les limites de l'innovation pour créer des yachts qui ne sont plus seulement des moyens de transport, mais de véritables œuvres d'art flottantes. Ces yachts conceptuels et futuristes représentent l'avant-garde du design nautique, alliant technologie de pointe, esthétique audacieuse et durabilité environnementale.
L'Innovation au Cœur des Yachts de Demain
Les yachts conceptuels se distinguent par leur capacité à intégrer les dernières avancées technologiques. L'utilisation de matériaux composites ultralégers, de systèmes de propulsion hybride ou entièrement électriques, et de dispositifs d'automatisation avancés sont autant de caractéristiques qui définissent ces navires du futur.
Exemples de Projets Innovants :
Le yacht solaire autonome :.
Ce concept mise sur l'énergie solaire pour une navigation plus écologique, tout en offrant des espaces de vie luxueux et modernes.
Le Yacht Modulaire :
Adaptable à différentes configurations, ce yacht peut être reconfiguré selon les besoins de ses propriétaires, offrant une flexibilité sans précédent.
Le Yacht Transparent :
Utilisant des matériaux translucides, ce design permet une immersion totale dans l'environnement marin, offrant une vue panoramique imprenable.
Design et Esthétique : Un Mariage d'Audace et d'Élégance
Les yachts futuristes se caractérisent par des lignes épurées, des formes audacieuses et des aménagements intérieurs innovants. Les designers n'hésitent pas à utiliser des formes géométriques complexes, des surfaces vitrées étendues et des éclairages LED intégrés pour créer des ambiances uniques.
Un Engagement Vers la Durabilité
Au-delà de l'innovation technologique et esthétique, les yachts conceptuels s'inscrivent dans une démarche de durabilité. L'utilisation de matériaux recyclables, de systèmes de gestion des déchets intégrés, et de technologies de propulsion propres témoigne de l'engagement de l'industrie vers des pratiques plus respectueuses de l'environnement.
Le Futur des Voyages Nautiques
Posséder un yacht conceptuel n'est pas seulement une question de prestige, c'est aussi une expérience unique en son genre. Ces navires offrent des fonctionnalités et des commodités qui surpassent de loin les yachts traditionnels. Les espaces de vie ouverts, les technologies intelligentes et les options de personnalisation presque illimitées font de chaque voyage une aventure unique.
L'Expérience Utilisateur : Au-Delà de la Simplicité
Pour les passionnés de yachting et les amateurs de luxe, découvrir ces yachts conceptuels ouvre un monde de possibilités. Chaque détail est pensé pour offrir une expérience utilisateur exceptionnelle, que ce soit à travers des interfaces de navigation intuitives, des systèmes de divertissement immersifs ou des solutions de connectivité avancées. Les yachts conceptuels et futuristes représentent l'essence même de l'innovation dans l'industrie nautique. En combinant design avant-gardiste, technologies de pointe et un engagement fort envers la durabilité, ces projets audacieux ouvrent la voie à une nouvelle génération de yachts. Pour ceux qui cherchent à allier luxe, performance et respect de l'environnement, ces navires du futur sont le choix idéal. L'avenir du yachting est prometteur, et il est passionnant de voir comment ces concepts révolutionnaires transformeront les expériences de navigation dans les années à venir. En explorant ces yachts avant-gardistes, les amateurs de nautisme peuvent déjà entrevoir ce que sera la prochaine étape de leur aventure sur les mers.
Vous aimerez aussi :

Jeanneau Cap Camarat
Explorez notre gamme de bateaux Cap Camarat à vendre. Trouvez les meilleures offres et réalisez...

Cap Camarat 12.5WA NEW VERSION
Le Jeanneau Cap Camarat 12.5 WA Nouvelle Version incarne l'excellence de Jeanneau en matière de...

Technologies Innovantes Yachts - 2024
Explorez les dernières technologies intégrées dans les yachts de luxe, offrant un confort, une...

Vers un avenir écologique dans la construction navale
Explorez l'avenir de la construction navale écologique avec notre gamme de bateaux innovants....
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A Boat Designed to Be a Breath of Fresh Air
The creators of the latest vessel from Azimut Yachts went to great lengths to reduce its emissions, but even they won’t call it green.

By Ian Volner
Reporting from Milan
This article is part of our Design special section about water as a source of creativity.
In the middle of Milan Design Week last month, in the middle of the Bagni Misteriosi — a historic bathing complex in the Porta Romana neighborhood — the Italian luxury shipbuilder Azimut Yachts hosted an unusual exhibition. It was a celebration of the company’s latest offering: the Seadeck 6, which made its debut last year and features interiors by the design team of Matteo Thun and Antonio Rodriguez.
Having been lowered into the facility by crane, the nearly 60-foot vessel was set afloat in an outdoor swimming pool. There it bobbed, traversed by hordes of well-coiffed guests while a concealed apparatus shrouded it in bursts of atmospheric steam. Surreal, elegant, not a little absurd, it was a scene straight out of Fellini, with overtones of Werner Herzog’s boat-hoisting epic “Fitzcarraldo.”
But the thing that made it most unusual? “Azimut wanted to make this the most sustainable boat on the market,” Mr. Rodriguez said. “We tried to do that.”
The ultimate playthings for the ultrawealthy, high-end pleasure craft would not seem optimal candidates for greening. Yet a growing number of manufacturers and designers are trying to change that, producing yachts both large and (comparatively) small assembled from fewer and less carbon-intensive materials, requiring a fraction of the power to run and drawing more of their energy from renewable sources.
In a peculiar twist for an industry uniquely exposed to supply-chain shocks and the vicissitudes of geopolitics (the loss of the once-lucrative Russian market continues to smart), global brand leaders appear to be making the move toward energy efficiency of their own accord, rather than in response to any explicit demand from their clientele.
“We will have to see if the world is ready,” said Giovanna Vitelli, Azimut’s chairwoman, as she stood aboard the Seadeck 6 during its not-quite maiden, not-quite voyage.
It is an approach that entails some risk. In January, Silent Yachts — an Austrian solar-electric catamaran company with facilities in Fano, Italy — was reported to be approaching bankruptcy amid problems with both its corporate parent and a key subcontractor. A former client stepped in to rescue the brand from insolvency, yet challenges remain. In a recent interview with the trade publication Superyacht News, the company’s new chief operating officer, Fabrizio Iarrera, spoke of the “costs associated with creating an entirely new market.”
Still, the push toward more sustainable yachting appears to be barreling forward, part of a broader shift in the role of design in the industry. Seven years ago, Bonetti/Kozerski Architecture in New York — known for its plush hotel interiors for the hospitality magnate Ian Schrager — was invited by Azimut’s sister company Benetti to develop a new yacht concept, the Oasis. It was one of the rare instances in which Benetti, founded in 1873, had sought out collaborators with no previous maritime experience, and all parties took it as an opportunity to import a set of values they viewed as lacking in the boating world.
According to Enrico Bonetti, the architecture firm’s co-founder, boat design previously favored grand spaces that no one actually liked. “There’s always this big table nobody’s using, then you step into another place with shiny things,” he said. “We didn’t follow that.” With its open, airy living space, wood paneling and notable lack of gold leaf, the Oasis represented a more humane vision for the yacht of the future, one constrained by at least the appearance of refinement and reserve, though it was ritzy nonetheless.
That low-key tendency is very much in line with the decarbonization campaign now underway at Azimut and other builders. In recent years, design studios like Zaha Hadid Architects and Pininfarina have turned out yacht proposals that pair sleek visuals with reduced reliance on fossil fuels; later this year, Yves Béhar, the Swiss-born product and furniture maestro, will unveil his own take on the trend — a catamaran designed for an as-yet unnamed manufacturer. “It’s essentially an E.V.,” said Mr. Béhar, who was also in Milan for the design fair.
Underlying the designer eco-yacht phenomenon is the intuitive sense, as Antonio Rodriguez put it, that “silent luxury” is fast displacing opulence. Where previous generations of yachters sought to flaunt their wealth, today’s owners may be less keen to draw attention to their own affluence. In reducing their carbon footprint, boatmakers are hoping to lure customers eager to reduce their profile, while still allowing them to ply the seven seas in style.
The Seadeck 6 certainly does that. With a crisp, white exterior — the work of the veteran yacht designer Alberto Mancini — the ship sleeps up to eight in three below-deck cabins. Topside, guests can sprawl in fore and aft lounges, or take lunch prepared in a semi-concealed galley, served on an elegant foldout table. The interior palette is muted, the contours soft, and everywhere, Ms. Vitelli said, the intention was to let people “feel close to water” rather than immuring them in an oceangoing penthouse.
Relatively speaking, the Seadeck’s ecological credentials are also impressive. Nearly every feature has been retooled for minimal environmental impact: replacing the customary teak deck with sustainably sourced cork; covering the walls and upholstering the seating with organic and recycled materials; even sealing the hull with something the company refers to as an ‘eco-gel finish.’” Most important, the craft incorporates a still-novel (for marine propulsion) hybrid engine, capable of a top speed of 33 knots with the ability to navigate about 200 miles offshore — enough for a quick spin from Fort Lauderdale to the Bahamas.
Add it together, and the company claims the Seadeck 6 and its larger cousin, the 71-foot Seadeck 7, achieve an operational carbon output 60 percent that of comparable vessels.
It’s a start, but only that. A comparative analysis with a similarly sized Azimut product — coupled with statistics from the Environmental Protection Agency — suggests that the cruise from Fort Lauderdale to Nassau would contribute roughly 4,400 pounds of carbon dioxide on the Seadeck 6, well over what the average American produces in a month.
And then there are the more immediate costs: around $2.8 million for the Seadeck 6 and $4.25 million for the Seadeck 7. Ms. Vitelli said the company hopes that enough buyers will come aboard to make price reductions possible in future.
A lot is riding on these hopes. Elsewhere in Milan, at the giant exhibition hall of the Salone del Mobile furniture fair, a talk session with a group of yacht experts underscored the stakes: During the panel, Stefano de Vivo, the chief commercial officer of the luxury yacht brand Ferretti Group, presented a slide showing Italy’s dominance in the custom-yacht sector, with domestic manufacturers taking a large share of the $9 billion global marketplace.
Mr. de Vivo declared sustainability essential to shipbuilding’s ongoing success and spoke of a general convergence with the design field at large. “As a shipyard, we’ve had to become less ‘marine,’” he said.
Back at the Bagni Misteriosi, mariners did seem in somewhat short supply, as various design lovers and Salone personalities (including the celebrated architect Michele de Lucchi, who helped create an on-site installation for Azimut) swanned around the bathhouse garden and its waterborne centerpiece. As an image of an ecologically sensitive future, the spectacle seemed off the mark — but then the Seadeck’s creators are careful not to make any overly sweeping claims as to whether their yacht, or any yacht for that matter, can truly be deemed an ecological asset.
“We don’t really like the word ‘sustainable,’” Mr. Rodriguez said. “We prefer to say it’s ‘conscious.’”
Explore Our Style Coverage
The latest in fashion, trends, love and more..
The Korean Cheerleaders Flooding TikTok: Videos of baseball cheerleaders performing an ultra-chill dance routine have taken over social media algorithms, intriguing millions of viewers.
Throwing an Egg Birthday Party: Frozen egg showers have become common on social media, but a Brooklyn woman has gone a step further by throwing her eggs a birthday party every year.
The Rise of the Husband: Much has been made of a new masculinity in this election cycle, but the biggest public transformation for men might be the role of the husband.
Does Alexa Chung Still Have ‘It’?: She calls herself a “geriatric ‘it’ girl.” The brand Madewell calls her an “original muse.” Just don’t call this look “indie sleaze.”
More Than a Lingerie Shop: For more than 90 years, Peress on the Upper East Side served socially ambitious women , including Brooke Astor, Gloria Vanderbilt, Diana Vreeland, Barbara Walters, Madonna and many more.
A New Generation of Club Kids: In New York, dance spots for tots and techno heads alike are thriving , with veteran D.J.s, oversize headphones and zero “Baby Shark.”

NORDIC TUGS
NORTHERN MARINE
BULLFROG BOATS
MY YACHT WORTH?
- USED YACHTS
FEATURED LISTINGS
YACHTS BY BUILDER
YACHTS BY LOCATION
YACHTS BY TYPE
WHY LIST WITH US
- BUYING A TRAWLER YACHT
- TRAWLER BOAT BUYER'S GUIDE
FT LAUDERDALE
MARINA DEL REY
SAN FRANCISCO BAY
VICTORIA B.C.
- SERVICE - PNW
FLOTILLA EVENTS
SEATTLE SAILING ACADEMY
- JOIN OUR TEAM
2018 Bertram C7.1 500HP
Boat Name: "GRIS GRIS"
GRIS GRIS is a 2018 Bertram C7.1 500HP currently available for sale in Fort Lauderdale Florida. This boat has a price of $640,000. Our team at Seattle Yachts is here to help you find the right boat for your needs, budget, and style. We have access to boats off the market that will never be seen online, so contact us today with your interest.
Price: $640,000

SPECIFICATIONS
| Price: | $640,000 |
| Boat Name: | GRIS GRIS |
| Make: | Bertram |
| Model: | C7.1 500HP |
| Year: | 2018 |
| Condition: | Used |
| Category: | Sport Fishing |
| Construction: | Fiberglass |
| Length: | 35 ft |
| Display Length: | 35 ft |
| Beam: | 12 ft 3 in |
| Max Draft: | 2 ft 9 in |
| Min Draft: | -- |
| Fuel Capacity (Gallons): | 310 |
| Fuel Type: | Diesel |
| Fresh Water Capacity (Gallons): | 50 |
| Max Speed: | 35 kn |
| Displacement: | 19 |
| Number of Engines: | 2 |
| Engine Make | Caterpillar |
| Engine Model | C7.1 Turbo charged |
| Engine Power | 507.00 HP |
| City: | Fort Lauderdale |
| State: | Florida |
| Country: | United States |
GRIS GRIS is a contemporary interpretation of a timeless Bertram design. It pays homage to the iconic Bertram 31 while incorporating modern luxuries and maintaining the brand's commitment to quality. With a wider and longer hull, this Bertram 35 offers enhanced fishing capabilities and can be fully equipped for fishing expeditions.
DETAILED SPECIFICATIONS
NOTEWORTHY FEATURES AT A GLANCE
• Seakeeper 6
• Garmin electronics
• Touch screen cat digital display
• Varnished, high-gloss helm pod with palm beach controls
• Rupp single spreader outriggers
• Pompanette Fighting Chair
MAIN CHARACTERISTICS
Name: GRIS GRIS
Type: Flybridge Sportfish
Builder: Bertram
Year (Model/Built): 2018 / 2017
Yacht Model: Bertram 35FB
LOA: 35’1” 10.69m
LWL: 31’5” 9.58m
Beam: 12’3” 3.73m
Draft: 2’9” 0.84m
Transom Deadrise: 21﮿
Seakeeper: 6
Hull & Superstructure Material: Fiberglass
Hull Configuration: Planing
Classification: Private
Main Engines: Twin 507 HP CAT C7.1, turbo charged. 600 hours (Dec. 2023)
Max Speed: 27 knots
Cruising Speed: 35 knots
Range: 310 nm @ 1,200 rpm (10kn)
Accommodations: 2 guests in 1 cabin
Gross Tonnage: 19 GRT
Net Tonnage: 15 NRT
Displacement (Full Load): 22,631 Lbs (10.27 MT)
Displacement (Dry): 17,937 Lbs (8.14 MT)
Fuel Capacity: 310 Gal (1,173 L)
Fresh Water Capacity: 50 Gal (189 L)
Waste Holding Tank: 30 Gal (114 L)
HULL & DECK CONSTRUCTION
• Flag Blue gel-coated hull
• Red painted boot stripe
• Hull infused using vinylester blend resin with solid fiberglass bottom and cored sides. Keel and strakes are reinforced with Kevlar.
• Molded, yacht-finish, sand-texture non-skid gelcoat on deck surfaces
• Teak Sole
• Deck and FRP components molded vinylester blend construction
• Hatches and doors with FRP liners
• Heavy-duty white vinyl rub rail with solid stainless insert and end caps
• Anti-fouling bottom paint
• Commissioning kit
HELM STATION AND FLYBRIDGE
• 3X Pompanette P2000 helm chairs
• Palm Beach style engine controls with
• integrated bow thruster controls
• CAT Marine 7” color display
• Molded footrest
• 2X waterproof JL Audio speakers
• Stainless steel steering wheel
• Drink box and storage compartment with drains
• USB outlet
• JL Audio Sound System Source Unit
DECK & COCKPIT
• Anchor with chain and rode accessed from foredeck
• Custom stainless steel bow chock
• Self-draining anchor locker
• Stainless steel bow rail
• Stainless steel flybridge ladder with teak steps
• 8X cleats: (2X 10” cleats at the bow, 4X 8” spring pull up style cleats, 2X 12” stern cleats with hawse pipes)
• Cockpit (port/stbd) under-gunwale storage with doors
• Tinted frameless tempered glass house windows
• 2” diameter fuel fills (port/stbd) and 1 ½” diameter water fill and 1 ½ diameter dockside pump out
• Foredeck hatch 19” with screen
• Port/stbd removable fish boxes in cockpit with macerators for each. Lids supported and gasketed with compression latches
• LED courtesy cockpit lights
• Power actuated engine room hatch with external jumper power studs, removable pin and manual service lift point
• Transom door with separate integral top gate
• Transom live well with aquarium view
• Rod holders (4X each in gunwale)
• 12-volt electric reel sockets in cockpit under gunwale
• Raw water washdown
• Freshwater washdown shower with hot/cold functions
• Engine box cushions with removable headrests
• Sliding white powder-coated aluminium salon door
• Frameless port/stbd aft salon windows
• 4X fender hangers, stainless-steel flush mount
SALON AND GALLEY
• 120-volt AC GFCI receptacles
• 16,000 BTU air conditioning (reverse cycle heat) with sound shield
• Amtico teak and holly flooring
• LED lighting overhead with dimmer switches
• LED indirect lighting
• Large U-shaped seating with teak dinette table (converts to berth with filler)
• Large overhead rod locker storage
• 120-volt AC double drawer Sub Zero drawer refrigerator/ freezer with ice maker and sea catches
• Two-burner induction cooktop
• Designer cabinets with soft close mechanism
• Solid surface countertop with custom stainlesssteel sink and hot/cold faucet
• Microwave oven
• Subwoofer, amplifier, and 2X JL Audio speakers
• USB outlets
• 120-volt AC GFCI receptacle
• Offset queen berth with large access to integrated storage beneath
• Nightstand with solid surface top and stainless-steel grab rail
• Cedar-lined hanging locker. Door converts
• to privacy feature for stateroom
• Designer cabinets with soft close mechanism
• Custom mattress with spread and shams
• LED overhead lighting with dimmer switches
• HD 24” TV with digital antenna
• LED overhead lighting with indirect on dimmer switches
• Designer cabinetry with soft close mechanism
• Corian countertop with porcelain sink
• Contemporary swivel and tilt faucet with hot/cold
• Exhaust blower
• Macerating marine toilet (freshwater) with key operated overboard discharge and dockside pump out
• Flexible handheld shower head with hot/cold water
• Air conditioning vent
• Automatic shower sump
ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS
• 50-amp shore power with 30’ shore power cord
• 12/24-volt main distribution panel with voltmeter, generator controls,
• magnetic circuit breakers and shore power selector switches
• 24-volt Mastervolt battery charger
• LED light fixtures on dimmers
• Vimar outlets and switches
• Alarm monitor panel with bilge flood signal for three compartments
• Flybridge main engine control panel
• 6X AGM heavy-duty batteries (4X house and 2X starting batteries)
• Bonding system with galvanic isolator
• Navigation lights, LED incorporated into the bridge
• NMEA2K digital network
• Digital fuel transfer control at helm
MECHANICAL SYSTEMS
• Twin 507 mHP CAT C7.1, turbo charged main engines with vibration dampening isolators, twin disc gears and controls, engine driven alternators, dual racor filters and custom exhaust. 600 hours (Dec.2023)
• Seakeeper stabilizer
• 24-volt bow thruster
• Electronic engine controls
• Oil change system
• Engine room intake and exhaust blowers with demister
• Engine room sound absorption insulation
• Isotherm 6.5-gallon electric water heater
• Aquamet 22 shafts 2” diameter
• High-performance rudders and struts
• Engine and machinery room LED lighting
• 2X heavy-duty aluminium epoxy-coated fuel tanks
• Fixed fire suppression system for engine and machinery spaces with emergency engine shutdown system plus audible and visual discharge indicators
• Seastar Optimus EPS hydraulic steering, power assisted
• Bronze seawater strainers for generator, air conditioning and raw water pumps
• Bronze seacocks on all underwater thru-hull fittings
• Bilge pumps (3X @ 2000 gph) automatic/manual
• 7.1 kW Mase generator with sound shield
• Grey water sump with automatic discharge for head shower and sink
• Electric trim tabs with zincs
• Hull zinc, recess transom mounted
• Bottom paint with epoxy primer coat
• Roto-molded 28-gallon holding tank with level indicator, electrical pump-out and plumbed for dockside pump-out
• Pressurized freshwater system with regulated dockside freshwater supply
• Roto-molded 48-gallon freshwater tank equipped with level indicators
NAVIGATION ELECTRONICS
• Dual Garmin 7616XSD MFD with built in 1 KW sounder,
• Caterpillar interface
• Garmin 424 XHD 2 Open Array (4ft) Radar.
• External 19x GPS antenna.
• Garmin reactor Autopilot.
• GRID Remote Input Device.
• Pocket keel mounted Chirp Transducer B275C
These particulars have been prepared by us from information provided by the sellers and are intended as a general guide to the vessel. We cannot, however, be liable for any inaccuracy. It is up to the purchaser to confirm details of concern to him by survey, inspection and/or enquiry of the seller and to ensure that the purchase contract properly reflects his concern and specific details upon which he may rely. We always advise an independent survey.
Listing MLS by Yachtr.com
For more information on this yacht, please contact us..
SIMILAR BOATS

Yachting World
- Digital Edition

The future of yachting: Smart technology for your next yacht
- Toby Hodges
- May 14, 2020
Could hydrogen-powered yachts be built from rocks or plants in the next decade? Toby Hodges investigates yachting’s eco future

It’s becoming abundantly clear that to meet greenhouse gas emissions targets set out in the 2016 Paris Agreement, we’ll need to adopt some radical changes in all lifestyles. Thankfully sailing is, by its very nature, a green activity. In fact, if you wanted to live as carbon neutral a lifestyle as possible, move onto a yacht and go sailing! But for how much longer will we be able to buy glass reinforced plastic boats, powered by diesel engines ?
When you consider the energy, materials and waste in composite boatbuilding, it can paint an ugly picture. Ironically, the best way forward might be to revert back to building wooden yachts with hemp ropes and cotton sails, but that is perhaps not the most practical answer to supplying today’s global boating demands.
However, researching this feature has filled me with optimism. There are brilliant minds working in the marine industry and many fascinating solutions for alternative materials and power sources. So how might eco-tech change boatbuilding in the next ten years and what will your next yacht look like?

This hydrogen electric cat is midway through build at Daedalus in North Carolina
The simple solution
Technology will continue to make yachts ever simpler to operate. The ability to go daysailing easily will be critical for an increasingly time-poor generation, while powerboaters drawn to the eco credentials of sailing will seek an intuitive format, in yachts that are easy to rig, dock and manage.
Boatbuilders are progressively incorporating greener propulsion and sustainable power sources, and are turning to natural and recyclable materials. Whether they are regulated to do so or not, this is a logical step to take, especially if we, the buyers, demand a more ethical product.
In the next decade we’ll certainly see a marked increase in the use of 3D printing in boatbuilding. Already employed for custom parts, this technology could be used to build hulls and decks – printed structures with natural fibre skins surrounding them could eliminate the need for wasteful moulds.
Article continues below…

4 eco-friendly improvements to upgrade your yacht
1. Ditch the teak Teak is no longer universally popular. The price has gone up dramatically, supply is dwindling, and…

How hybrid sailing yachts finally became a feasible option
Every sailor is familiar with the wet cough of the diesel engine, and the acrid smell of its exhaust. For…
There are already bodies in place concentrating on the reduction of waste and energy use in boatbuilding, while promoting recycled and low-impact materials. 11th Hour Racing is doing commendable work here. The common boatbuilding technique of using hand laid-up polyester certainly looks increasingly endangered.
Search for speed
The most effective way to minimise your carbon footprint afloat is to sail, so there is a strong argument for choosing performance yachts , which can harness the wind more efficiently. Large yachts and catamarans have an advantage too as they provide the deck space to host numerous solar panels and the speed to incorporate regenerative propulsion.
During its research for the Outremer 4E project, and new 55, Grand Large Yachting found that the usage of a yacht accounts for a much higher carbon footprint than its build. If you are able to sail in five knots of wind, then you can sail 95% of time in the Mediterranean, it says (data from western Med June-September).

Outremer’s 4E prototype will be used by cruising guru Jimmy Cornell for his next circumnavigation
To achieve this performance requires minimising weight, but what are the best alternatives to using the traditional high strength-to-weight ratio synthetic fibres such as glass and carbon?
Basalt fibre has long shown promise and is being used by new French catamaran brand Windelo to build its hulls, with PET (recycled plastic bottles) cores. Basalt is transformed from volcanic rock (with minimal CO 2 emissions), so the fibres are particularly resistant to heat and are recyclable.
However, it is the fibres from plants that could offer the most potential for boatbuilding. Flax in particular, the plant from which linen is derived, looks like becoming one of the most effective alternatives for use in high-strength composite applications.
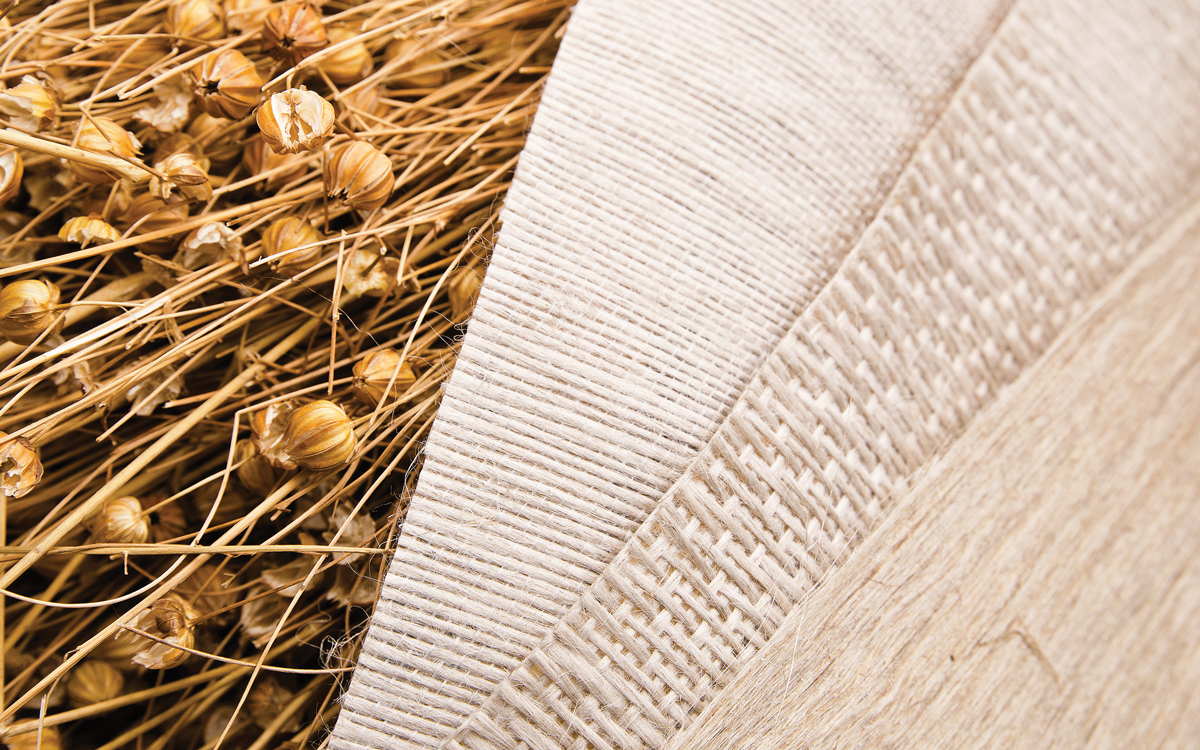

Natural promise: Linen fibres are derived from quick-growing flax plants
Boats from plants?
The flax-based products of Swiss company Bcomp have already been used effectively in motorsport bodywork and snow skis for their combination of stiffness and vibration damping.
Paul Riley, a composites expert now marketing Bcomp products for marine use, says that flax is lighter than glass fibres, with similar stiffness and significantly lower cost than carbon fibres, yet with up to 75% CO 2 savings. “I think we’ll see this coming into mainstream yachting in the next two to three years,” he says. “Manufacturers need to take a stand and switch to less environmentally impactful materials, which will also provide improved health and safety for their workers.”
Flax grows from seed to crop in eight weeks, rarely needs irrigation, and chemicals are not required. Thus far it has been used by German yard Greenboats, including on the 2016-built GreenBente 24, and superyacht builders Baltic Yachts. News that Gurit, global leader in composite material supply, will be the worldwide distributor for Bcomp, could lead to a broad adoption by marine manufacturers.

A Tesla Model S electric race car clothed in Bcomp flax composite bodywork
Visitors to the Düsseldorf Boat Show this year may have seen the potential of this fibre on the Greenboats stand. Its Judel/Vrolijk-designed Flax 27 daysailer became a test-bed for numerous natural and recycled materials. The hull is made from flax and bio resin with a PET core, the deck from cork.
Greenboats’ founder Friedrich Deimann told me how frustrated he became with using composite materials, especially coming from a wooden boatbuilding background. “It takes five times as much energy to produce glassfibre than linen fibre,” Deimann reports, showing me the plants from which he built his beautiful clear-coated daysailer.
Greenboats has been using Flax or Natural Fibre Composites (NFC) since 2010. And it minimises the use of moulds by using a stitch-and-glue technique to build panels. Deimann’s company shows what is possible, but he admits a lack of trained personnel and the costs of small-scale production are the current issues.

The Greenboats Flax 27 daysailer has a hull made of linen fibre and bio resin with a core of recycled plastic bottles
Another is resin control. “You can’t use hand lay-up with flax because it’s a natural material, and without compression the fibres can absorb a lot of resin,” says Deimann. “By vacuum-infusing the resin, you compress and control it.” Vacuum-infusing resin brings its own environmental issues because the plastic used in the bagging process creates a significant amount of landfill. Some boatbuilders have already found a clever solution here in reusable silicone bags.
But the resin itself still remains an issue for chemists to solve. Pure bio resins exist already, but for the high-performance epoxies required in boatbuilding the natural content might only be around 30%. Entropy resins, bio-epoxies used in marine, snow and surfboards for example, are manufactured by replacing petroleum-based carbon with renewable plant-based carbon – by-products from the agricultural industry.
Recyclable boats
Elsewhere, yards have been forging ahead with various technologies that offer a cleaner end of life potential. The hull of the mini 6.50 raceboat Arkema 3 was made from a recyclable thermoplastic composite using Elium acrylic resin, for example, which can be ground down and reused to manufacture new parts. And many RS dinghy hulls are made from rotomoulded and recyclable polyethylene.

Meanwhile, the benefits of using high-tech timber construction are clear for all to see thanks to Spirit Yachts . Its strip-planked technique makes for a very stiff, lightweight structure, with hulls made from largely renewable materials. Indeed, the beautiful new Spirit 111 flagship is being labelled as one of the most environmentally friendly superyachts ever.
Managing director Nigel Stuart has instigated a network of green initiatives at the Ipswich yard and in its yachts. The Spirit 111 includes energy-saving appliances throughout, including ultra-efficient hydraulics and genset, and a regenerative propulsion system for its Torqeedo electric drive.
And it is this latter element – power – that will surely be the primary focus for making cruising yachts greener in the coming decade.
Going electric
Torqeedo and Oceanvolt have led this drive so far, with Volvo Penta now ramping up its electromobility technology. And although Torqeedo has already delivered 100,000 electric drives, this represents only a small fraction of the market, according to CEO Dr Christoph Ballin.
“So far, only about 1.3% of marine propulsion systems are electric… we need to put the foot down and do more,” he states. Over the next decade, Ballin sees serial hybrid power as the optimum solution for yachts, systems that involve a large battery bank with a mix of solar and hydro power generation. This reduces the CO 2 footprint by around 90%, but with the safety net of a ‘diesel range extender’ – a compact generator, says Ballin.
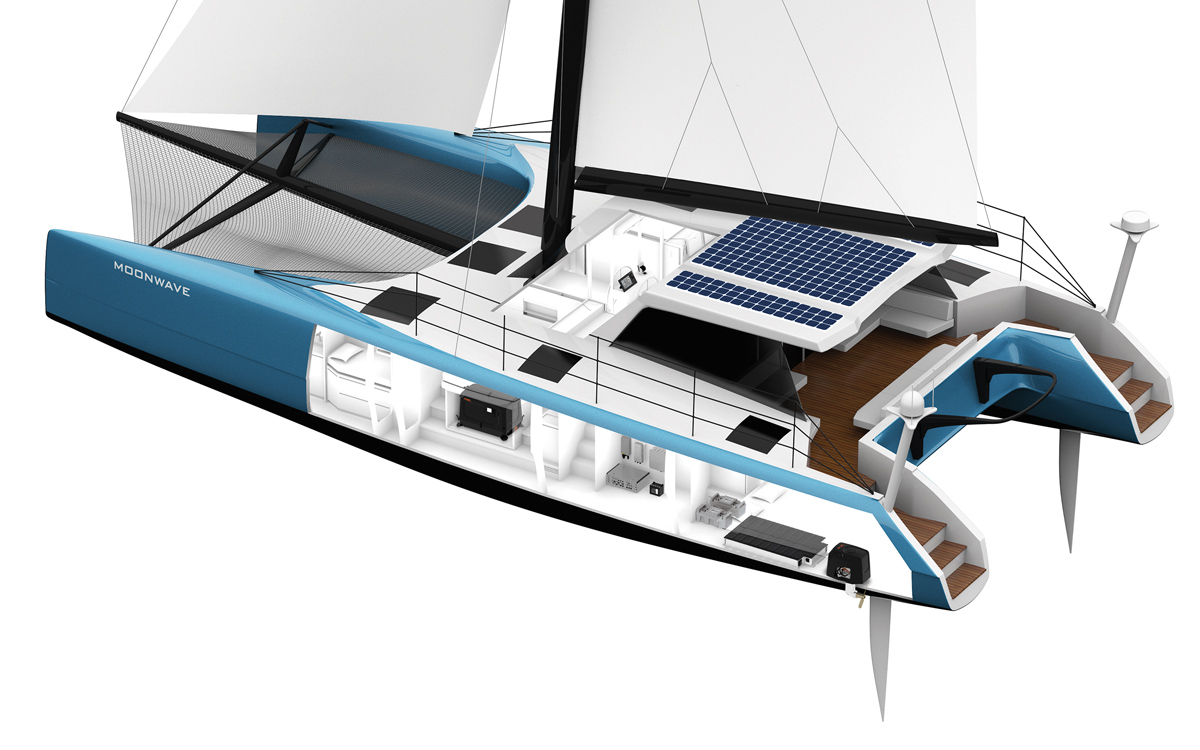

Moonwave is a Gunboat 60 recently refitted with the latest generation of Torqeedo’s Deep Blue electric drive system
Such a system caters for normal sailing and living requirements using only battery power. “The role of the generator is reduced from providing everyday energy for living on board (heating, cooking, washing, aircon) to emergency use, if you will. And the role of the combustion engine for driving the boat is completely eliminated.”
But what about hydrogeneration? Combined with enough solar panels, surely this will enable us to dispense with fossil fuels on board altogether? “I fully agree, hydrogeneration in terms of using the propeller to create power under sail is one thing that is here to stay,” Ballin believes.

ZF steerable saildrives are being integrated with Torqeedo systems for hydrogeneration
But it is dependent on the speed and size of the vessel. He points out that if you have a fast boat you can generate all the electricity you need while sailing: “We have a customer with Gunboat 60 which generates 10-15kW”.
Battery storage
“The limitation here,” points out Ballin, “is how much energy you can store in a battery, because of the energy density that batteries offer.” Torqeedo’s Deep Blue technology and use of BMW’s i3 high voltage lithium-ion batteries gives it an edge on competitors.
But is the reliance on lithium boat batteries as a ‘clean’ source of energy storage simply solving one problem by adding another? The questionable mining ethics surrounding the cobalt used in many lithium batteries has been widely reported and the question of battery recycling still remains unanswered.
Ballin foresees supply chains becoming more ethical from a human rights standpoint. He explains that BMW is now controlling the entire supply chain for its batteries, including sourcing the raw materials, to avoid inhumane working conditions.
This makes for another whole topic, as does the recycling issue, to which Ballin alludes to the potential for a second life for marine batteries in powerwalls and energy storage before they go into any recycling for cobalt extraction.
“We are in front of the largest mobility revolution since the introduction of combustion engines,” Ballin states. “We have to live with the fact that the stages in this transformation programme are all imperfect – and will be for more than ten years.”
Looking ahead, Ballin sees three key scenarios for what is possible for climate neutrality on boats: battery electric vehicles; hydrogen-power; and synthetic fuels. “The rule for sailors I think will be that wherever battery electric vehicles are feasible those are the preferred ways to go forward.
“If battery electric vehicles do not give you enough power, which is almost always the case for oceangoing vessels, then you can go to hydrogen for example… It will become mainstream to have a climate-neutral range extender.”
Hydrogen power
So could hydrogen be the holy grail of energy for yachts? Hydrogen fuel cells work by converting hydrogen (from seawater) to positive and negative electron charges. So far this process has been used as an energy source only by a few pioneering vessels, including Energy Observer , the first energy autonomous hydrogen boat to circumnavigate. And Race for Water , a solar and kite-powered multihull carrying a conservative amount of hydrogen (200kg) in 25 bottles, is currently three quarters of the way round the world.
Solo racing sailor Phil Sharp has been demonstrating a hydrogen fuel cell in place of a diesel engine to generate power aboard his Class 40 OceansLab . He believes larger scale commercial shipping and marine craft can adopt the technology to reduce their carbon emissions to zero.
For leisure yachts, however, hydrogen fuel cells are not yet economically feasible. Torqeedo’s Ballin explains the practical limitations: “The energy density of hydrogen per kg is a lot better than petrol or diesel, but the volumetric energy density is about 1/13th of diesel.” This means much larger fuel tanks are necessary – although these volumes can be reduced under pressure.
That helps to explain why hydrogen has been adopted by only a handful of (large) yachts thus far. A pioneer of the technology is Daedalus Yachts, which is midway through building the first hydrogen-powered superyacht. “Over the past two years we have conceived and developed not only a complete hydrogen electric marine propulsion system but also a clean energy micro grid with the only emissions being oxygen and pure water,” says Daedalus’s founder Michael Reardon.
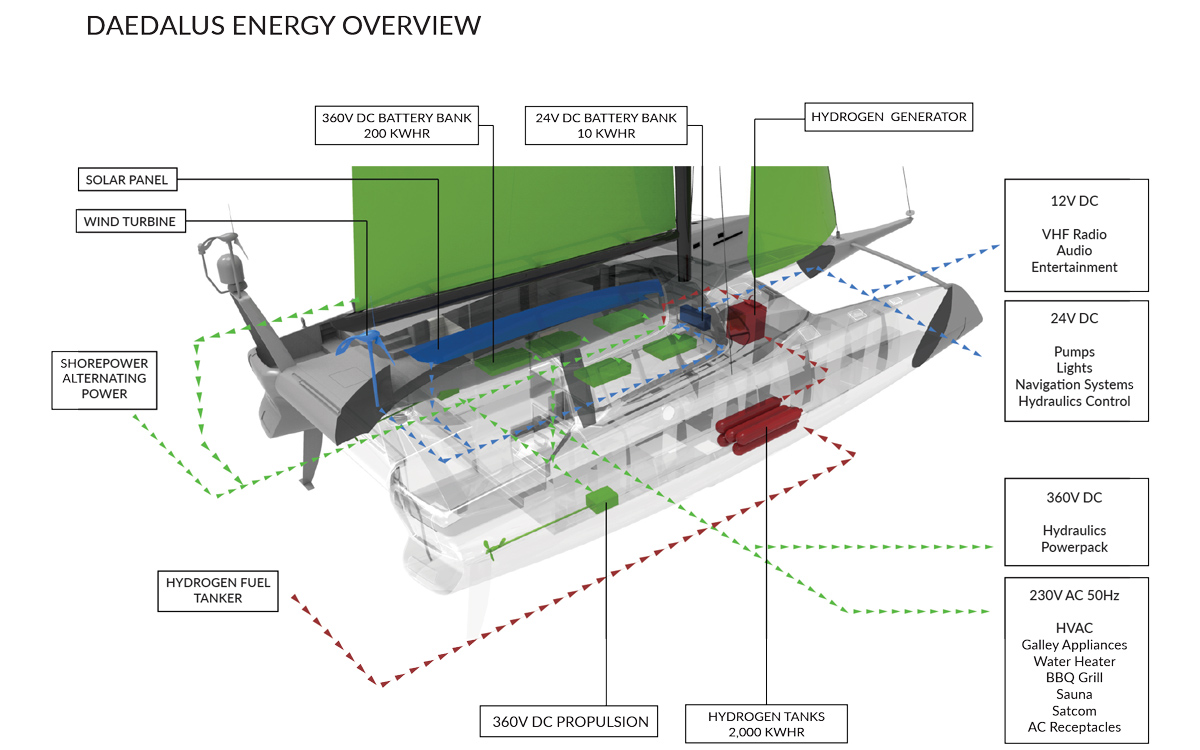
The overview of the Daedalus renewable energy and power system
The 88ft catamaran is being built to full commercial survey for world cruising for visionary Stephan Muff, who created the technology for Google Maps. The Daedalus electrolyser (which converts water to hydrogen) is the same as has been used in US spaceships and NATO submarines, so the North Carolina company is quietly confident it’s onto a reliable power source.
For the shorter term however, sailors should look to solar and battery technology, where we can assume continued improvements in efficiency and capacity for reduced costs. Building photovoltaic cells into biminis, decks, masts, and sails is already feasible.
Using sail power alone whenever possible is an obvious objective. But it’s the sailcloth itself that is arguably the most disposable component, particularly aboard racing yachts. Laminate sails with a Mylar membrane can’t be recycled, so many used sails go to landfill, or are abandoned in sheds and shipping containers.
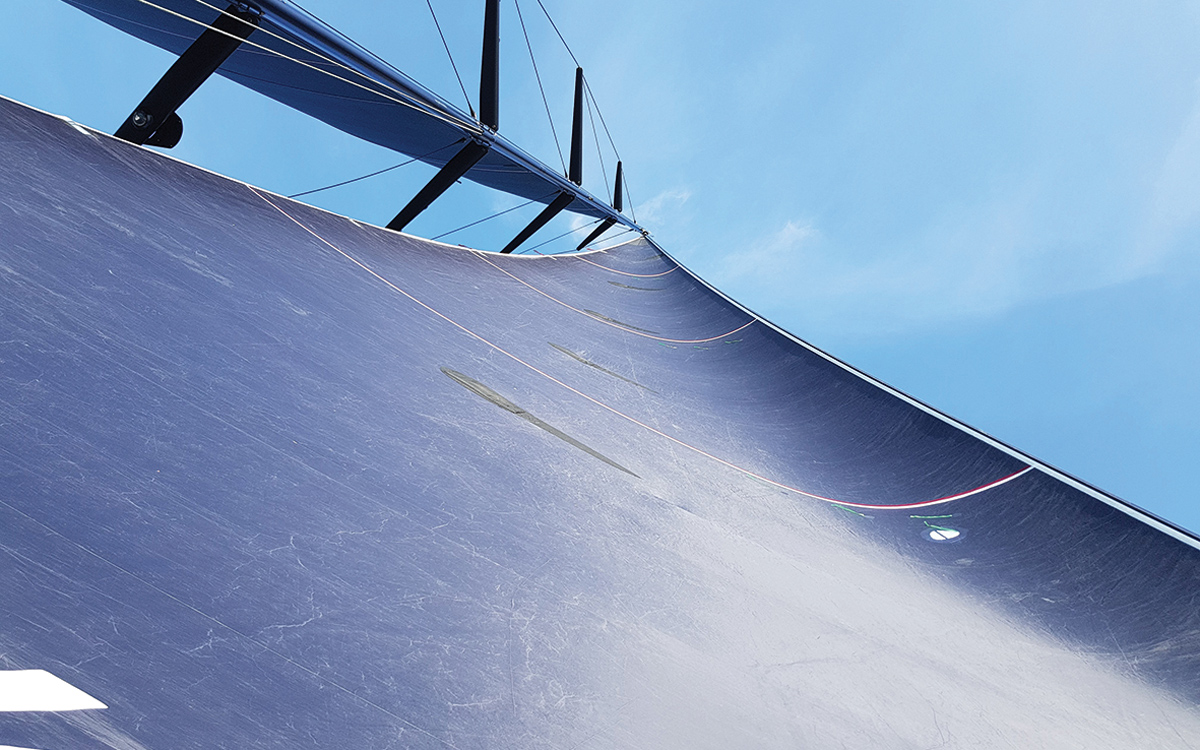

OneSails 4T Forte membranes are recyclable sails that use STR stripes, a high modulus fibre produced by compaction of polymer to create a flat ribbon
Polyester/Dacron sails are largely thermoplastic so can be melted and reformed (although typically coatings such as melamine render this highly problematic). However, other than turning them into bags and accessories, what are the options for sails with synthetic fibres, high modulus yarns, which are notoriously difficult to chop up and repurpose?
OneSails has been ahead of the game here with its 4T technology. It uses a recyclable base polymer and replaces the glues and resins with heat fusion. The result is a composite single structure sail, which uses a low-stretch technology to avoid Mylar or taffeta, for a completely recyclable sail. “This technology is the only genuine sailmaking system that offers the opportunity for sailors to recycle ‘end of life’ sails,” says OneSails UK’s John Parker.
North Sails’ 3Di products also avoid Mylar film and the company is working to recover raw material from used sails to turn it back into polyester fibres. North’s commercial director Tom Davis, who has overseen its cloth business for the last 20 years, sees two key areas of development with greener sails. Firstly with the raw materials: “I will be very surprised in the next few years if materials going into sails aren’t substantially bio-based.”
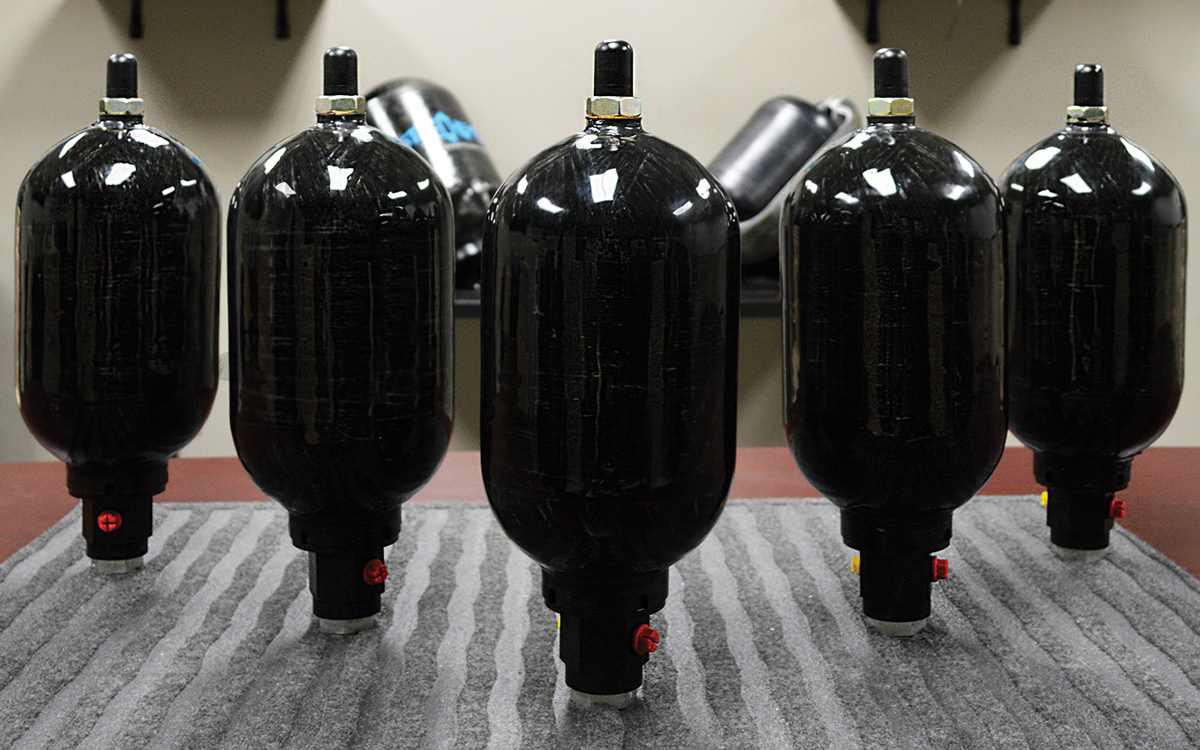

With its partner, Steelhead Composites, Daedalus has built the world’s only certified hydrogen containment vessel
And secondly, with what he terms the ‘back end’: “A very high percentage of the total acreage of sailcloth in all areas will be repurposed/recycled.” Again, he sees the quickest changes happening with polyester and reports that North is already using recycled PET films, which are chemically indistinguishable from oil-based film.
Davis has been impressed by the speed of the technology in these areas. “In the sailcloth/making business, we’re not big enough to be producing new yarn or filaments – that’s really a petrochemical level business. But we are the beneficiaries of the technologies those companies develop.”
So in the case of high modulus yarn products, North is working with a company that is producing a bio source for the monomers that become polymers and then become high performance yarn and fibre. “So instead of pumping oil out of the ground and converting it to plastic, they’re starting with trees and ending up with very high performance plastics,” Davis explains.
Positive thinking
It goes without saying that future yachts should be well insulated, durable and with very low energy loss and consumption. Battery banks and renewable regeneration will mean there’s little requirement for fossil fuels. Water filtration in and out of the boat is increasingly important. For those who spend long periods aboard, the growing energy efficiency of watermakers means there is simply no call to ship bottled water. Self-sufficiency rules.
The dissolving print your anchor leaves in the sand should be the only evidence a yacht ever leaves behind! I’m confident the next decade will bring a tidal wave of innovation in the marine sector. And with the right collective mindset, the future is indeed bright – it’s exciting and it’s green.
First published in the April 2020 edition of Yachting World.

Search boats for sale
Neel 47 (sailboat) for sale

Boat data Neel 47
Technical data, buy neel 47 - equipment sailing trimaran - sailboat for sale, neel 47 - info without obligation - sailing trimaran.

Other boats (like Neel 47) - for buy and for sale

Neel 45 Evolution

Bénéteau First 50

Ta Chiao TW 41

Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 490
These sailboats could also be of interest to you.
- Places - European, Western and Northern Russia
YEKATERINBURG: FACTORIES, URAL SIGHTS, YELTSIN AND THE WHERE NICHOLAS II WAS KILLED
Sverdlovsk oblast.
Sverdlovsk Oblast is the largest region in the Urals; it lies in the foothills of mountains and contains a monument indicating the border between Europe and Asia. The region covers 194,800 square kilometers (75,200 square miles), is home to about 4.3 million people and has a population density of 22 people per square kilometer. About 83 percent of the population live in urban areas. Yekaterinburg is the capital and largest city, with 1.5 million people. For Russians, the Ural Mountains are closely associated with Pavel Bazhov's tales and known for folk crafts such as Kasli iron sculpture, Tagil painting, and copper embossing. Yekaterinburg is the birthplace of Russia’s iron and steel industry, taking advantage of the large iron deposits in the Ural mountains. The popular Silver Ring of the Urals tourist route starts here.
In the summer you can follow in the tracks of Yermak, climb relatively low Ural mountain peaks and look for boulders seemingly with human faces on them. You can head to the Gemstone Belt of the Ural mountains, which used to house emerald, amethyst and topaz mines. In the winter you can go ice fishing, ski and cross-country ski.
Sverdlovsk Oblast and Yekaterinburg are located near the center of Russia, at the crossroads between Europe and Asia and also the southern and northern parts of Russia. Winters are longer and colder than in western section of European Russia. Snowfalls can be heavy. Winter temperatures occasionally drop as low as - 40 degrees C (-40 degrees F) and the first snow usually falls in October. A heavy winter coat, long underwear and good boots are essential. Snow and ice make the sidewalks very slippery, so footwear with a good grip is important. Since the climate is very dry during the winter months, skin moisturizer plus lip balm are recommended. Be alert for mud on street surfaces when snow cover is melting (April-May). Patches of mud create slippery road conditions.
Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg (kilometer 1818 on the Trans-Siberian Railway) is the fourth largest city in Russia, with of 1.5 million and growth rate of about 12 percent, high for Russia. Located in the southern Ural mountains, it was founded by Peter the Great and named after his wife Catherine, it was used by the tsars as a summer retreat and is where tsar Nicholas II and his family were executed and President Boris Yeltsin lived most of his life and began his political career. The city is near the border between Europe and Asia.
Yekaterinburg (also spelled Ekaterinburg) is located on the eastern slope of the Ural Mountains in the headwaters of the Iset and Pyshma Rivers. The Iset runs through the city center. Three ponds — Verkh-Isetsky, Gorodskoy and Nizhne-Isetsky — were created on it. Yekaterinburg has traditionally been a city of mining and was once the center of the mining industry of the Urals and Siberia. Yekaterinburg remains a major center of the Russian armaments industry and is sometimes called the "Pittsburgh of Russia.". A few ornate, pastel mansions and wide boulevards are reminders of the tsarist era. The city is large enough that it has its own Metro system but is characterized mostly by blocky Soviet-era apartment buildings. The city has advanced under President Vladimir Putin and is now one of the fastest growing places in Russia, a country otherwise characterized by population declines
Yekaterinburg is technically an Asian city as it lies 32 kilometers east of the continental divide between Europe and Asia. The unofficial capital of the Urals, a key region in the Russian heartland, it is second only to Moscow in terms of industrial production and capital of Sverdlovsk oblast. Among the important industries are ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, machine building and metalworking, chemical and petrochemicals, construction materials and medical, light and food industries. On top of being home of numerous heavy industries and mining concerns, Yekaterinburg is also a major center for industrial research and development and power engineering as well as home to numerous institutes of higher education, technical training, and scientific research. In addition, Yekaterinburg is the largest railway junction in Russia: the Trans-Siberian Railway passes through it, the southern, northern, western and eastern routes merge in the city.
Accommodation: There are two good and affordable hotels — the 3-star Emerald and Parus hotels — located close to the city's most popular landmarks and main transport interchanges in the center of Yekaterinburg. Room prices start at RUB 1,800 per night.
History of Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg was founded in 1723 by Peter the Great and named after his wife Catherine I. It was used by the tsars as a summer retreat but was mainly developed as metalworking and manufacturing center to take advantage of the large deposits of iron and other minerals in the Ural mountains. It is best known to Americans as the place where the last Tsar and his family were murdered by the Bolsheviks in 1918 and near where American U-2 spy plane, piloted by Gary Powers, was shot down in 1960.
Peter the Great recognized the importance of the iron and copper-rich Urals region for Imperial Russia's industrial and military development. In November 1723, he ordered the construction of a fortress factory and an ironworks in the Iset River Valley, which required a dam for its operation. In its early years Yekaterinburg grew rich from gold and other minerals and later coal. The Yekaterinburg gold rush of 1745 created such a huge amount of wealth that one rich baron of that time hosted a wedding party that lasted a year. By the mid-18th century, metallurgical plants had sprung up across the Urals to cast cannons, swords, guns and other weapons to arm Russia’s expansionist ambitions. The Yekaterinburg mint produced most of Russia's coins. Explorations of the Trans-Baikal and Altai regions began here in the 18th century.
Iron, cast iron and copper were the main products. Even though Iron from the region went into the Eiffel Tower, the main plant in Yekaterinburg itself was shut down in 1808. The city still kept going through a mountain factory control system of the Urals. The first railway in the Urals was built here: in 1878, the Yekaterinburg-Perm railway branch connected the province's capital with the factories of the Middle Urals.
In the Soviet era the city was called Sverdlovsk (named after Yakov Sverdlov, the man who organized Nicholas II's execution). During the first five-year plans the city became industrial — old plants were reconstructed, new ones were built. The center of Yekaterinburg was formed to conform to the historical general plan of 1829 but was the layout was adjusted around plants and factories. In the Stalin era the city was a major gulag transhipment center. In World War II, many defense-related industries were moved here. It and the surrounding area were a center of the Soviet Union's military industrial complex. Soviet tanks, missiles and aircraft engines were made in the Urals. During the Cold War era, Yekaterinburg was a center of weapons-grade uranium enrichment and processing, warhead assembly and dismantlement. In 1979, 64 people died when anthrax leaked from a biological weapons facility. Yekaterinburg was a “Closed City” for 40 years during the Cold Soviet era and was not open to foreigners until 1991
In the early post-Soviet era, much like Pittsburgh in the 1970s, Yekaterinburg had a hard struggle d to cope with dramatic economic changes that have made its heavy industries uncompetitive on the world market. Huge defense plants struggled to survive and the city was notorious as an organized crime center in the 1990s, when its hometown boy Boris Yeltsin was President of Russia. By the 2000s, Yekaterinburg’s retail and service was taking off, the defense industry was reviving and it was attracting tech industries and investments related to the Urals’ natural resources. By the 2010s it was vying to host a world exhibition in 2020 (it lost, Dubai won) and it had McDonald’s, Subway, sushi restaurants, and Gucci, Chanel and Armani. There were Bentley and Ferrari dealerships but they closed down
Transportation in Yekaterinburg
Getting There: By Plane: Yekaterinburg is a three-hour flight from Moscow with prices starting at RUB 8,000, or a 3-hour flight from Saint Petersburg starting from RUB 9,422 (direct round-trip flight tickets for one adult passenger). There are also flights from Frankfurt, Istanbul, China and major cities in the former Soviet Union.
By Train: Yekaterinburg is a major stop on the Trans-Siberian Railway. Daily train service is available to Moscow and many other Russian cities.Yekaterinburg is a 32-hour train ride from Moscow (tickets RUB 8,380 and above) or a 36-hour train ride from Saint Petersburg (RUB 10,300 and above). The ticket prices are round trip for a berth in a sleeper compartment for one adult passenger). By Car: a car trip from Moscow to Yekateringburg is 1,787 kilometers long and takes about 18 hours. The road from Saint Petersburg is 2,294 kilometers and takes about 28 hours.
Regional Transport: The region's public transport includes buses and suburban electric trains. Regional trains provide transport to larger cities in the Ural region. Buses depart from Yekaterinburg’s two bus stations: the Southern Bus Station and the Northern Bus Station.
Regional Transport: According the to Association for Safe International Road Travel (ASIRT): “Public transportation is well developed. Overcrowding is common. Fares are low. Service is efficient. Buses are the main form of public transport. Tram network is extensive. Fares are reasonable; service is regular. Trams are heavily used by residents, overcrowding is common. Purchase ticket after boarding. Metro runs from city center to Uralmash, an industrial area south of the city. Metro ends near the main railway station. Fares are inexpensive.
“Traffic is congested in city center. Getting around by car can be difficult. Route taxis (minivans) provide the fastest transport. They generally run on specific routes, but do not have specific stops. Drivers stop where passengers request. Route taxis can be hailed. Travel by bus or trolleybuses may be slow in rush hour. Trams are less affected by traffic jams. Trolley buses (electric buses) cannot run when temperatures drop below freezing.”
Entertainment, Sports and Recreation in Yekaterinburg
The performing arts in Yekaterinburg are first rate. The city has an excellent symphony orchestra, opera and ballet theater, and many other performing arts venues. Tickets are inexpensive. The Yekaterinburg Opera and Ballet Theater is lavishly designed and richly decorated building in the city center of Yekaterinburg. The theater was established in 1912 and building was designed by architect Vladimir Semyonov and inspired by the Vienna Opera House and the Theater of Opera and Ballet in Odessa.
Vaynera Street is a pedestrian only shopping street in city center with restaurants, cafes and some bars. But otherwise Yekaterinburg's nightlife options are limited. There are a handful of expensive Western-style restaurants and bars, none of them that great. Nightclubs serve the city's nouveau riche clientele. Its casinos have closed down. Some of them had links with organized crime. New dance clubs have sprung up that are popular with Yekaterinburg's more affluent youth.
Yekaterinburg's most popular spectator sports are hockey, basketball, and soccer. There are stadiums and arenas that host all three that have fairly cheap tickets. There is an indoor water park and lots of parks and green spaces. The Urals have many lakes, forests and mountains are great for hiking, boating, berry and mushroom hunting, swimming and fishing. Winter sports include cross-country skiing and ice skating. Winter lasts about six months and there’s usually plenty of snow. The nearby Ural Mountains however are not very high and the downhill skiing opportunities are limited..
Sights in Yekaterinburg
Sights in Yekaterinburg include the Museum of City Architecture and Ural Industry, with an old water tower and mineral collection with emeralds. malachite, tourmaline, jasper and other precious stone; Geological Alley, a small park with labeled samples of minerals found in the Urals region; the Ural Geology Museum, which houses an extensive collection of stones, gold and gems from the Urals; a monument marking the border between Europe and Asia; a memorial for gulag victims; and a graveyard with outlandish memorials for slain mafia members.
The Military History Museum houses the remains of the U-2 spy plane shot down in 1960 and locally made tanks and rocket launchers. The fine arts museum contains paintings by some of Russia's 19th-century masters. Also worth a look are the History an Local Studies Museum; the Political History and Youth Museum; and the University and Arboretum. Old wooden houses can be seen around Zatoutstovsya ulitsa and ulitsa Belinskogo. Around the city are wooded parks, lakes and quarries used to harvest a variety of minerals. Weiner Street is the main street of Yekaterinburg. Along it are lovely sculptures and 19th century architecture. Take a walk around the unique Literary Quarter
Plotinka is a local meeting spot, where you will often find street musicians performing. Plotinka can be described as the center of the city's center. This is where Yekaterinburg holds its biggest events: festivals, seasonal fairs, regional holiday celebrations, carnivals and musical fountain shows. There are many museums and open-air exhibitions on Plotinka. Plotinka is named after an actual dam of the city pond located nearby (“plotinka” means “a small dam” in Russian).In November 1723, Peter the Great ordered the construction of an ironworks in the Iset River Valley, which required a dam for its operation. “Iset” can be translated from Finnish as “abundant with fish”. This name was given to the river by the Mansi — the Finno-Ugric people dwelling on the eastern slope of the Northern Urals.
Vysotsky and Iset are skyscrapers that are 188.3 meters and 209 meters high, respectively. Fifty-story-high Iset has been described by locals as the world’s northernmost skyscraper. Before the construction of Iset, Vysotsky was the tallest building of Yekaterinburg and Russia (excluding Moscow). A popular vote has decided to name the skyscraper after the famous Soviet songwriter, singer and actor Vladimir Vysotsky. and the building was opened on November 25, 2011. There is a lookout at the top of the building, and the Vysotsky museum on its second floor. The annual “Vysotsky climb” (1137 steps) is held there, with a prize of RUB 100,000. While Vysotsky serves as an office building, Iset, owned by the Ural Mining and Metallurgical Company, houses 225 premium residential apartments ranging from 80 to 490 square meters in size.
Boris Yeltsin Presidential Center
The Boris Yeltsin Presidential Center (in the city center: ul. Yeltsina, 3) is a non-governmental organization named after the first president of the Russian Federation. The Museum of the First President of Russia as well as his archives are located in the Center. There is also a library, educational and children's centers, and exposition halls. Yeltsin lived most of his life and began his political career in Yekaterinburg. He was born in Butka about 200 kilometers east of Yekaterinburg.
The core of the Center is the Museum. Modern multimedia technologies help animate the documents, photos from the archives, and artifacts. The Yeltsin Museum holds collections of: propaganda posters, leaflets, and photos of the first years of the Soviet regime; portraits and portrait sculptures of members of Politburo of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of various years; U.S.S.R. government bonds and other items of the Soviet era; a copy of “One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich” by Alexander Solzhenitsyn, published in the “Novy Mir” magazine (#11, 1962); perestroika-era editions of books by Alexander Solzhenitsyn, Vasily Grossman, and other authors; theater, concert, and cinema posters, programs, and tickets — in short, all of the artifacts of the perestroika era.
The Yeltsin Center opened in 2012. Inside you will also find an art gallery, a bookstore, a gift shop, a food court, concert stages and a theater. There are regular screenings of unique films that you will not find anywhere else. Also operating inside the center, is a scientific exploritorium for children. The center was designed by Boris Bernaskoni. Almost from the its very opening, the Yeltsin Center has been accused by members of different political entities of various ideological crimes. The museum is open Tuesday to Sunday, from 10:00am to 9:00pm.
Where Nicholas II was Executed
On July, 17, 1918, during this reign of terror of the Russian Civil War, former-tsar Nicholas II, his wife, five children (the 13-year-old Alexis, 22-year-old Olga, 19-year-old Maria and 17-year-old Anastasia)the family physician, the cook, maid, and valet were shot to death by a Red Army firing squad in the cellar of the house they were staying at in Yekaterinburg.
Ipatiev House (near Church on the Blood, Ulitsa Libknekhta) was a merchant's house where Nicholas II and his family were executed. The house was demolished in 1977, on the orders of an up and coming communist politician named Boris Yeltsin. Yeltsin later said that the destruction of the house was an "act of barbarism" and he had no choice because he had been ordered to do it by the Politburo,
The site is marked with s cross with the photos of the family members and cross bearing their names. A small wooden church was built at the site. It contains paintings of the family. For a while there were seven traditional wooden churches. Mass is given ay noon everyday in an open-air museum. The Church on the Blood — constructed to honor Nicholas II and his family — was built on the part of the site in 1991 and is now a major place of pilgrimage.
Nicholas and his family where killed during the Russian civil war. It is thought the Bolsheviks figured that Nicholas and his family gave the Whites figureheads to rally around and they were better of dead. Even though the death orders were signed Yakov Sverdlov, the assassination was personally ordered by Lenin, who wanted to get them out of sight and out of mind. Trotsky suggested a trial. Lenin nixed the idea, deciding something had to be done about the Romanovs before White troops approached Yekaterinburg. Trotsky later wrote: "The decision was not only expedient but necessary. The severity of he punishment showed everyone that we would continue to fight on mercilessly, stopping at nothing."
Ian Frazier wrote in The New Yorker: “Having read a lot about the end of Tsar Nicholas II and his family and servants, I wanted to see the place in Yekaterinburg where that event occurred. The gloomy quality of this quest depressed Sergei’s spirits, but he drove all over Yekaterinburg searching for the site nonetheless. Whenever he stopped and asked a pedestrian how to get to the house where Nicholas II was murdered, the reaction was a wince. Several people simply walked away. But eventually, after a lot of asking, Sergei found the location. It was on a low ridge near the edge of town, above railroad tracks and the Iset River. The house, known as the Ipatiev House, was no longer standing, and the basement where the actual killings happened had been filled in. I found the blankness of the place sinister and dizzying. It reminded me of an erasure done so determinedly that it had worn a hole through the page. [Source: Ian Frazier, The New Yorker, August 3, 2009, Frazier is author of “Travels in Siberia” (2010)]
“The street next to the site is called Karl Liebknecht Street. A building near where the house used to be had a large green advertisement that said, in English, “LG—Digitally Yours.” On an adjoining lot, a small chapel kept the memory of the Tsar and his family; beneath a pedestal holding an Orthodox cross, peonies and pansies grew. The inscription on the pedestal read, “We go down on our knees, Russia, at the foot of the tsarist cross.”
Books: The Romanovs: The Final Chapter by Robert K. Massie (Random House, 1995); The Fall of the Romanovs by Mark D. Steinberg and Vladimir Khrustalëv (Yale, 1995);
See Separate Article END OF NICHOLAS II factsanddetails.com
Execution of Nicholas II
According to Robert Massie K. Massie, author of Nicholas and Alexandra, Nicholas II and his family were awakened from their bedrooms around midnight and taken to the basement. They were told they were to going to take some photographs of them and were told to stand behind a row of chairs.
Suddenly, a group of 11 Russians and Latvians, each with a revolver, burst into the room with orders to kill a specific person. Yakob Yurovsky, a member of the Soviet executive committee, reportedly shouted "your relatives are continuing to attack the Soviet Union.” After firing, bullets bouncing off gemstones hidden in the corsets of Alexandra and her daughters ricocheted around the room like "a shower of hail," the soldiers said. Those that were still breathing were killed with point black shots to the head.
The three sisters and the maid survived the first round thanks to their gems. They were pressed up against a wall and killed with a second round of bullets. The maid was the only one that survived. She was pursued by the executioners who stabbed her more than 30 times with their bayonets. The still writhing body of Alexis was made still by a kick to the head and two bullets in the ear delivered by Yurovsky himself.
Yurovsky wrote: "When the party entered I told the Romanovs that in view of the fact their relatives continued their offensive against Soviet Russia, the Executive Committee of the Urals Soviet had decided to shoot them. Nicholas turned his back to the detachment and faced his family. Then, as if collecting himself, he turned around, asking, 'What? What?'"
"[I] ordered the detachment to prepare. Its members had been previously instructed whom to shoot and to am directly at the heart to avoid much blood and to end more quickly. Nicholas said no more. he turned again to his family. The others shouted some incoherent exclamations. All this lasted a few seconds. Then commenced the shooting, which went on for two or three minutes. [I] killed Nicholas on the spot."
Nicholas II’s Initial Burial Site in Yekaterinburg
Ganina Yama Monastery (near the village of Koptyaki, 15 kilometers northwest of Yekaterinburg) stands near the three-meter-deep pit where some the remains of Nicholas II and his family were initially buried. The second burial site — where most of the remains were — is in a field known as Porosyonkov (56.9113628°N 60.4954326°E), seven kilometers from Ganina Yama.
On visiting Ganina Yama Monastery, one person posted in Trip Advisor: “We visited this set of churches in a pretty park with Konstantin from Ekaterinburg Guide Centre. He really brought it to life with his extensive knowledge of the history of the events surrounding their terrible end. The story is so moving so unless you speak Russian, it is best to come here with a guide or else you will have no idea of what is what.”
In 1991, the acid-burned remains of Nicholas II and his family were exhumed from a shallow roadside mass grave in a swampy area 12 miles northwest of Yekaterinburg. The remains had been found in 1979 by geologist and amateur archeologist Alexander Avdonin, who kept the location secret out of fear that they would be destroyed by Soviet authorities. The location was disclosed to a magazine by one his fellow discovers.
The original plan was to throw the Romanovs down a mine shaft and disposes of their remains with acid. They were thrown in a mine with some grenades but the mine didn't collapse. They were then carried by horse cart. The vats of acid fell off and broke. When the carriage carrying the bodies broke down it was decided the bury the bodies then and there. The remaining acid was poured on the bones, but most of it was soaked up the ground and the bones largely survived.
After this their pulses were then checked, their faces were crushed to make them unrecognizable and the bodies were wrapped in bed sheets loaded onto a truck. The "whole procedure," Yurovsky said took 20 minutes. One soldiers later bragged than he could "die in peace because he had squeezed the Empress's -------."
The bodies were taken to a forest and stripped, burned with acid and gasoline, and thrown into abandoned mine shafts and buried under railroad ties near a country road near the village of Koptyaki. "The bodies were put in the hole," Yurovsky wrote, "and the faces and all the bodies, generally doused with sulfuric acid, both so they couldn't be recognized and prevent a stink from them rotting...We scattered it with branches and lime, put boards on top and drove over it several times—no traces of the hole remained.
Shortly afterwards, the government in Moscow announced that Nicholas II had been shot because of "a counterrevolutionary conspiracy." There was no immediate word on the other members of the family which gave rise to rumors that other members of the family had escaped. Yekaterinburg was renamed Sverdlov in honor of the man who signed the death orders.
For seven years the remains of Nicholas II, Alexandra, three of their daughters and four servants were stored in polyethylene bags on shelves in the old criminal morgue in Yekaterunburg. On July 17, 1998, Nicholas II and his family and servants who were murdered with him were buried Peter and Paul Fortress in St. Petersburg along with the other Romanov tsars, who have been buried there starting with Peter the Great. Nicholas II had a side chapel built for himself at the fortress in 1913 but was buried in a new crypt.
Near Yekaterinburg
Factory-Museum of Iron and Steel Metallurgy (in Niznhy Tagil 80 kilometers north of Yekaterinburg) a museum with old mining equipment made at the site of huge abandoned iron and steel factory. Officially known as the Factory-Museum of the History of the Development of Iron and Steel Metallurgy, it covers an area of 30 hectares and contains a factory founded by the Demidov family in 1725 that specialized mainly in the production of high-quality cast iron and steel. Later, the foundry was renamed after Valerian Kuybyshev, a prominent figure of the Communist Party.
The first Russian factory museum, the unusual museum demonstrates all stages of metallurgy and metal working. There is even a blast furnace and an open-hearth furnace. The display of factory equipment includes bridge crane from 1892) and rolling stock equipment from the 19th-20th centuries. In Niznhy Tagil contains some huge blocks of malachite and
Nizhnyaya Sinyachikha (180 kilometers east-northeast of Yekaterinburg) has an open air architecture museum with log buildings, a stone church and other pre-revolutionary architecture. The village is the creation of Ivan Samoilov, a local activist who loved his village so much he dedicated 40 years of his life to recreating it as the open-air museum of wooden architecture.
The stone Savior Church, a good example of Siberian baroque architecture. The interior and exterior of the church are exhibition spaces of design. The houses are very colorful. In tsarist times, rich villagers hired serfs to paint the walls of their wooden izbas (houses) bright colors. Old neglected buildings from the 17th to 19th centuries have been brought to Nizhnyaya Sinyachikha from all over the Urals. You will see the interior design of the houses and hear stories about traditions and customs of the Ural farmers.
Verkhoturye (330 kilometers road from Yekaterinburg) is the home a 400-year-old monastery that served as 16th century capital of the Urals. Verkhoturye is a small town on the Tura River knows as the Jerusalem of the Urals for its many holy places, churches and monasteries. The town's main landmark is its Kremlin — the smallest in Russia. Pilgrims visit the St. Nicholas Monastery to see the remains of St. Simeon of Verkhoturye, the patron saint of fishermen.
Ural Mountains
Ural Mountains are the traditional dividing line between Europe and Asia and have been a crossroads of Russian history. Stretching from Kazakhstan to the fringes of the Arctic Kara Sea, the Urals lie almost exactly along the 60 degree meridian of longitude and extend for about 2,000 kilometers (1,300 miles) from north to south and varies in width from about 50 kilometers (30 miles) in the north and 160 kilometers (100 miles) the south. At kilometers 1777 on the Trans-Siberian Railway there is white obelisk with "Europe" carved in Russian on one side and "Asia" carved on the other.
The eastern side of the Urals contains a lot of granite and igneous rock. The western side is primarily sandstone and limestones. A number of precious stones can be found in the southern part of the Urals, including emeralds. malachite, tourmaline, jasper and aquamarines. The highest peaks are in the north. Mount Narodnaya is the highest of all but is only 1884 meters (6,184 feet) high. The northern Urals are covered in thick forests and home to relatively few people.
Like the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States, the Urals are very old mountains — with rocks and sediments that are hundreds of millions years old — that were one much taller than they are now and have been steadily eroded down over millions of years by weather and other natural processes to their current size. According to Encyclopedia Britannica: “The rock composition helps shape the topography: the high ranges and low, broad-topped ridges consist of quartzites, schists, and gabbro, all weather-resistant. Buttes are frequent, and there are north–south troughs of limestone, nearly all containing river valleys. Karst topography is highly developed on the western slopes of the Urals, with many caves, basins, and underground streams. The eastern slopes, on the other hand, have fewer karst formations; instead, rocky outliers rise above the flattened surfaces. Broad foothills, reduced to peneplain, adjoin the Central and Southern Urals on the east.
“The Urals date from the structural upheavals of the Hercynian orogeny (about 250 million years ago). About 280 million years ago there arose a high mountainous region, which was eroded to a peneplain. Alpine folding resulted in new mountains, the most marked upheaval being that of the Nether-Polar Urals...The western slope of the Urals is composed of middle Paleozoic sedimentary rocks (sandstones and limestones) that are about 350 million years old. In many places it descends in terraces to the Cis-Ural depression (west of the Urals), to which much of the eroded matter was carried during the late Paleozoic (about 300 million years ago). Found there are widespread karst (a starkly eroded limestone region) and gypsum, with large caverns and subterranean streams. On the eastern slope, volcanic layers alternate with sedimentary strata, all dating from middle Paleozoic times.”
Southern Urals
The southern Urals are characterized by grassy slopes and fertile valleys. The middle Urals are a rolling platform that barely rises above 300 meters (1,000 feet). This region is rich in minerals and has been heavily industrialized. This is where you can find Yekaterinburg (formally Sverdlovsk), the largest city in the Urals.
Most of the Southern Urals are is covered with forests, with 50 percent of that pine-woods, 44 percent birch woods, and the rest are deciduous aspen and alder forests. In the north, typical taiga forests are the norm. There are patches of herbal-poaceous steppes, northem sphagnous marshes and bushy steppes, light birch forests and shady riparian forests, tall-grass mountainous meadows, lowland ling marshes and stony placers with lichen stains. In some places there are no large areas of homogeneous forests, rather they are forests with numerous glades and meadows of different size.
In the Ilmensky Mountains Reserve in the Southern Urals, scientists counted 927 vascular plants (50 relicts, 23 endemic species), about 140 moss species, 483 algae species and 566 mushroom species. Among the species included into the Red Book of Russia are feather grass, downy-leaved feather grass, Zalessky feather grass, moccasin flower, ladies'-slipper, neottianthe cucullata, Baltic orchis, fen orchis, helmeted orchis, dark-winged orchis, Gelma sandwart, Krasheninnikov sandwart, Clare astragalus.
The fauna of the vertebrate animals in the Reserve includes 19 fish, 5 amphibian and 5 reptile. Among the 48 mammal species are elks, roe deer, boars, foxes, wolves, lynxes, badgers, common weasels, least weasels, forest ferrets, Siberian striped weasel, common marten, American mink. Squirrels, beavers, muskrats, hares, dibblers, moles, hedgehogs, voles are quite common, as well as chiropterans: pond bat, water bat, Brandt's bat, whiskered bat, northern bat, long-eared bat, parti-coloured bat, Nathusius' pipistrelle. The 174 bird bird species include white-tailed eagles, honey hawks, boreal owls, gnome owls, hawk owls, tawny owls, common scoters, cuckoos, wookcocks, common grouses, wood grouses, hazel grouses, common partridges, shrikes, goldenmountain thrushes, black- throated loons and others.
Activities and Places in the Ural Mountains
The Urals possess beautiful natural scenery that can be accessed from Yekaterinburg with a rent-a-car, hired taxi and tour. Travel agencies arrange rafting, kayaking and hiking trips. Hikes are available in the taiga forest and the Urals. Trips often include walks through the taiga to small lakes and hikes into the mountains and excursions to collect mushrooms and berries and climb in underground caves. Mellow rafting is offered in a relatively calm six kilometer section of the River Serga. In the winter visitor can enjoy cross-mountains skiing, downhill skiing, ice fishing, dog sledding, snow-shoeing and winter hiking through the forest to a cave covered with ice crystals.
Lake Shartash (10 kilometers from Yekaterinburg) is where the first Ural gold was found, setting in motion the Yekaterinburg gold rush of 1745, which created so much wealth one rich baron of that time hosted a wedding party that lasted a year. The area around Shartash Lake is a favorite picnic and barbecue spot of the locals. Getting There: by bus route No. 50, 054 or 54, with a transfer to suburban commuter bus route No. 112, 120 or 121 (the whole trip takes about an hour), or by car (10 kilometers drive from the city center, 40 minutes).
Revun Rapids (90 kilometers road from Yekaterinburg near Beklenishcheva village) is a popular white water rafting places On the nearby cliffs you can see the remains of a mysterious petroglyph from the Paleolithic period. Along the steep banks, you may notice the dark entrance of Smolinskaya Cave. There are legends of a sorceress who lived in there. The rocks at the riverside are suited for competitive rock climbers and beginners. Climbing hooks and rings are hammered into rocks. The most fun rafting is generally in May and June.
Olenii Ruchii National Park (100 kilometers west of Yekaterinburg) is the most popular nature park in Sverdlovsk Oblast and popular weekend getaway for Yekaterinburg residents. Visitors are attracted by the beautiful forests, the crystal clear Serga River and picturesque rocks caves. There are some easy hiking routes: the six-kilometer Lesser Ring and the 15-kilometer Greater Ring. Another route extends for 18 km and passes by the Mitkinsky Mine, which operated in the 18th-19th centuries. It's a kind of an open-air museum — you can still view mining an enrichment equipment here. There is also a genuine beaver dam nearby.
Among the other attractions at Olenii Ruchii are Druzhba (Friendship) Cave, with passages that extend for about 500 meters; Dyrovaty Kamen (Holed Stone), created over time by water of Serga River eroding rock; and Utoplennik (Drowned Man), where you can see “The Angel of Sole Hope”., created by the Swedish artist Lehna Edwall, who has placed seven angels figures in different parts of the world to “embrace the planet, protecting it from fear, despair, and disasters.”
Image Sources: Wikimedia Commons
Text Sources: Federal Agency for Tourism of the Russian Federation (official Russia tourism website russiatourism.ru ), Russian government websites, UNESCO, Wikipedia, Lonely Planet guides, New York Times, Washington Post, Los Angeles Times, National Geographic, The New Yorker, Bloomberg, Reuters, Associated Press, AFP, Yomiuri Shimbun and various books and other publications.
Updated in September 2020
- Google+
Page Top
This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been authorized by the copyright owner. Such material is made available in an effort to advance understanding of country or topic discussed in the article. This constitutes 'fair use' of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond 'fair use', you must obtain permission from the copyright owner. If you are the copyright owner and would like this content removed from factsanddetails.com, please contact me.
Yekaterinburg
| and the from | |
| Show map of Russia Show map of Sverdlovsk Oblast | |
| Coordinates: 60°36′46″E / 56.83556°N 60.61278°E / 56.83556; 60.61278 | |
| Country | |
| Founded | 18 November 1723 |
| City status since | 1781 |
| Government | |
| • Body | |
| • Head | Alexey Orlov |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,111 km (429 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 237 m (778 ft) |
| Population ( Census) | |
| • Total | 1,349,772 |
| • Estimate | 1,536,183 |
| • Rank | in 2010 |
| • Density | 1,200/km (3,100/sq mi) |
| • Subordinated to | of Yekaterinburg |
| • of | , City of Yekaterinburg |
| • Urban okrug | Yekaterinburg Urban Okrug |
| • of | Yekaterinburg Urban Okrug |
| ( ) | |
| +7 343 | |
| ID | 65701000001 |
| City Day | 3rd Saturday of August |
| Website | |
Yekaterinburg [lower-alpha 1] is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District , Russia. The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia , with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, [14] up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in the Ural Federal District, and one of Russia's main cultural and industrial centres. Yekaterinburg has been dubbed the "Third capital of Russia", as it is ranked third by the size of its economy, culture, transportation and tourism. [15] [16] [17] [18]
Imperial era
Contemporary era, demographics, administrative districts, administration, living costs and the labor market, finance and business, retail and services, transportation, public transit, media and telecommunications, life and culture, architecture, international relations, bric summit, twin towns – sister cities, notable people, bibliography, external links.
Yekaterinburg was founded on 18 November 1723 and named after the Orthodox name of Catherine I (born Marta Helena Skowrońska), the wife of Russian Emperor Peter the Great . The city served as the mining capital of the Russian Empire as well as a strategic connection between Europe and Asia. In 1781, Catherine the Great gave Yekaterinburg the status of a district town of Perm Province , and built the historical Siberian Route through the city. [3] Yekaterinburg became a key city to Siberia, which had rich resources. In the late 19th century, Yekaterinburg became one of the centres of revolutionary movements in the Urals. In 1924, after the Russian SFSR founded the Soviet Union , the city was renamed Sverdlovsk after the Bolshevik leader Yakov Sverdlov . During the Soviet era, Sverdlovsk was turned into an industrial and administrative powerhouse. On 23 September 1991 the city returned to its historical name.
Yekaterinburg is one of Russia's most important economic centres and was one of the host cities of the 2018 FIFA World Cup . The city is currently experiencing an economic and population boom, which resulted in some of the tallest skyscrapers of Russia being located in the city. Yekaterinburg is home to the headquarters of the Central Military District of the Russian Armed Forces , as well as the presidium of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences .
Yekaterinburg is famous for its constructivist architecture [19] [20] [21] and is also considered the "Russian capital of street art ". [22] [23] [24]

The area was settled in prehistory. The earliest settlements date to 8000–7000 BC, in the Mesolithic period . The Isetskoe Pravoberezhnoye I archaeological site contains a Neolithic settlement dated to 6000–5000 BC. It includes stone processing workshops with artefacts such as grinding plates, anvils, clumps of rock, tools, and finished products. Over 50 different types of rock and minerals were used in tool making, indicating extensive knowledge of the region's natural resources. The Gamayun peninsula (left bank of the Verkh-Isetsky Pond) has archaeological findings from the Chalcolithic Period : workshops for producing stone tools (upper area) and two dwellings of the Ayat culture (lower area). There are also traces of the Koptyak culture from 2000 BC: dishes decorated with bird images and evidence of metallurgical production. The Tent I site contains the only Koptyak culture burials discovered in the Ural Mountains . In the Bronze Age , the people of Gamayun culture lived in the area. They left fragments of ceramics, weapons, and ornaments. [25] [26] [27]
Archaeological artifacts in the vicinity of Yekaterinburg were first discovered during railway construction, at the end of the 19th century. Excavation and research began in the 20th century. Artifacts are held at the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum of Local Lore , at the Hermitage , at the Museum of Anthropology and Ethnography of the Academy of Sciences, and at other museums. [26]

The first Russian settlements within the boundaries of modern Yekaterinburg appeared in the second half of the 17th century — in 1672, an Old Believers village arose in the area of Shartash lake [28] (this fact is disputed by historians, since no evidence of the founding of the village at that time was found in the sources), [29] and in 1680 – 1682, the villages of Nizhny and Verkhny Uktus appeared on the banks of Uktus River (now the territory of the Chkalovsky district of the city). [30] In 1702, by the initiative of the head of Sibirskiy prikaz Andrew Vinius , the Uktus state ironwork plant was founded near Nizhny Uktus — the first ironworks within the boundaries of modern Yekaterinburg. [31] In 1704, the Shuvakish ironworks was built (now the territory of the Zheleznodorozhny district of the city). [28] With the beginning of active construction of factories in the Urals in the 18th century, relations with their southern neighbors, the Bashkirs , became strained. As a result of the Bashkir raid in 1709, the village of Verkhny Uktus was devastated, all buildings, including the wooden church and chapel, were burned, the residents fled to the protection of the Uktus plant fortifications. [30] On the night of 5 April 1718, a fire destroyed all the factory buildings of the Uktus plant, except for the dam, and the plant was restored only by 1720 under the supervision of Timofey Burtsev. [32] However, the plant did not receive further development due to the lack of water in Uktus river.
In 1720, by decree of Peter I , a delegation led by mining specialist Johann Blüher and statesman Vasily Tatishchev was sent to the Urals . [33] They were entrusted with managing the mining industry, identifying the causes of the collapse and reduction of production at state-owned factories. [33] On 29 December 1720, [33] Tatishchev and Blüher arrive at the Uktus plant, which became their main residence in the Urals. As a result of familiarizing himself with the state of nearby state-owned factories, Tatishchev came to the conclusion that on the basis of these factories, even if they were reconstructed and expanded, it would not be possible to quickly increase the production of iron, and it would be more profitable to build a new large plant. After inspecting the immediate area, together with the commissary of the Uktus plant, Timofey Burtsev, a place rich in ore and forest was chosen on the banks of the more full-flowing Iset River , 7 versts from Uktus. [33] On 6 February 1721, Tatishchev sent a message to the Collegium of Mining , in which he asked permission to begin construction of the plant, with detailed explanations and justification for this project. [33] On 1 March 1721, without waiting for a response from the Collegium, Tatishchev began construction of the new plant, [28] but he failed to convince Collegium, and by the Collegium decree of 10 December 1721, he was removed from the leadership of mining affairs in the Urals. [28] In 1722, by decree of Peter the Great, a mining engineer, Major General Georg Wilhelm de Gennin , was sent to the Urals in place of Tatishchev. Having studied all the circumstances, de Gennin fully supported Tatishchev’s project, and on 12 March 1723, construction of the plant on Iset resumed. [28]

Russian historian Vasily Tatishchev and Russian engineer Georg Wilhelm de Gennin founded Yekaterinburg with the construction of a massive iron-making plant under the decree of Russian emperor Peter the Great in 1723. [34] They named the city after the emperor's wife, Yekaterina, who later became empress regnant Catherine I . [2] Officially, the city's founding date is 18 November 1723, when the shops carried out a test run of the bloomery for trip hammers. [2] The plant was commissioned 6 days later, on 24 November. [35] 1723 also saw the establishment of Yekaterinburg fortress , which would encompass many of the settlement's earliest buildings. Dmitry Mamin-Sibiryak very vividly described the beginning of the construction of a mining plant and a fortress: "Imagine completely deserted banks of the Iset river, covered with forest. In the spring of 1723, soldiers from Tobolsk, peasants of the assigned settlements, hired craftsmen appeared, and everything around came to life, as if by the dictates of a fairy tale. They dropped the forest, prepared a place for the dam, laid blast furnaces, raised the rampart, set up barracks and houses for the authorities... ". [36]
In 1722–1726 the Verkhne-Uktussky mining plant was built, [37] which was officially called the plant of the princess Elizabeth (the future village of Elizabeth, or Elizavetinskoe) and became a part of modern Yekaterinburg in 1934. [38] In 1726, Wilhelm de Gennin founded an auxiliary Verkh-Isetsky plant with a working settlement 2 versts from Yekaterinburg upstream ('verkh' in Russian) the Iset River. [39] The plant's dam formed the Verkh-Isetsky pond. Colloquially called by the Russian acronym VIZ, it was a satellite town until in 1926, with a population of over 20,000 people by this time, it was incorporated into Yekaterinburg as the core of the Verkh-Isetsky district. [39]

Yekaterinburg was one of the industrial cities of Russia prompted at the beginning of the 18th century by decrees of Tsar Peter the Great which demanded the development of the metalworking industry. With extensive use of iron, the city was built to a regular square plan with ironworks and residential buildings at the centre. These were surrounded by fortified walls so that Yekaterinburg was at the same time both a manufacturing centre and a fortress at the frontier between Europe and Asia. It, therefore, found itself at the heart of Russia's strategy for further development of the entire Ural region. The so-called Siberian Route became operational in 1763 and placed the city on an increasingly important transit route, which led to its development as a focus of trade and commerce between east and west, and gave rise to the description of the city as the "window to Asia". With the growth in trade and the city's administrative importance, the ironworks became less critical, and the more important buildings were increasingly built using expensive stone. Small manufacturing and trading businesses proliferated. In 1781 Russia's empress, Catherine the Great, granted Yekaterinburg town status and nominated it as the administrative centre for the wider region within Perm Governorate . [3] In 1807, the role of the capital of the mining and smelting region was confirmed by assigning it the status of the only "mountain city" in Russia. Until 1863, Yekaterinburg remained subordinate to the head of the mining plants of the Ural ridge , the minister of finance and personally to the emperor, and enjoyed considerable freedom from the governor's power. Since the 1830s, mountainous Yekaterinburg has become the center of mechanical engineering. [36]

In 1820–1845, 45% of the world's gold was mined in Yekaterinburg. This is the first ever "Gold Rush". [40] Until 1876, 80% of the coins in circulation in the Russian Empire were produced at the Yekaterinburg mint. [41]
Following the October Revolution , the family of deposed Tsar Nicholas II was sent to internal exile in Yekaterinburg where they were imprisoned in the Ipatiev House in the city. In July 1918, the Czechoslovak Legions were closing on Yekaterinburg. In the early hours of the morning of 17 July, the deposed Tsar, his wife Alexandra , and their children Grand Duchesses Olga , Tatiana , Maria , Anastasia , and Tsarevich Alexei were murdered by the Bolsheviks at the Ipatiev House. Other members of the Romanov family were killed at Alapayevsk later the same day. The Legions arrived less than a week later and captured the city. [42] [43] The city remained under the control of the White movement in which a provisional government was established. The Red Army took back the city and restored Soviet authority on 14 July 1919. [44] [45]

In the years following the Russian Revolution and the Russian Civil War , political authority of the Urals was transferred from Perm to Yekaterinburg. On 19 October 1920, Yekaterinburg established its first university, the Ural State University , as well as polytechnic, pedagogical, and medical institutions under the decree of Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin . Enterprises in the city ravaged by the war were nationalised, including: the Metalist (formerly Yates) Plant, the Verkh-Isetsky (formerly Yakovleva) Plant, and the Lenin flax-spinning factory (formerly Makarov). In 1924, the city of Yekaterinburg was renamed Sverdlovsk after the Bolshevik leader Yakov Sverdlov . [46] [28] [44]
By the 1934, following a series of administrative reforms carried by the early Soviet government, the earliest Russian settlements which predated Yekaterinburg and laid the basis of its founding, were incorporated into the city proper. [38] [47]
During the reign of Stalin, Sverdlovsk was one of several places developed by the Soviet government as a centre of heavy industry. Old factories were reconstructed and new large factories were built, especially those specialised in machine-building and metalworking. These plants included Magnitogorsk and the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant in Chelyabinsk oblast , and Uralmash in Sverdlovsk. During this time, the population of Sverdlovsk tripled in size, and it became one of the fastest-growing cities of the Soviet Union. At that time, very large powers were given to the regional authorities. By the end of the 1930s, there were 140 industrial enterprises, 25 research institutes, and 12 higher education institutions in Sverdlovsk. [48] [49]
During World War II, the city became the headquarters of the Ural Military District on the basis of which more than 500 different military units and formations were formed, including the 22nd Army and the Ural Volunteer Tank Corps. Uralmash became the main production site for armoured vehicles. Many state technical institutions and whole factories were relocated to Sverdlovsk away from cities affected by war (mostly Moscow), with many of them staying in Sverdlovsk after the victory. The Hermitage Museum collections were also partly evacuated from Leningrad to Sverdlovsk in July 1941 and remained there until October 1945. [50] In the postwar years, new industrial and agricultural enterprises were put into operation and massive housing construction began. [51] [44] The lookalike five-story apartment blocks that remain today in Kirovsky, Chkalovsky, and other residential areas of Sverdlovsk sprang up in the 1960s, under the direction of Nikita Khrushchev 's government. [52] In 1977, Ipatiev House was demolished by order of Boris Yeltsin in accordance to a resolution from the Politburo in order to prevent it from being used as a rallying location for monarchists . Yeltsin later became the first President of Russia and represented the people at the funeral of the former Tsar in 1998. [53] There was an anthrax outbreak in Sverdlovsk in April and May 1979, which was attributed to a release from the Sverdlovsk-19 military facility . [54]
During the 1991 coup d'état attempt , Sverdlovsk, the home city of President Boris Yeltsin, was selected by him as a temporary reserve capital for the Russian Federation, in case Moscow became too dangerous for the Russian government. A reserve cabinet headed by Oleg Lobov was sent to the city, where Yeltsin enjoyed strong popular support at that time. [55] Shortly after the failure of the coup and subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union, the city regained its historical name of Yekaterinburg on 23 September 1991. However, Sverdlovsk Oblast, of which Yekaterinburg is the administrative centre, kept its name. [56] [57]
In the 2000s, an intensive growth of trade, business, and tourism began in Yekaterinburg. In 2003, Russian President Vladimir Putin and German Chancellor Gerhard Schröder negotiated in Yekaterinburg. On 15–17 June 2009, the SCO and BRIC summits were held in Yekaterinburg, which greatly improved the economic, cultural, and tourist situation in the city. On 13–16 July 2010, a meeting between Russian President Dmitry Medvedev and German Chancellor Angela Merkel took place in the city. [58]
In 2018, Yekaterinburg hosted four matches of the 2018 FIFA World Cup and hosted the inaugural University International Sports Festival in 2023. [59]

Geographically, Yekaterinburg is in North Asia, close to the Ural Mountains (which divide Europe from Asia), 1,667 km (1,036 mi) east of the nation's capital Moscow.
The city has a total area of 1,111 km 2 (429 sq mi) .
Yekaterinburg is on the eastern side of the Urals. The city is surrounded by wooded hills, partially cultivated for agricultural purposes. Yekaterinburg is located on a natural watershed, so there would be many bodies of water close and in the city. The city is bisected by the Iset River , which flows from the Urals into the Tobol River . There are two lakes in the city, Lake Shuvakish and Lake Shartash. The city borders Verkh-Isetskiy Pond, through which the Iset River flows. Lake Isetskoye and Lake Baltym are both near the city, with Lake Isetskoye located near Sredneuralsk , and Lake Baltym located near the towns of Sanatornyy and Baltym.
Yekaterinburg uses the Yekaterinburg Time, which is five hours ahead of UTC (UTC+5), and two hours ahead of Moscow Time . [60]
The city possesses a humid continental climate ( Dfb ) under the Köppen climate classification . [61] It is characterised by sharp variability in weather conditions, with well-marked seasons. The Ural Mountains, despite their insignificant height, block air from the west, from the European part of Russia. As a result, the Central Urals are open to the invasion of cold arctic air and continental air from the West Siberian Plain. Equally, warm air masses from the Caspian Sea and the deserts of Central Asia can freely penetrate from the south. Therefore, the weather in Yekaterinburg is characterised by sharp temperature fluctuations and weather anomalies: in winter, from frost at −40 °C to thaw and rain; in summer, from frosts to temperatures above 35 °C (95 °F) . [61]

The distribution of precipitation is determined by the circulation of air masses, relief, and air temperatures. The main part of the precipitation is brought by cyclones with a western air mass transfer, that is, from the European part of Russia, while their average annual amount is 601 mm. The maximum falls on a warm season, during which about 60–70% of the annual amount falls. For the winter period is characterized by snow cover with an average capacity of 40–50 cm. The coefficient of moistening(the ratio of yearly precipitation and potential evaporation ) – 1. [61]
- The average temperature in January is −12.6 °C (9.3 °F) . The record minimum temperature is −44.6 °C (−48.3 °F) (6 January 1915);
- The average July temperature is 18.9 °C (66.0 °F) . The record maximum temperature is 40.0 °C (104.0 °F) (11 July 2023);
- The average annual temperature is 2.1 °C (35.8 °F) ;
- The average annual wind speed is 2.9 m/s (10 km/h; 6.5 mph) ;
- The average annual humidity is 75%;
- The average annual precipitation is 534 mm (21.0 in) ;
| Climate data for Yekaterinburg (1991–2020, extremes 1831–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 5.6 (42.1) | 9.4 (48.9) | 18.1 (64.6) | 28.8 (83.8) | 34.7 (94.5) | 36.4 (97.5) | 40.0 (104.0) | 37.2 (99.0) | 31.9 (89.4) | 24.7 (76.5) | 13.5 (56.3) | 5.9 (42.6) | 40.0 (104.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −9.3 (15.3) | −6.6 (20.1) | 0.9 (33.6) | 10.1 (50.2) | 18.3 (64.9) | 22.6 (72.7) | 24.3 (75.7) | 21.4 (70.5) | 15.0 (59.0) | 6.9 (44.4) | −2.6 (27.3) | −7.8 (18.0) | 7.8 (46.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −12.6 (9.3) | −10.8 (12.6) | −3.6 (25.5) | 4.7 (40.5) | 12.2 (54.0) | 16.9 (62.4) | 18.9 (66.0) | 16.2 (61.2) | 10.4 (50.7) | 3.6 (38.5) | −5.4 (22.3) | −10.7 (12.7) | 3.3 (37.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −15.5 (4.1) | −14.1 (6.6) | −7.3 (18.9) | 0.3 (32.5) | 6.9 (44.4) | 12.0 (53.6) | 14.4 (57.9) | 12.2 (54.0) | 6.8 (44.2) | 1.0 (33.8) | −7.8 (18.0) | −13.3 (8.1) | −0.4 (31.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −44.6 (−48.3) | −42.4 (−44.3) | −39.2 (−38.6) | −21.8 (−7.2) | −13.5 (7.7) | −5.3 (22.5) | 1.5 (34.7) | −2.2 (28.0) | −9.0 (15.8) | −22.0 (−7.6) | −39.2 (−38.6) | −44.0 (−47.2) | −44.6 (−48.3) |
| Average mm (inches) | 25 (1.0) | 19 (0.7) | 25 (1.0) | 31 (1.2) | 47 (1.9) | 73 (2.9) | 93 (3.7) | 75 (3.0) | 45 (1.8) | 41 (1.6) | 33 (1.3) | 28 (1.1) | 534 (21.0) |
| Average extreme snow depth cm (inches) | 33 (13) | 42 (17) | 38 (15) | 5 (2.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.4) | 8 (3.1) | 21 (8.3) | 42 (17) |
| Average rainy days | 1 | 1 | 5 | 13 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 22 | 22 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 147 |
| Average snowy days | 26 | 23 | 18 | 10 | 4 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 13 | 23 | 25 | 144 |
| Average (%) | 79 | 75 | 68 | 60 | 58 | 63 | 68 | 73 | 75 | 75 | 78 | 79 | 71 |
| Mean monthly | 47 | 94 | 164 | 206 | 256 | 272 | 269 | 217 | 143 | 78 | 51 | 37 | 1,834 |
| Source 1: Pogoda.ru | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
| Year | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1897 | 37,399 | — |
| 1926 | 134,831 | +260.5% |
| 1939 | 425,533 | +215.6% |
| 1959 | 778,602 | +83.0% |
| 1970 | 1,025,045 | +31.7% |
| 1979 | 1,211,172 | +18.2% |
| 1989 | 1,364,621 | +12.7% |
| 2002 | 1,293,537 | −5.2% |
| 2010 | 1,349,772 | +4.3% |
| 2021 | 1,544,376 | +14.4% |
According to the results of the 2021 Census , the population of Yekaterinburg was 1,544,376 ; [64] up from 1,349,772 recorded in the 2010 Census . [7]
As of 2021, the ethnic composition of Yekaterinburg was: [65]
| Ethnicity | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1,172,704 | 91.0% | |
| 27,431 | 2.1% | |
| 13,102 | 1.0% | |
| 8,769 | 0.7% | |
| 6,121 | 0.5% | |
| 4,987 | 0.4% | |
| 4,755 | 0.4% | |
| 4,307 | 0.3% | |
| 4,014 | 0.3% | |
| Others | 42,033 | 3.3% |

Christianity is the predominant religion in the city, of which most are adherents to the Russian Orthodox Church. The Yekaterinburg and Verkhotursky diocese is located in the Holy Trinity Cathedral in the city. Other religions practised in Yekaterinburg include Islam , Old Believers , Catholicism , Protestantism , and Judaism .
Yekaterinburg has a significant Muslim community, but it suffers from a lack of worship space: there are only two small mosques . Another mosque was built in the nearby city of Verkhnyaya Pyshma . On 24 November 2007, the first stone was laid in the construction of a large Cathedral Mosque with four minarets , and space for 2,500 parishioners in the immediate vicinity of the cathedral and a synagogue , thus forming the "area of the three religions". [66] The mosque was planned to be built for the SCO summit, but due to funding problems, construction did not move from zero and is now frozen.
Construction of a Methodist church started in 1992, and with the help of American donations, finished in 2001. [67] A synagogue was opened in 2005, on the same place a 19th-century synagogue was demolished in 1962.
Most of the city's religious buildings were destroyed during the Soviet era, in addition to the synagogue, the three largest Orthodox churches in Yekaterinburg were demolished – the Epiphany Cathedral, the Ekaterininsky Cathedral, and the Great Zlatoust Church . Other Christian churches such as the Lutheran Church of Yekaterinburg and the Roman Catholic Church of St. Anne (a new Catholic St. Anne's Church was built in 2000) were demolished as well. Other churches were used as warehouses and industrial sites. The only religious building in Yekaterinburg in the Soviet era was the Cathedral of St. John the Baptist. Recently, some churches are being rebuilt. Since 2006, according to the surviving drawings, the Great Zlatoust Church was restored in 2012. On 17 April 2010, the city was visited by Patriarch Kirill . [68]
Yekaterinburg is the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast . [1] Within the framework of the administrative divisions , it is, together with twenty-nine rural localities , incorporated as the City of Yekaterinburg, [9] an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts . [1] As a municipal division, the City of Yekaterinburg is incorporated as Yekaterinburg Urban Okrug. [10]
| Administrative districts of Yekaterinburg | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | Name | Area (2019) | Population (2019) | Founded | Head | Website | Dialing code(s) | Subdivisions | |||
| 1 | Akademicheskiy | 81,000 | 2020 | Smirnyagin Nikolai Sergeevich | +7 3432, +7 3433 | 3 | |||||
| 2 | Verkh-Isetsky | 240 square kilometres (93 sq mi) | 221,207 | 1919 | Morozov Andrey Mikhailovich | 1 December 2021 at the | +7 3432, +7 3433 | 5 | |||
| 3 | Zheleznodorozhnyy | 126.3 square kilometres (48.8 sq mi) | 221,207 | 1938 | Pershin Vitaly Pavlovich | 1 March 2022 at the | +7 343 | 8 | |||
| 4 | Kirovsky | 72 square kilometres (28 sq mi) | 228,864 | 1943 | Bolikov Vladimir Yurievich | 15 March 2022 at the | +7 343 | 7 | |||
| 5 | Leninsky | 25 square kilometres (9.7 sq mi) | 156,723 | 1934 | Beruashvili Elena Zauryevna | 15 March 2022 at the | +7 343 | 3 | |||
| 6 | Oktyabrsky | 157 square kilometres (61 sq mi) | 148,981 | 1934 | Kostenko Igor Vitalievich | 10 November 2021 at the | +7 3432 | 11 | |||
| 7 | Ordzhonikidzevsky | 102 square kilometres (39 sq mi) | 286,482 | 1934 | Kravchenko Roman Gennadievich | 16 March 2022 at the | +7 3433 | 6 | |||
| 8 | Chkalovsky | 402 square kilometres (155 sq mi) | 275,571 | 1943 | Shipitsyn Evgeny Viktorovich | 9 May 2019 at the | +7 3432 | 10 | |||
Each district is not a municipal formation, and the historical centre of the city is divided into five inner-city districts (except Chkalovsky and Ordzhonikidzevsky).
A district named Akademicheskiy was formed from the parts of Leninsky and Verkh-Isetsky districts on 3 January 2020. [70] On 1 October 2021, more settlements were transferred from Verkh-Isetsky to Akademicheskiy district. [71]

The Charter of Yekaterinburg establishes a four-link system for the organisation of local authorities, which includes: the Head of Yekaterinburg, who serves as the chairman of the Yekaterinburg City Duma, the Yekaterinburg City Duma, the Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg, and the Chamber of Accounts. [74]
According to the charter of Yekaterinburg, the highest official of the municipal formation is the mayor of Yekaterinburg. The mayor is elected by universal suffrage, but since 3 April 2018, the procedure for direct elections of the mayor of the City of Yekaterinburg was abolished. The mayor of the city is endowed with representative powers and powers to organize activities and guide the activities of the City Duma. In addition, the mayor of the city exercises other powers such as concluding a contract with the head of the city administration and ensuring compliance with the Russian Constitution, Russian legislation, the city charter, and other normative acts. [75] [76]
In the event of a temporary absence of the mayor of Yekaterinburg, his authority under his written order is exercised by the deputy mayor of Yekaterinburg. [77]
The representative body of the municipal formation is the Yekaterinburg City Duma, which represents the city's entire population. The membership of the Duma is 36 deputies (18 deputies were elected in single-mandate constituencies and 18 in a single electoral district). Residents of the city elect deputies on the basis of universal suffrage for a period of 5 years. [74]
The executive and administrative body of the municipal formation is the Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg, led by the head of the Administration, currently held by Aleksandr Yacob. The administration is endowed with its own powers to resolve issues of local importance, but it is under the control and accountable to the Yekaterinburg City Duma. The building of the Administration of Yekaterinburg is located on 1905 Square . [76]
The Chamber of Accounts is a permanently operating body of external municipal financial control. The Chamber is formed by the apparatus of the City Duma and is accountable to it. The Chamber consists of the chairman, deputy chairman, auditors and staff. The structure and number of staff of the chamber, including the number of auditors, is determined by the decision of the City Duma. The term of office of the Chamber staff is 5 years. The Chamber of Accounts is a legal entity. [77]

In accordance with the regional charter, Yekaterinburg is the administrative centre of the Sverdlovsk Oblast. [1] The executive power is exercised by the governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast, the legislative power by the legislative assembly of Sverdlovsk Oblast, and the judicial power by the Sverdlovsk Regional Court, located in the building of the Palace of Justice. [78] The building serving the regional government is the White House and the building serving the legislative assembly is located next to it on October Square. The ministries of the Sverdlovsk Region are located in the building of the regional government, as well as in other separate buildings of the city. [79]

Yekaterinburg serves as the centre of the Ural Federal District. As a result, it serves as the residence of the presidential envoy , the highest official of the district and part of the administration of the President of Russia. The residence is located the building of the regional government on October Square near the Iset River embankment.

In addition, Yekaterinburg serves as the centre of the Central Military District and more than 30 territorial branches of the federal executive bodies, whose jurisdiction extends not only to Sverdlovsk Oblast, but also to other regions in the Ural Mountains, Siberia, and the Volga Region.
According to the results of the September 2013 elections, the mayor of the city was Yevgeny Roizman , nominated by the Civil Platform party. Out of the 36 seats in the City Duma, 21 belong to United Russia , 7 to A Just Russia , 3 to the Civil Platform, 2 to the Communist Party and 1 seat to the LDPR . The turnout in the mayoral elections was 33.57%. [80]
| 78,289 | 38.4% | ||||
| 31,288 | 15.4% | ||||
| 25,869 | 12.7% | ||||
| 22,293 | 10.9% | ||||
| 11,340 | 5.6% | ||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
It was the last popular vote in Yekaterinburg. Since 2018, there have been no elections, but a vote in the Municipal Duma. On 25 September 2018 the majority of the representatives in the Duma voted in favour of the Vice-Governor of Sverdlovsk oblast, Alexander Vysokinskiy.
Yekaterinburg is one of the largest economic centres in Russia. It is included in the City-600 list (it unites the 600 largest cities in the world that produce 60% of global GDP), compiled by the McKinsey Global Institute, a research organisation. In 2010, the consulting company estimated the gross product of Yekaterinburg to be about $19 billion (according to the calculations of the company, it should grow to $40 billion by 2025). [82] [83]
By volume of the economy, Yekaterinburg ranks third in the country, after Moscow and St. Petersburg. According to a research of the Institute for Urban Economics, in the ranking of the largest cities and regional capital cities according to economic standards for 2015, Yekaterinburg ranked third. The city's gross urban product (GVP) was 898 billion rubles. Per capita GDP was 621.0 thousand rubles (18th place). [84] In 2015, the gross urban product of the Yekaterinburg metropolitan area amounted to 50.7 billion international dollars (the fourth place in the country) or 25.4 thousand international dollars in terms of per inhabitant of the metropolitan area. [85]
In the Soviet era, Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) was a purely industrial city, with a share of industry in the economy of 90% (of which 90% were in defense production). With Chelyabinsk and Perm, the three cities formed what to be the Urals industrial hub. [86]
The former head of Yekaterinburg, Arkady Chernetsky, has set the goal of diversifying the city's economy, which has resulted in the development of sectors such as warehousing, transportation, logistics, telecommunications, financial sector, wholesale and retail trade, etc. in Yekaterinburg. [86] Economist-geographer Natalia Zubarevich points out that at the present stage, Yekaterinburg has practically lost its industrial specialisation. [87]

The standard of living in Yekaterinburg exceeds the average standard across Russia. According to the Department of Sociology of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, it is among the top ten cities with the highest standard of living. Compared to other Russian cities with a population of around or over one million, in 2015, Yekaterinburg held a leading position in terms of average monthly wages and retail turnover, in terms of the total volume of investments in fourth place of fixed assets, and second place in housing placement. [88] [89]

The average monthly wage in Yekaterinburg following the results of 2019 was 54,976 rubles. This is the first place among the millionth municipalities of the Russian Federation. [90] There are on average 440,300 people employed by large and middle-sized organisations and companies. The unemployment rate at the end of 2015 was 0.83% of the total economically active population. Locals labelled the main problems of the city such the current state of the healthcare system, housing system, and transportation system. [89] [91]
The budget of Yekaterinburg in 2015 was executed on income in the amount of 32,063.6 million rubles, for expenses in the amount of 32,745.8 million rubles. Among the budget expenditures: 17 billion rubles were spent on education, over 1 billion rubles on culture, and about 900 million rubles on health. The main part of the revenue of the city treasury was its own tax and non-tax revenues (more than 18 billion rubles). The revenues from the regional and federal budgets were at the lowest level in 10 years. Specialists noted a decrease in tax revenues and an increase in tax debt (exceeded 2 billion rubles). [89] [92]
The main budget expenditures are the development of the economy (which accounts for 19% of expenditures) and the social security of the townspeople (11% of expenditures go). Cities such as Perm, Kazan and Ufa, spend for these purposes in a smaller percentage of costs (from 2 to 6%). Also, a fairly strict budgetary discipline is noted—the budget deficit is kept at the level of 2% of its volume. [93]

Yekaterinburg is one of the largest financial and business centres in Russia, with offices of multinational corporations, representative offices of foreign companies, and a large number of federal and regional financial and credit organisations. The financial market of Yekaterinburg is characterised by stability and independence, based both on the broad presence of large foreign and Moscow credit organisations and on the availability of large and stable local financial holdings. [94]
The financial sector of Yekaterinburg has more than 100 banks, including 11 foreign banks. The list of the largest Russian banks for assets for 2016 included 10 banks registered in Yekaterinburg, including but not all: Ural Bank for Reconstruction and Development, SKB-Bank, Uraltransbank, and UM Bank. [95] [96]
IT "SKB Kontur" from Yekaterinburg – the largest software manufacturer in Russia – first place according to the RAEX rating [97]
Also in Yekaterinburg is the Ural headquarters of the Central Bank of Russia. Since 7 August 2017, by order of the Bank of Russia, the branches of the Siberian, Far Eastern and part of the Prevolzhsky Federal Districts have been transferred to the control of the Ural Megaregal Directorate. Thus, this is one of the three main departments of the Mega-regulator in the territory of Russia. [98]
A major role in the formation of Yekaterinburg as a business centre has its infrastructural potential, which is growing at a high rate: transport accessibility for Russian and foreign economic entities, the availability of hotels, advanced communication services, business related services (consulting, exhibition activities, etc.). [94] Yekaterinburg has its own central business district, Yekaterinburg City. [99]

Yekaterinburg has been a major industrial centre since its foundation. In the 18th century, the main branches were smelting and processing of metal. Since the beginning of the 19th century, machine building appeared, and in the second half of the 19th century, light and food (especially milling) industry was widely spread. A new stage in the development of production occurred during the period of industrialisation – at this time in the city, factories were built, which determined the industry specialisation of heavy engineering. During World War II, Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) hosted about sixty enterprises evacuated from Central Russia and Ukraine. As a result, there was a sharp increase in the production capacity of existing plants and the emergence of new branches of the Urals industry.
At present, more than 220 large and medium-sized enterprises are registered in Yekaterinburg, 197 of them in manufacturing industries. [94] In 2015, they shipped 323,288 million rubles worth of own-produced goods. Production by industry was divided accordingly: metallurgical production and metalworking 20.9%, food production 13.3%, production of electrical equipment, electronic and optical equipment 9.2%, production of vehicles 8.4%, production of machinery and equipment 6.4%, chemical production 5.5%, production of other nonmetallic mineral products 3.7%, production of rubber and plastic products 2.8%, pulp and paper production, publishing and printing 0.5%, and other 29.3%. [100]
Several headquarters of large Russian industrial companies are located in the city: IDGC of Urals, Enel Russia, Steel-Industrial Company, Russian Copper Company, Kalina, NLMK-Sort, VIZ-Stal, Sinara Group, Uralelectrotyazhmash, Automation Association named after academician NA Semikhatov, Ural Heavy Machinery Plant (Uralmash), Fat Plant, Fores, confectionery association Sladko, Machine Building Plant named after M.I. Kalinin, Ural Turbine Plant, Uralkhimmash and others. [101]

Yekaterinburg ranks first in retail trade of the Russian Federation per capita, ahead of Moscow. [102] The consumer market contributes significantly to Yekaterinburg's economy. Revenue of retail stores in 2015 amounted to 725.9 billion rubles, and the number of retailers totaled 4,290. [103] As of 1 January 2016, 36 shopping centers operate in the city, taking up a total area of which was 1,502,700 m 2 (16,175,000 sq ft) . The availability of shopping centres per 1,000 inhabitants increased to 597.2 m 2 (6,428 sq ft) . [104]
Retail areas amounted to 2,019,000 m 2 (21,730,000 sq ft) , with the availability of retail space reached 1,366.3 m 2 (14,707 sq ft) per 1,000 inhabitants. According to these statistics, Yekaterinburg holds leading positions among other major cities of Russia. In the consumer market of Yekaterinburg, 1041 network operators are represented. The number of wholesale enterprises totalled 1,435. Among the Federal construction stores represented in the city, you can select: Leroy Merlin, [105] Castorama, [106] Domostroy, [107] Maxidom, [108] OBI, [109] Sdvor. [110] Yekaterinburg has an agricultural market named Shartashsky. [104] [111]
The revenue of catering in 2015 totalled 38.6 billion rubles. The network of catering enterprises in Yekaterinburg is presented as follows: 153 restaurants, 210 bars, 445 cafes, 100 coffee houses, 582 dining rooms, 189 eateries, 173 fast-food establishments, 10 tea shops, 319 other types of institutions (buffets, cafeterias, catering companies). 82.6% of catering enterprises provide additional services to consumers. [112]
The revenue of the services industry in 2015 totalled 74.9 billion rubles. The fastest pace in the city is developing hairdressing services, sewing and knitting atelier services, pawnshop services, fitness centre services. The network of public service enterprises in Yekaterinburg includes 5,185 facilities. In 2015, the provision of service areas for service enterprises totaled 382.1 m 2 (4,113 sq ft) per 1,000 citizens. The highest concentration of household services is observed in the Verkh-Isetsky, Oktyabrsky and Leninsky districts. [113]
Greenwich Shopping Center, as of 2021, is the largest shopping center in Europe. [114]
The largest store in the world by area is Sima-Land. [115]
Yekaterinburg is a major centre for the Russian tourist industry. In 2015, the city was one of the top five most visited Russian cities (others being Moscow, St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk , and Vladivostok ) according to the Global Destinations Cities Index, which represents the payment system Mastercard . [116] In recent years, a lot of work has been done to create a positive image of Yekaterinburg as a centre for international tourism, including holding of summits for the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) in 2008 and 2009 and the international exhibition Innoprom in 2009 and 2010. [117] In 2014, Yekaterinburg ranked third among Russian cities in popularity among foreign tourists after Moscow and St. Petersburg. [118]
In 2015, the total flow of inbound tourism grew by 10% compared to the previous year and amounted to 2.1 million people. [119] In recent years, there has been a tendency to reduce the role of business tourism in the overall flow: if in 2013 about 80% of trips were business, in 2015 their number was already 67%. Most tourists go to "bow to the memory of the last [czar] and his family." In addition, new tourist ideas are developing such as the Bazhov theme, the geological and mineralogical theme, industrial tourism, and the event calendar. [120]
Yekaterinburg is the third largest transport hub of Russia, behind Moscow and St. Petersburg. The city has 6 federal highways, 7 main railway lines, and an international airport. The location of Yekaterinburg in the central part of the region allows for 7 to 10 hours to get from it to any large city of the Urals. [121] The formation of Yekaterinburg as an important transportation hub is largely due to the city's favourable geographical location on a low stretch of the Ural Mountains, through which it was convenient to lay the main roads connecting the European and Eastern parts of Russia. [122]

Yekaterinburg is one of the ten Russian megacities with the largest car fleet (0.437 megacars were registered in the city in 2014), which has been intensively increasing in recent years (by 6–14% annually). [123] [124] The level of car ownership in 2015 has reached 410 cars per 1,000 people. [125] Its pace in the past few years has seriously exceeded the pace of development and the capacity of the road infrastructure. For the first time, transport problems started to appear in Yekaterinburg in the 1980s and though it did not seem threatening at first, the situation gets worse every year. Studies have shown that as early as 2005, the capacity limit for the road network was reached, which has now led to permanent congestion. [126] To increase the capacity of the street-road network, stage-by-stage reconstruction of streets is being carried out, as well as multi-level interchanges being built. In order to reduce the transit traffic, the Sverdlovsk Oblast administration announced two road projects in 2014: the Yekaterinburg Ring Road (EKAD) and an overpass road on Sovetskaya Street. The Yekaterinburg Ring Road would surround the largest municipalities of Yekaterinburg. Its purpose would be to help the city's economy and reduce traffic on the Middle Ring Road of the city, making it easier for civilians to commute around the city than going through the city's traffic congestion. Eventually, the Ring Road would connect to other federal roads in order for easier access between other Russian cities. Construction of the road started in the same year. The projects were assigned to the Ministry of Transport and Communications since the projects were crucial to the city's economy. Officials hope the road projects will build environments more conducive to improving local quality of life and outside investments. Completing these major inter-regional roads will increase productive traffic by 50% to 100%, improving the local economy with its ease of access to industries. [127]
Since 2014, the project for the introduction of paid parking in the central part of Yekaterinburg is being implemented. The project is implemented in parallel with the increase in the number of intercepting parking lots and the construction of parking lots. At the end of 2015, in the central part of the city there were 2,307 paid parking places. [125]
The total length of the road network in Yekaterinburg is 1,311.5 km (814.9 mi) , of which 929.8 km (577.8 mi) is cobbled carriageways, 880 km (550 mi) is with upgraded coverage, 632 km (393 mi) is backbone networks, of which 155 km (96 mi) are on the citywide backbone network movement. 20 interchanges have been constructed at different levels within the city limits, including 11 on the EKAD and 9 on the middle ring. 74 transport facilities (27 bridges across the Iset River, Patrushikha, Mostovka, Istok Rivers, 13 dams on the Iset, Patrushikha, Istok, Olkhovka, Warm, Shilovka Rivers, 23 road overpasses , and 18 out-of-the-way pedestrian crossings) were built as well. [128]
Yekaterinburg is served by the following highways: [129]

Yekaterinburg uses almost all types of public transport. The largest transportation services—the Municipal Association of Bus Enterprises, the Tram-Trolleybus Office, and the Yekaterinburg Metro —transported 207.4 million people in 2015. [130] The total volume of passenger transportation by all land transport modes decreases annually. If the annual passenger traffic of municipal transport was 647.1 million people in 2002, and according to this index the city occupied the third place in the country with a wide margin, then in 2008 this figure would be 412 million people (the fourth place in Russia). [131] [132]

Since 1991, the city operates the sixth metro in Russia and the thirteenth in the CIS . At the moment there is one line with 9 stations. In 2015 49.9 million passengers were transported; according to this metric the Yekaterinburg Metro is the fourth in Russia, behind the Moscow Metro, Saint Petersburg Metro, and Novosibirsk Metro . [133] Although the metro is the second most popular type of public transport, in recent years significant problems have appeared in its work: loss-making, obsolete rolling stock, and a shortage of funds for modernisation. [134] The tram network was established in 1929 and currently [ when? ] plays a leading role in the urban transport system. The volume of passengers carried for 2013 is 127.8 million, [135] but this declines every year (245 million people in 2013 [136] ). In 2016 there were 30 routes operating 459 cars. The total length of the tracks is 185.5 km. As of 2016 [ update ] , the construction of a tram line "Ekaterinburg-Verkhnyaya Pyshma" was planned. [137]

There are 93 bus routes operating in Yekaterinburg, including 30 municipal ones (EMUP "MOAP"). [138] In 2007, 114.5 million passengers were transported by municipal intercity buses (124.6 million in 2006). [139] The decrease in volume is due to the increasing role of the fixed-route taxis in the urban transport system of Yekaterinburg, as well as the high cost of travel. However, the city bus transport network provides significant employment for the people of Ekaterinburg, including the formidable babushkas who collect passenger fares. In the park of EMPU, there are 537 buses. [140] In 2013, there are 19 routes, which employ 250 trolleybuses. The total length of trolleybus lines is 168.4 km. The number of passengers transported by trolleybus in 2007 amounted to 78.4 million (84.3 million in 2006). [139]
In addition, the city operates an electric train route linking the north-western and the southern parts of Yekaterinburg, from Sem' Klyuchey to Elizavet.

Yekaterinburg is a major railway junction. In the Yekaterinburg node, 7 main lines converge (to Perm , Tyumen , Kazan , Nizhny Tagil , Chelyabinsk , Kurgan , and Tavda ). The Sverdlovsk Railway Administration is located in the city, which serves trains on the territory of the Sverdlovsk and Tyumen Regions, the Perm Territory, the Khanty-Mansiysk and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Districts, as well as parts of the Omsk Region, and there is a single road traffic control centre. The Perm–Yekaterinburg–Tyumen section is now part of the main route of the Trans-Siberian Railway .

Yekaterinburg is served by two primary airports: Koltsovo International Airport (SVX) and the smaller Yekaterinburg Aramil Airport . Koltsovo Airport is one of the largest airports in the country, serving 5.404 million passengers (including 3.485 million serviced by domestic airlines, 1.919 million at international flights) in 2017, making it the sixth busiest airport in Russia . [141]

Yekaterinburg has an extensive network of municipal, regional and federal health facilities. There are 54 hospitals, designed at a capacity of 18,200 beds, [142] 272 ambulatory polyclinics, and 156 dental clinics and offices. [143] Some health facilities are based on medical research institutes such as the Research Institute of Phthisiopulmonology, [144] the Research Institute of Dermatology and Immunopathology, [145] and the Ural State Medical University, as well as others.
In clean areas of the city, there is the Yekaterinburg Medical Centre, which includes the Sverdlovsk Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1 (also includes a polyclinic and a boarding house), Central City Hospital No. 40 (polyclinic, therapeutic building, surgical building, infectious body, neuro-surgical building, maternity hospital), Regional Cardiology Centre, Centre for Prevention and Control of AIDS, and MNTK Eye Microsurgery. [146]
Other large medical centres are the Uralmash Health Centre (Hospital No. 14), the Hospital of veterans of the Great Patriotic War, the district hospital of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the district military hospital, the Oncology Centre, the Sverdlovsk Oblast Psychiatric Hospital, the Disaster Medicine Centre, the Sanguis Blood Transfusion Centre, children's versatile hospital No. 9, and the regional rehabilitation centre on Chusovsky lake. There are about 300 pharmacies in the city. [143] The number of doctors in public medical institutions is 11,339 people (83.9 per 10,000 people) and the number of nurses is 16,795 (124 per 10,000 people).
Private medical institutions also operate in the city. [147]

Yekaterinburg's education system includes institutions of all grades and conditions: preschool, general, special (correctional), and vocational (secondary and higher education), as well as others. Today, the city is one of the largest educational centres of Russia, with Yekaterinburg considered to be the leading educational and scientific centre of the Urals . [148]

There are 164 educational institutions in Yekaterinburg: 160 of them operate in the morning and the other 4 in the evening. In 2015, 133,800 people were enrolled in general education institutions, which holds a capacity of 173,161 people. [149] Yekaterinburg's education system also includes state pre-school educational institutions, non-state pre-school institutions, out-of-town health camps, and municipal city health facilities with a one-day stay. [150] Five educational institutions of the city: SUNC UrFU, Gymnasium No. 2, Gymnasium No. 9, Gymnasium No. 35, and Lyceum No. 135, were included in the rating of the five hundred best schools in the country by the Moscow Center for Continuous Mathematical Education and the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation . [151]
On 16 July 1914, the Ural Mining Institute of Emperor Nicholas II (now the Ural State Mining University ) was established as Yekaterinburg's first educational institution. [152] In 1930, the Sverdlovsk Power Engineering College (now the Ural Technical Institute of Communications and Informatics) was opened to train specialists in the field of communications. The Alexei Maximovich Gorky Ural State University (now the Ural Federal University ) became the first university in Yekaterinburg by decree of the Council of People's Commissars of the RSFSR , signed by Vladimir Lenin on 19 October 1920. The Sverdlovsk Engineering and Pedagogical Institute (today the Russian State Vocational and Pedagogical University) became the first university of the USSR for the training of engineering and pedagogical personnel when it was opened in 1979.

In terms of the level of qualification of the graduates, Yekaterinburg's universities are among the leading in Russia, in particular in terms of the number of graduates representing the current managing elite of the country, Yekaterinburg universities are second only to the educational institutions of Moscow and Saint Petersburg. [153] [154] Currently, there are 20 state universities in the city, which currently holds a total of 140,000 students. [155] In addition, there are 14 non-state institutions of higher education in the city, such as the Yekaterinburg Academy of Contemporary Art and the Yekaterinburg Theological Seminary. The prestigious architecture school, the Ural State Academy of Architecture and Arts , is also located within the city limits. Other institutions of higher education Ural State Pedagogical University, Ural State University of Forestry, Ural State University of Railway Transport, Ural State University of Economics, Military Institute of Artillery, Ural State Conservatory , Ural State Agricultural Academy, Ural State Law Academy , Ural State Medical University, Ural State Academy of Performing Arts, Ural Academy of Public Service, and Institute of International Relations .
In May 2011, the Ural State University and Ural State Technical University merged to form the Boris N. Yeltsin Ural Federal University , making it the largest university in the Urals and the largest university in Russia. As of 1 January 2016, the university had 35,300 students and 2,950 teachers. The university's budget in 2015 totalled 9,1 billion rubles and the volume of research and development work totalled 1,6 billion rubles. [156] As of 2021, UrFU is the largest university in Russia in terms of the number of students, being on the 351st place in the QS World University Rankings. [157] [158] The number of publications of the university in the Web of Science database is about a thousand per year. [159]
There are many branches of non-resident universities in the city, including the Ural branch of the Siberian State University of Telecommunications and Informatics, the Ural branch of the Russian Academy of Private Law, the Yekaterinburg branch of the Plekhanov Russian Economic Academy, the Yekaterinburg branch of the University of the Russian Academy of Education, the Yekaterinburg branch of the Moscow State University, and Sholokhov Humanitarian University, as well as others.

In Yekaterinburg, a large number of print publications are published: about 200 newspapers, the most read being the Ural Worker , Vecherny Yekaterinburg , Oblastnaya Gazeta , and For Change! , and 70 magazines, with most read being Red Burda and I'm Buying . [160] [161]
A television studio was built in Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) in 1955 and on 6 November of the same year, the first telecast appeared. Coloured television later appeared in 1976. [162] Now the television is broadcast by 19 companies, including but not all: STRC Ural, Channel Four, 41 Home, Channel 10, OTV, Union (Orthodox), and UFO 24. Broadcasting is carried out from the TV tower on Lunacharsky street (television studio GTRK Ural), the TV tower on the Moskovskiy Hill, and from the TV tower (radio relay tower) on Blyukher Street. In 1981, construction of a new television tower was started, which was to become the second tallest in Russia after the Ostankino Tower and cover the territory of most of the Sverdlovsk region, but economic difficulties postponed construction. As a result, the television tower was the tallest uncompleted structure in the world. On 24 March 2018, the television tower was demolished by detonation for the city's beautification in preparation of the 2018 FIFA World Cup . [163] The Shartash radio mast, which broadcasts, is the tallest structure in the city, with a height of 263 meters. [164] In addition, several dozens of national and local news agencies are broadcast in Yekaterinburg, with the most watched being ITAR-TASS Ural, RUIA-Ural, and Interfax-Ural.
At the moment [ when? ] , there are 26 internet providers and 6 cellular operators in the city. [165] According to Yekaterinburg News , the city has signed a cooperative agreement with the Russian mobile operator Vimpelcom , working under the Beeline brand. The partnership will involve cooperation on investment projects and social programmes focused on increasing access to mobile services in the city. Beeline has launched an initiative to provide Wi-Fi services in 500 public trams and trolley buses in Yekaterinburg. [166]
| Generation | Mobile communication standard | Operators |
|---|---|---|
| , , , , Motive | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia, Motive | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia, Motive | ||
| , | MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia | |
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia, Motive, | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, |

Yekaterinburg is a multipurpose cultural centre of the Urals Federal District. [148] There are about fifty libraries in the city. The largest library organisations are the Sverdlovsk Oblast Universal Scientific Library, the V.G. Belinsky Scientific Library, which is the largest public library in Sverdlovsk Oblast, and the Municipal Library Association, which is composed of 41 libraries throughout the city, including the AI Herzen Central City Library. [167]
There are about 50 different museums in the city. [168] Yekaterinburg has unique museum collections, such as the collections of Russian paintings in the Yekaterinburg Museum of Fine Arts and the Nevyansk icons in the Nevyansk Icon Museum , with more than 300 icons representing the eighteenth through the twentieth centuries on display. There is also a unique exhibit, the Kaslinsky cast iron pavilion, which received main awards at the 1900 World Exhibition in Paris. The Kasli Pavilion was registered by UNESCO as the only cast-iron architectural structure in the world, which is in the museum collection. [169] Museums of the city also have collections of jewellery and stone ornaments. The United Museum of Writers of the Urals presents exhibitions in memory of writers such as Dmitry Mamin-Sibiryak and Pavel Bazhov . It also is the home of the Shigirskaya Kladovaya ( Шигирская кладовая ), or Shigir Collection, which includes the oldest known wooden sculpture in the world. The sculpture was found near Nevyansk and originally estimated to have been made approximately 9,500 years ago, but now is estimated to have been made 11,500 years ago. [170] Yekaterinburg museums annually participate in the international event Long Night of Museums .
Yekaterinburg has the third most theatres in Russia. [171] The influence of theatrical life of the city was made by the Moscow Art Academic Theater and the Central Theater of the Soviet Army when they evacuated to Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) during World War II, and they had their own theater in the city. [172] Notable theatres that operate in the city are Academic Theater of Musical Comedy, Drama Theater, Kolyada-Theater , the youth theatre, and the puppet theatre, as well as others. The Yekaterinburg Opera and Ballet Theater received four awards at the Golden Mask 2020 Festival in Moscow, including the main Golden Mask for the Best Opera Performance [173]
In 2014, the city showcased its education, literary, art, and theatre culture through the Russian Year of Culture Programme. [174]
The city has a well-developed film industry. Opened back in 1909, Laurage was the first cinema in Yekaterinburg. In 1943, the Sverdlovsk Film Studio was opened and produced its first feature film Silva a year later. After the Second World War, the studio produced up to ten feature films a year. There are more than 20 cinemas in Yekaterinburg, the oldest of which is the Salyut, while the most capacious is the Cosmos spacecraft. [175] [176] There are also chains of movie theatres such as Premier-Zal, Kinomaks, and Kinoplex, which usually open in shopping and entertainment centres.
A number of popular Russian rock bands, such as Urfin Dzhyus, Chaif , Chicherina , Nautilus Pompilius , Nastya, Trek, Agata Kristi , Slaughter to Prevail and Smyslovye Gallyutsinatsii , were originally formed in Yekaterinburg ( Ural Rock is often considered as a particular variety of rock music. Yekaterinburg and St. Petersburg are actually considered to be the main centres of the genre in Russia). Also, opera singers like Boris Shtokolov , Yuri Gulyayev , Vera Bayeva graduated from the Urals State Conservatory. The Ural Philharmonic Orchestra (currently conducted by Dmitry Liss ), founded by Mark Paverman and located in Yekaterinburg, is also very popular in Russia and in Europe, as well as the Ural Academic Popular Chorus, a folk-singing and dance ensemble. [ citation needed ]

Yekaterinburg V. I. Filatov State Circus is located in the centre of the city, on the western bank of the Iset River. In 2012, the Yekaterinburg Circus was nominated "Best Circus of the Year" for the circus show Sharivari by the Rosgoscirk and the Ministry of Culture . [177]
The Presidential Center named after Boris Yeltsin was built in Yekaterinburg in 2015. It is considered to be a public, cultural and educational center. Center has its art gallery, library, museum equipped with the newest multimedia technologies that help to present the documents, video materials and archive photos. In 2017, the Yeltsin Center was recognized as the best museum in Europe by the Council of Europe, the first of the museums in Russia. [178]
The Urals Society of Natural Science Lovers pushed Yekaterinburg to have a zoo. Currently, the zoo has more than 1,000 animals that belong to more than 350 species. The zoo covers an area of 2.7 hectares.
On 18 June 2011, Yekaterinburg launched Red Line as a pedestrian tourist route for self-guided tours by residents and visitors to go to 34 landmarks in the historical section of the city. [179]

Many buildings of Yekaterinburg are ranged from a different number of architectural styles. The city had a regular layout, based on the fortresses of the Renaissance and by the principles of French town planning during the 17th century. By the 18th century, the Baroque movement was not that influential in Yekaterinburg, with the style being seen in churches which later declined [180]
In the first half of the 19th century, neoclassicism grew influential in the Yekaterinburg's architecture. The estates were built in the neoclassic style, including the main house, wings, services, and often an English-style park. This style's influence in Yekaterinburg is mostly due to the contributions of architect Michael Malakhov, who worked in the city from 1815 to 1842. He designed the assemblies of the Verkhne-Isetsky factory as well as the Novo-Tikhvinsky Monastery. [180]
At the beginning of the 20th century, eclecticism became a dominant influence in Yekaterinburg's architecture. Buildings such as the Opera House and Yekaterinburg railway station were built in this style. During the 1920s and the 1930s, constructivism took effect, influencing residential complexes, industrial buildings, stadiums, etc. Architects Moses Ginzburg, Jacob Kornfeld, the Vesnina brothers, Daniel Friedman, and Sigismund Dombrovsky contributed greatly to the constructivism in the city. More than 140 structures in Yekaterinburg are designed through the constructivist style. [181]

During the 1930s to 1950s, there was a turn back to neoclassicism, with much attention paid to public buildings and monuments. Notable examples include the buildings of the Ural Industrial Institute on Lenin Avenue, the City Party Committee and the City Council Executive Committee building (now the City Administrative building), the District Officers' House, and the House of Defense complex. Cultural buildings are built in the squares in orderly composition. In these years, architects Golubev, K. T. Babykin, Valenkov worked fruitfully in Yekaterinburg with this style. In the 1960s, changes in the approach to construction led to widespread distribution of apartment blocks common in the Khrushchev era . Buildings built by individuals were rare, among them being: KKT "Kosmos", the Palace of Youth, and DK UZTM. [182]
From the 1960s to the 1980s, as industrial development grew in Yekaterinburg, so did rationalism . The situation changed in the 1990s when Russia transferred into a market economy. At that time, older buildings were restored, giving the urban area a new environment such as: the Cosmos Concert Hall, the Puppet Theater, the children's ballet theatre The Nutcracker, the Palace of Justice, the Cathedral of the Blood, and the Church of the Transfiguration . At the same time, the construction of new buildings was accompanied by the demolition of historical buildings, leading to the development of the "facade" phenomenon, where the facades of historic buildings are preserved while adjacent modern buildings are built. [183]
The centre of Yekaterinburg became the centre of new construction, where banks, business centres, hotels, luxury residential complexes, and sports and shopping centres were built. High-tech architecture grew influential, with buildings such as the Center for Railway Transportation Management, the Summit business centre, the Aquamarine residential complex, and the retail strip at Vaynera Street being notable examples. Along with this, postmodernism revived interest in the older architectural styles of Yekaterinburg, growing more emphasis on historicalism and contextualism. In the late 1990s, architects grew interested in regionalism . [183]
At the beginning of the 21st century, Yekaterinburg architects turned back to the Soviet-based avant-garde, and influence future city buildings with the neoconstructivist style. The practice of attracting large foreign investors to projects has become popular. In 2007, the construction of the Central business district started, being headed by the French architect Jean Pistre. [183] In 2010, Yekaterinburg became one of the largest centers for the construction of High-rise buildings. In the city, 1,189 high-rise buildings were built, including 20 skyscrapers, the tallest of which is the Iset Tower , with a height of 209 meters. [184]
Yekaterinburg is also a leading sports centre in Russia. A large number of well-known athletes, both world and Olympics champions, are associated with the city. Since 1952, Yekaterinburg athletes have won 137 medals at the Olympic Games (46 gold, 60 silver and 31 bronze). In the 2008 Summer Olympics , 8 residents of Yekaterinburg returned with medals (1 gold, 3 silver and 4 bronze). [185]

In 1965, Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk), along with a number of Russian cities, hosted the Bandy World Championship . In 2018, Yekaterinburg was one of the 11 Russian cities that hosted the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The matches were played on the upgraded Yekaterinburg Arena (called Central Stadium before the World Cup). [186]
Yekaterinburg has a total of 1728 sports facilities, including 16 stadiums with stands, 440 indoor gyms and 45 swimming pools. There are 38 sports children's and youth schools for reserves for the Olympic Games, in which more than 30,000 people are participating. [187]
Sport clubs
Yekaterinburg has many professional sports clubs in sports such as volleyball, basketball, futsal , bandy , and ice hockey for both women and men. Bandy club SKA-Sverdlovsk , women's volleyball club VC Uralochka-NTMK , women's basketball club UMMC Yekaterinburg , and futsal club MFK Sinara Yekaterinburg were among the best teams in Russia and Europe.
| Club | Sport | Founded | Current League | League Tier | Stadium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 1st | ||||
| 2006 | 1st | ||||
| Avto Yekaterinburg | 2009 | Jr. 1st | |||
| Spartak-Merkury | 1992 | Women's Hockey Championship | 1st | Sports Palace Snezhinka | |
| 1937 | 1st | ||||
| 1935 | 2nd | ||||
| 2006 | 2nd | ||||
| 1938 | 1st | ||||
| Lokomotiv-Izumrud Yekaterinburg | 1945 | 2nd | |||
| 1966 | Women's Volleyball Superleague | 1st | Metallurg-Forum | ||
| 1992 | 1st |
2018 FIFA World Cup

Yekaterinburg hosted four matches of the 2018 FIFA World Cup [59] Yekaterinburg is one of the 11 Russian cities that hosted the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The matches were played on the upgraded Yekaterinburg Arena . [186]
For the World Cup 2018, from 7 October 2015 to 29 December 2017, the Central Stadium was upgraded to bring it into compliance with FIFA requirements for the World Cup and was renamed Yekaterinburg Arena. The architectural concept of the new stadium is built on a combination of historical walls and the built-in core of the modern arena. During the reconstruction of the sports facility, which is a monument of history and culture, the facades are carefully preserved, and the arena itself is equipped with the latest technical achievements of the sports industry. Temporary stands extending outside the stadium's original perimeter were erected to comply with the FIFA requirement of seating for 35,000 spectators. They can hold a total of 12,000 spectators, but the seating will be removed after the World Cup, decreasing the seating capacity back to 23,000. [188] [189]
The FIFA Fan Fest in Yekaterinburg is located in the Mayakovsky Central Park of Entertainment and Culture. Located just outside the city centre in a popular and well-known amusement park, it will have a capacity to hold 17,000 people. [190]
Koltsovo Airport was also reconstructed and had a second runway built. In addition, work was done to prepare another passenger terminal, modernize the technical infrastructure, and launch the business aviation hangar. The airport's capacity in preparation for the World Cup has increased to two thousand people per hour. The street and road network was also upgraded. [191]
The United States, [192] United Kingdom, [193] Germany, [194] France, [195] China [196] and several other countries have consulates in Yekaterinburg.
The BRIC countries met for their first official summit on 16 June 2009, in Yekaterinburg, [197] with Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva , Dmitry Medvedev , Manmohan Singh , and Hu Jintao , the respective leaders of Brazil, Russia, India and China, all attending.
The foreign ministers of the BRIC countries had also met in Yekaterinburg previously on 16 May 2008.
In June 2013, at the 153rd General Assembly of the Bureau of International Expositions held in Paris, representatives from Yekaterinburg presented the city's bid to host the 2020 World Expo . Yekaterinburg's concept for the upcoming exhibition relates to the impact of globalisation on the modern world.
Russian President Vladimir Putin confirmed during a televised statement in English to earmark the required funds to build an exhibition complex large enough to receive the estimated 30 million visitors from more than 150 countries. [198]
Yekaterinburg later bid for the Expo 2025 . Yekaterinburg's concept for the bid exhibition relates to the technologies to make people happy by changing the world with innovation and quality of life. The host was announced on 23 November 2018 and Yekaterinburg lost out to Osaka, Japan.
Yekaterinburg hosted the Global Summit on Manufacturing and Industrialization (GMIS — 2019) GMIS under the auspices of the United Nations. [199] The annual INNOPROM exhibition is among the five largest industrial exhibitions in the world. [200]
Yekaterinburg is twinned with: [201]
- Anton Bakov , Leader of the Monarchist Party
- Irina Antonenko , Miss Russia 2010
- Aleksei Balabanov , film director, screenwriter, producer
- Vera Bazarova , pairs figure skater
- Pavel Bazhov , folklorist and children's author
- Old Man Bukashkin , artist and poet
- Pavel Datsyuk , ice hockey player
- Nikolay Durakov , bandy legend
- Chiang Fang-liang , former first lady of Taiwan
- Aleksey Fedorchenko , film director, producer
- Denis Galimzyanov , sprinter cyclist
- Anna Gavrilenko , Group rhythmic gymnast Olympic Gold medalist
- Nikolay Karpol , national women volleyball team coach
- Nikolai Khabibulin , ice hockey player
- Alexei Yashin , ice hockey player
- Alexei Khvostenko , avant-garde poet, singer-songwriter, artist, and sculptor
- Nikolay Kolyada , actor, director, writer, playwright, and playwriting teacher
- Ilya Kormiltsev , poet, translator, publisher
- Olga Kotlyarova , Olympic runner
- Maxim Kovtun , figure skater
- Vladislav Krapivin , children's author
- Valeria Savinykh , WTA Professional player
- Nikolay Krasovsky , mathematician
- Yulia Lipnitskaya , figure skater
- Iskander Makhmudov , businessman
- Vladimir Malakhov , ice hockey player
- Gennady Mesyats , vice-president of the Russian Academy of Sciences
- Maxim Miroshkin , pairs figure skater
- Vladimir Mulyavin (1941 – 2003), Belarusian musician and the founder of the folk-rock band Pesniary [202]
- Alfia Nazmutdinova , rhythmic gymnast
- Ernst Neizvestny , sculptor
- Oleg Platonov , writer, historian, and economist
- Daria Pridannikova , rhythmic gymnast
- Eduard Rossel , ex-governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast
- Boris Ryzhy , poet
- Mikhail Shchennikov , race walker
- Vera Sessina , rhythmic gymnast
- Georgy Shishkin , painter
- Vassily Sigarev , playwright, screenwriter, film director
- Anastasiia Tatareva , Group rhythmic gymnast Olympic Gold medalist
- Sergei Tchepikov , Olympic biathlon competitor
- Vladimir Tretyakov , ex-rector of the Ural State University
- Lev Vainshtein , Olympic shooter
- Sergei Vonsovsky , physicist
- Alexander Dudoladov , writer
- Alexander Malinin , singer
- Petr Yan , Former UFC Bantamweight Champion
- A ballistic missile submarine of the Project 667BDRM Delfin class ( NATO reporting name: Delta IV ) is named Ekaterinburg (K-84/"807") in honour of the city.
- The asteroid 27736 Ekaterinburg was named in the city's honour on 1 June 2007.
Related Research Articles
Sverdlovsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia located in the Ural Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Yekaterinburg, formerly known as Sverdlovsk. Its population is 4,268,998.

Irbit is a town in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located 203 kilometers (126 mi) from Yekaterinburg by train or 250 kilometers (160 mi) by car, on the right bank of the Nitsa. Population: 37,009 (2021 Census) ; 38,357 (2010 Census) ; 43,318 (2002 Census) ; 51,708 (1989 Soviet census) .

Koltsovo International Airport is the international airport serving Yekaterinburg, Russia, located 16 km (10 mi) southeast of the city. Being the largest airport in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Koltsovo also serves nearby towns such as Aramil, Sysert, and Polevskoy. In general, the airport is responsible for serving approximately 4,290,000 people yearly. The airport is a hub for Ural Airlines, RusLine and Aviacon Zitotrans. Due to its location in the center of Russia, Yekaterinburg's airport is included in the "Priority Airports" list of Russia's Federal Air Transport Agency (Rosaviatsia).

Serov is a mining and commercial town in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the eastern foothills of the Ural Mountains, on the left bank of the Kakva River, about 350 kilometers (220 mi) north of Yekaterinburg. Population: 99,373 (2010 Census) ; 99,804 (2002 Census) ; 104,158 (1989 Soviet census) .

Pervouralsk is a city in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Chusovaya River 39 kilometers (24 mi) west of Yekaterinburg, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 124,528 (2010 Census) ; 132,277 (2002 Census) ; 142,193 (1989 Soviet census) ; 122,000 (1974); 90,000 (1959); 44,000 (1939).

Sredneuralsk is a town under the administrative jurisdiction of the Town of Verkhnyaya Pyshma in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the shore of Iset Lake, at the head of the Iset River, 25 kilometers (16 mi) north of Yekaterinburg. Population: 20,449 (2010 Census) ; 19,555 ; 18,786 (1989 Soviet census) .

Anton Alekseyevich Bakov is a Russian businessman, monarchist politician, traveler, writer and human rights activist. He is the chairman of the Russian Monarchist Party, was a member of the 4th convocation of the State Duma of Russia from 2003 to 2007 and was a candidate at 2018 Russian presidential election. Due to being known for a long series of unusual political projects such as Ural franc, the writer Alexei Ivanov coined him a "political Leonardo".

Alexander Sergeevich Misharin is the former governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast, a region in Russia. He was appointed in 2009 after resignation of the previous governor, Eduard Rossel and resigned on May 14, 2012. Prior to his governorship, he made a career in the railway industry, rising to Russia's Deputy Railway Minister. He was appointed first vice-president of Russian Railways and head of Skorostniye Magistrali, the Russian high-speed rail developer and operator on November 28, 2012.

Isetsky District is an administrative district (raion), one of the twenty-two in Tyumen Oblast, Russia. As a municipal division, it is incorporated as Isetsky Municipal District . It is located in the west of the oblast. The area of the district is 2,751 square kilometers (1,062 sq mi). Its administrative center is the rural locality of Isetskoye. Population: 26,061 ; 26,565 (2002 Census) ; 25,862 (1989 Soviet census) . The population of Isetskoye accounts for 28.7% of the district's total population.

Gostiny Dvor – is a shopping (merchant) center in the historical center of Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

The Men's College building is a mansion in the historical center of Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Zyryanov manor house is located in the historical center of Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Church of the Intercession of the Most Holy Mother of God - is an Orthodox church in Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Ural Aluminum Smelter Proletarian's Group of Houses is a complex of residential buildings in Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

The Rail Bridge over the Iset River - is an experimental bridge over the Iset River is a unique engineering structure made according to the advanced technology of the late 1930s in Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Boris Yeltsin Street is a street in Yekaterinburg, Russia.
The coat of arms of Yekaterinburg is the official municipal coat of arms of Yekaterinburg, Russia. The current symbol was adopted on 23 May 2008 and consists of a French shield divided horizontally into two fields, with a white mine shaft and a white furnace within the top field, which is green, and a blue wavy bend within the bottom field, which is gold. A gold bear and gold sable are located to the left and right of the shield, respectively. A gold crown with a gold laurel wreath is located above the shield and a gold ribbon is located below the shield. A grey druse is located at the bottom center of the shield.

Yevgeny Vladmirovich Kuyvashev is a Russian politician serving as Governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast since 29 May 2012. He served as the acting governor from 14 May 2012 to 29 May 2012, and again from 17 April 2017 to 18 September 2017.

Alexander Leonidovich Burkov is a Russian politician who served as governor of Omsk Oblast from 2017 to 2023. He is a member of the Central Council of A Just Russia — For Truth party.
The 2022 Sverdlovsk Oblast gubernatorial election took place on 11 September 2022, on common election day. Governor Yevgeny Kuyvashev was re-elected for a third term.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Law #30-OZ
- 1 2 3 Haywood, A. J. (2010). Siberia: A Cultural History , Oxford University Press, p. 32
- ↑ Charter of Yekaterinburg, Article 24.1
- ↑ Official website of Yekaterinburg. Alexander Edmundovich Yakob, Head of Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg Archived 12 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- ↑ "Проект о внесении изменений в Генеральный план развития городского округа – муниципального образования «город Екатеринбург» на период до 2025 года" (in Russian). p. 168. [ permanent dead link ]
- 1 2 Federal State Statistics Service (21 May 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [ Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000 ] (XLS) . Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ↑ "Federal State Statistic Service" . Government of Russia. 1 January 2024 . Retrieved 6 June 2024 .
- 1 2 Государственный комитет Российской Федерации по статистике. Комитет Российской Федерации по стандартизации, метрологии и сертификации. №ОК 019-95 1 января 1997 г. « Общероссийский классификатор объектов административно-территориального деления. Код 65 401 », в ред. изменения №278/2015 от 1 января 2016 г.. (State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation. Committee of the Russian Federation on Standardization, Metrology, and Certification. # OK 019-95 January 1, 1997 Russian Classification of Objects of Administrative Division (OKATO). Code 65 401 , as amended by the Amendment # 278/2015 of January 1, 2016. ).
- 1 2 3 Law #85-OZ
- ↑ "Об исчислении времени" . Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). 3 June 2011 . Retrieved 19 January 2019 .
- 1 2 "Срок регистрации домена закончился" . www.ekaterinburg.com . Archived from the original on 21 January 2013 . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ Upton, Clive ; Kretzschmar, William A. Jr. (2017). The Routledge Dictionary of Pronunciation for Current English (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 1552. ISBN 978-1-138-12566-7 .
- ↑ "RUSSIA: Ural'skij Federal'nyj Okrug: Ural Federal District" . City Population.de . 4 August 2020 . Retrieved 2 October 2020 .
- ↑ "Рейтинг столичных городов России от Фонда "Институт экономики города" " . Urbaneconomics.ru .
- ↑ Kolossov, Vladimir; Eckert, Denis (1 January 2007). "Russian regional capitals as new international actors: the case of Yekaterinburg and Rostov" . Belgeo (1): 115–132. doi : 10.4000/belgeo.11686 .
- ↑ "Central Asian Chapter by Eurasian Respiratory and Allergy Consortium" . Era-cac.org . Archived from the original on 12 June 2018 . Retrieved 1 June 2018 .
- ↑ "Yekaterinburg - Entertainment - Russia.com" . Russia.com .
- ↑ "Конструктивизм. Жемчужина архитектуры Екатеринбурга" . www.e1.ru (in Russian). 16 January 2018 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Как Екатеринбург за 10 лет стал столицей конструктивизма" . Strelka Mag (in Russian). Archived from the original on 5 March 2021 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ Урал, Наш (19 May 2016). "Советская утопия: эпоха конструктивизма в Екатеринбурге" . Наш Урал (in Russian) . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Все кругом храпят, а Екатеринбург — пробужденный Когда уральский город объявил себя российской столицей стрит-арта, многие смеялись. А потом он стал ею" . Meduza (in Russian) . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Как Екатеринбург становится столицей стрит-арта" . Российская газета (in Russian). 16 April 2019 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Екатеринбург – столица стрит-арта. Часть первая" . www.uralweb.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 3 March 2021 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Памятникик археологии" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "1.2. Палкинские каменные палатки. Проект 1. | "Образование Урала" " . uraledu.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 5 April 2012 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ ГАМАЮНСКАЯ КУЛЬТУРА – Уральская Историческая Энциклопедия . ural.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 22 July 2014 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Екатеринбург" . Геральдика Свердловской области . Официальный сайт областной думы законодательного собрания. Archived from the original on 8 March 2013 . Retrieved 6 December 2009 .
- ↑ Юрий, Коновалов (26 March 2004). "Первые русские поселения на реке Уктус" . www.okorneva.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 7 June 2024 .
- 1 2 Кулешов, Николай (2001). "Горных заводов щит" . Домострой (4).
- ↑ Архипова, Нина (2001). "Тайны "превысочайшего Камня" ". Родина (11).
- ↑ Корепанов Н. С. Уктус — исток Екатеринбурга — Екатеринбург: Грачёв и партнёры, 2012. — 40 экз. — ISBN 978-5-91256-129-0
- 1 2 3 4 5 Юхт, Александр (1985). Государственная деятельность В. Н. Татищева в 20-е — начале 30-х годов XVIII века (in Russian). Moscow: Наука .
- ↑ "Библиотека истории: Ремесло историка в России – Бердинских В.А." history-library.com . Archived from the original on 1 April 2019 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Завод-крепость – История основания Екатеринбурга – Информационный портал Екатеринбурга . ekburg.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "Основание Екатеринбурга" . Histrf.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ Металлургические заводы Урала XVII—XX вв.: Энциклопедия / глав. ред. В. В. Алексеев. — Екатеринбург : Издательство «Академкнига», 2001.
- 1 2 ipravo.info. "О ликвидации Баженовского и Сысертского районов Уральской области и о расширении городской черты и пригородной зоны города Свердловска – Российский Правовой Портал" (in Russian). ipravo.info. Archived from the original on 19 June 2018 . Retrieved 19 June 2018 .
- 1 2 "History of the Verkh-Isetsky district" . Administration of Verkh-Isetsky district . Archived from the original on 16 December 2021 . Retrieved 7 June 2024 .
- ↑ "Золотой век Екатеринбурга" . Уралнаш. Интересно о Екатеринбурге . 9 October 2019. Archived from the original on 14 August 2021 . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ "50 интересных фактов об Екатеринбурге — Общенет" . obshe.net . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ Massie, Robert K. (22 February 2012). The Romanovs: The Final Chapter . Random House Publishing Group. ISBN 9780307873866 .
- ↑ "FSU News" . fsu.edu . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 История Екатеринбурга – Информационный портал Екатеринбурга . ekburg.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Временное Областное Правительство Урала – Энциклопедия Екатеринбурга – Энциклопедии & Словари" . enc-dic.com . Archived from the original on 20 May 2018 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Главная: НОВОСТИ . familii.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Справочник по административно-территориальному делению Свердловской области" (PDF) . ГАСО (State Archive of the Sverdlovsk oblast). p. 37. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2017 . Retrieved 2 February 2013 .
- ↑ Rappaport, Helen (1999). Joseph Stalin: A Biographical Companion . ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-084-0 .
- ↑ Беркович Артём. "Пермь и Екатеринбург: история соперничества" . Муниципальный музей истории Екатеринбурга. Archived from the original on 25 May 2013 . Retrieved 16 December 2009 .
- ↑ In the name of Victory. Sverdlovsk-Yekaterinburg during the Great Patriotic War of 1941–1945 . 2005 – via Ekaterinburg: Institute of History and Archeology of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
- ↑ "Свердловск – 1983 год" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Интервью – АПИ-Урал" . apiural.ru . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- ↑ "President Yeltsin speaks about Tsar Murder" . BBC News . 17 July 1998 . Retrieved 4 April 2012 .
- ↑ Matthew S. Meselson, et al., "The Sverdlovsk Anthrax Outbreak of 1979", Science 266:5188 (18 November 1994): 1202–1208.
- ↑ Martin McCauley, "Who's who in Russia since 1900", Routledge , 1997: p.133.
- ↑ Ровно 18 лет назад Свердловск снова стал Екатеринбургом . Официальный портал Екатеринбурга (in Russian). Archived from the original on 16 April 2013 . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- ↑ "О возвращении городу Свердловску его исторического названия Екатеринбург, Указ Президиума Верховного Совета РСФСР от 23 сентября 1991 года №1674-1" . docs.cntd.ru . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- ↑ (www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "First BRIC summit concludes | DW | 16 June 2009" . DW.COM . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 FIFA.com. "2018 FIFA World Cup Russia" . fifa.com . Archived from the original on 12 April 2014 . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Russia moves to year-round winter time" . BBC News . 22 July 2014 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 Грязнов Олег Николаевич; Гуляев Александр Николаевич; Рубан Наталья Валентиновна (2015). "Факторы инженерно-геологических условий города Екатеринбурга" . Izvestiia Uralʹskogo Gorno-Geologicheskoĭ Akademii (журнал) (3) (Известия Уральского государственного горного университета ed.). Екатеринбург: Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Уральский государственный горный университет": 5–21. ISSN 2307-2091 .
- ↑ Погода и Климат – Климат Екатеринбург [ Weather and Climate – The Climate of Yekaterinburg ] (in Russian). Weather and Climate (Погода и климат) . Retrieved 8 November 2021 .
- ↑ "WMO Climate Normals for Sverdlovsk 1961–1990" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved 29 October 2021 .
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service. Всероссийская перепись населения 2020 года. Том 1 [ 2020 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1 ] (XLS) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service .
- ↑ "Национальный состав населения" (PDF) . Территориальный орган Федеральной службы государственной статистики по Свердловской области и Курганской области . Retrieved 7 June 2023 .
- ↑ "В Екатеринбурге заложили первый камень в основание соборной мечети – Уральская палата недвижимости" . upn.ru . Archived from the original on 10 October 2012 . Retrieved 5 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Четвертый канал" . channel4.ru . Archived from the original on 20 December 2010 . Retrieved 5 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Встреча Святейшего Патриарха Кирилла с общественностью Уральского федерального округа / Видеоматериалы / Патриархия.ru" . Патриархия.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Устав Свердловской области (с изменениями на 7 декабря 2017 года), Устав Свердловской области от 23 декабря 2010 года №105-ОЗ, Закон Свердловской области от 23 декабря 2010 года №105-ОЗ" . docs.cntd.ru . Retrieved 2 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "Закон Свердловской области Губернатора Свердловской области № 141-ОЗ" . www.pravo.gov66.ru . Retrieved 12 March 2022 .
- 1 2 "Закон Свердловской области от 18.02.2021 № 9-ОЗ ∙ Официальное опубликование правовых актов ∙ Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации" . publication.pravo.gov.ru . Archived from the original on 12 March 2022 . Retrieved 12 March 2022 .
- 1 2 The population of the Russian Federation for municipalities as of 1 January 2019 Archived 16 October 2019 at the Wayback Machine (2 May 2019)
- ↑ "К 2023 году население Академического района вырастет до 120 тысяч человек" . Новый День (in Russian). 27 March 2019 . Retrieved 12 March 2022 .
- 1 2 "Chapter IV. Bodies and officials of local self-government of the municipality "city of Yekaterinburg" " . екатеринбург.рф . 25 July 2017. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016 . Retrieved 19 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации" . publication.pravo.gov.ru .
- 1 2 "Вы точно человек?" . КиберЛенинка . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "О внесении изменений в Устав муниципального образования "город Екатеринбург", Решение Екатеринбургской городской Думы Свердловской области от 12 октября 2010 года №62/29" . docs.cntd.ru .
- ↑ Article 42 of the Charter of Sverdlovsk Oblast
- ↑ "О ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИИ И РЕОРГАНИЗАЦИИ АДМИНИСТРАЦИИ СВЕРДЛОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ (с изменениями на: 06.02.1997), Постановление Правительства Свердловской области от 27 сентября 1995 года №13-П" . docs.cntd.ru .
- ↑ "Сведения о проводящихся выборах и референдумах" . sverdlovsk.vybory.izbirkom.ru . Archived from the original on 22 September 2013 . Retrieved 21 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Voting results for the Federal Electoral District – Election of Deputies of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation of the Seventh Convocation – September 18, 2016" . CEC. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016 . Retrieved 21 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Российские города отстают в развитии" . НИУ ВШЭ . 28 August 2014. Archived from the original on 5 February 2017 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ "Urban world: Mapping the economic power of cities" . McKinsey Global Institute . March 2011. Archived from the original on 2 April 2024 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ "Рейтинг столичных городов России от Фонда "Институт экономики города" | Институт экономики города" . urbaneconomics.ru . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Economics of Russian cities and urban agglomeration , Institute for Urban Economics
- 1 2 Алексей Белоусов, Орнат Валентина. (13 October 2015). "Екатеринбург – глобальный город" . Мегаполис. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ Зубаревич Н.В. (2013). "Крупные города России: лидеры и аутсайдеры" (PDF) . Demoskop Weekly (журнал) (551–552) (Демоскоп Weekly ed.). М.: НИУ ВШЭ: 1–17. ISSN 1726-2887 .
- ↑ "Екатеринбург вошел в топ-10 городов с самым высоким уровнем жизни" . JustMedia . 17 December 2014 . Retrieved 14 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 "Results of social and economic development of the municipal formation "city of Yekaterinburg" in 2015" . 2016. p. 202 – via Ekaterinburg: Department of Economics of the Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg.
- ↑ "Итоги социально-экономического развития Екатеринбурга" . Archived from the original on 2 December 2020 . Retrieved 19 October 2022 .
- ↑ Дарья Воронина. (19 June 2013). "Главными проблемами Екатеринбурга назвали медицину, ЖКХ и дороги" . Российская газета . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ Юлия Позднякова. (22 April 2016). "Расходы бюджета Екатеринбурга за 2015 год составили почти 33 млрд рублей" . Коммерсантъ . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ Полина Путякова. (30 August 2016). "Меряемся бюджетами: Откуда города берут деньги и на что тратят" . zvzda.ru. Archived from the original on 2 September 2016 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- 1 2 3 Kachanova E.A. Strategic Priorities for the formation of finance for municipalities in the context of reforming the budgetary system Archived 15 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine , – Moscow: Russian Academy of National Economy and State Service under the President of the Russian Federation, 2013. – 354 p.
- ↑ Vyacheslav, Kostyuk (12 December 2014). "His alien" . The Ural Worker . Archived from the original on 10 April 2018 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Крупнейшие банки России по капиталу" . Журнал "Коммерсантъ Деньги" . 25 July 2016. p. 60 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Крупнейшие производители ПО" .
- ↑ "О распределении обязанностей по контролю и надзору за соблюдением законодательства Российской Федерации организациями, осуществляющими профессиональную деятельность на рынке ценных бумаг, деятельность центрального депозитария, деятельность по проведению организованных торгов, клиринговую деятельность и деятельность центрального контрагента, репозитарную деятельность, а также деятельность саморегулируемых организаций в сфере финансового рынка, объединяющих профессиональных участников рынка ценных бумаг, и об отмене отдельных распорядительных актов Банка России, Приказ Банка России от 07 августа 2017 года №ОД-2228" . docs.cntd.ru .
- ↑ "Падающие пиксели и огромный шар: как может выглядеть "Екатеринбург-Сити" " . РБК Недвижимость . 13 September 2016 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 76
- ↑ "ТОП-100 крупнейших предприятий Свердловской области Екатеринбург" . Деловой квартал. 11 October 2011 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ "ИТОГИ социально-экономического развития муниципального образования «город Екатеринбург» в 2019 году" . Archived from the original on 29 November 2020 . Retrieved 19 October 2022 .
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , p. 127–128
- 1 2 Development results, 2016 , p. 129
- ↑ "Леруа Мерлен" . Archived from the original on 18 October 2021 . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ↑ "Castorama – строительный гипермаркет: купить товары для дома, дачи и ремонта" . Castorama.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Домострой" . Archived from the original on 30 July 2019 . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ↑ "Максидом - интернет-магазин товаров для дома" . www.maxidom.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ "ОБИ строительный гипермаркет: товары для дачи, сада, дома и ремонта: каталог ОБИ" . Obi.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Строительный Двор – интернет-магазин стройматериалов, купить с доставкой строительные материалы в магазинах сети" . Sdvor.com . Archived from the original on 13 May 2020 . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 130
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 131–132
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 133–135
- ↑ "Топ-20 самых больших торговых центров РФ" . marketmedia.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 11 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Сима-Ленд" . 20 October 2016.
- ↑ Вячеславовна, Логунцова Ирина (2015). "Специфика и перспективы Российской индустрии туризма на современном этапе" . Государственное управление. Электронный вестник (52): 259–278.
- ↑ Геннадьевич, Шеломенцев Андрей; Сергеевна, Головина Анна (2011). "Индустрия туризма региона в контексте принципов саморегулирования региональных социально-экономических систем" . Экономика региона (1): 166–170. ISSN 2072-6414 .
- ↑ Екатеринбург поднялся на третье место в топе российских городов по популярности среди иностранных туристов . URBC.RU – новости экономики (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Число посетивших Екатеринбург туристов выросло в 2015 году на 10%" . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Туристический мастер-класс" . expert.ru . Archived from the original on 13 September 2016 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Маренков Г.В. (2012). "Транспортная инфраструктура Свердловской области – связующее звено между Европой и Азией" (PDF) . Инфраструктура России (Том 1 ed.). М.: Центр стратегического партнёрства. pp. 254–260. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2018 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ Мальцева Ю.; Волкова М.В. (2015). "Изучение возможности постройки современного экологического жилья в Свердловской области" (PDF) (сборник трудов IX заочной международной научно-практической конференции (Екатеринбург, 30–31 мая 2015 г.)) (Система управления экологической безопасностью ed.). Екатеринбург: УрФУ. pp. 138–141.
- ↑ Ведомости (10 March 2015). "Автопарк России увеличился в 2014 году на 1 млн легковых машин" . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Вы точно человек?" . КиберЛенинка . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- 1 2 "ИТОГИ социально-экономического развития муниципального образования в 2015 году" . 2016. Archived from the original on 16 August 2021 . Retrieved 7 July 2022 .
- ↑ Цариков А.А.; Обухова Н.А.; Оглы Мирзоев Н.З. (2015). "Эволюция системы заторов на улично-дорожной сети города Екатеринбурга" (PDF) (журнал) (Эксплуатация автомобильного транспорта ed.). Екатеринбург: Общероссийская общественная организация "Российская академия транспорта". pp. 74–86. ISSN 2311-164X . Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2016 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ Reports, Yekaterinburg News. "Sverdlovsk focusing on two road projects" . Archived from the original on 6 October 2017 . Retrieved 14 June 2017 .
- ↑ Крицкий В.П. (2009). "Дорожное хозяйство Екатеринбурга" (PDF) . Дороги России-2009. Информационно-аналитический каталог (Издание второе, подготовлено к IХ Международной выставке-форуму "Дороги России XXI века" и Дню работников дорожного хозяйства 3000 экз ed.). Екатеринбург: Информационно-издательский холдинг "Реал-Медиа". pp. 204–205, 302. ISBN 978-5-98266-061-9 . Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2018 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Google Maps" . Google Maps . Retrieved 1 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Скандальный бывший МУП Мирошника лидер сферы общественного транспорта Екатеринбурга? По данным мэрии, именно трамваи перевезли больше всего горожан за 2015 год" . Ведомости-Урал. 18 March 2016. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ "БГД" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 20 May 2016 . Retrieved 17 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Города Свердловской области" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 10 July 2009 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Основные технико-эксплуатационные характеристики метрополитенов за 2015 год" (PDF) . asmetro.ru. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2016 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ Дмитрий Ольшванг. (18 March 2016). "Проблемы екатеринбургского метро: убытки, снижение пассажиропотока! Общественник Беззуб: "Если учитывать стоимость строительства станций, то цена билета на метро должна быть 144 рубля"..." Ведомости-Урал. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ "Шины для трамваев, бензин для поездов. Документы: на что транспортные МУПы Екатеринбурга тратят деньги" . uralpolit.ru . Retrieved 13 March 2014 .
- ↑ "Города Свердловской области" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 30 June 2013 . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Строительство трамвайной линии Екатеринбург – Верхняя Пышма начнут в 2016 году" . Портал 66.ru. 22 July 2015 . Retrieved 22 July 2015 .
- ↑ "Официальный портал Екатеринбурга" . Официальный портал Екатеринбурга . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- 1 2 "Города Свердловской области" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 10 July 2009 . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ Автобусный парк Екатеринбурга утепляют к зиме . УралИнформБюро (in Russian) . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Более 5,4 миллионов пассажиров обслужил аэропорт Кольцово в 2017 году (АвиаПорт)" . АвиаПорт.Ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 1 May 2018 .
- ↑ "БГД" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 15 June 2009 . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- 1 2 According to the city directory Dubl.
- ↑ Уральский научно-исследовательский институт фтизиопульмонологии – филиал ФГБУ "НМИЦ ФПИ" Минздрава России . urniif.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Официальный сайт ГБУ СО "Уральский научно-исследовательский институт дерматовенерологии и иммунопатологии" " . urniidvi.ru . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ Екатеринбургский центр МНТК "Микрохирургия глаза" . eyeclinic.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ Открытие второго центра МРТ-диагностики в городе Екатеринбурге! . ekaterinburg.ldc.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- 1 2 М.м, Рогалёва (2014). "Екатеринбург как современный мегаполис" . Человек в мире культуры (4): 14–17. ISSN 2227-9857 .
- ↑ Report of the head of the Yekaterinburg administration, 2016 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine , p. 14.
- ↑ Report of the head of the Yekaterinburg administration, 2016 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine , p. 13, 15.
- ↑ Лучшие школы России-2015 . РИА Новости (in Russian). 12 October 2015 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Общие сведения об университете – ФГБОУ ВО "Уральский государственный горный университет" " . about.ursmu.ru . Archived from the original on 7 July 2016 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ The second business rating of higher education Archived 29 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine – Federal Portal Russian Education, 22 May 2018
- ↑ Formation of the state elite 2008 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine – Federal Portal Russian Education, 22 May 2018
- ↑ "Российская академия наук намерена готовить кадры самостоятельно | Новости образования | Обучение Екатеринбург" . uchim66.ru . Archived from the original on 4 March 2016 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "УрФУ перестраивается в школы" . Коммерсантъ (Екатеринбург) . 22 April 2016 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "По количеству бюджетных мест мы уже обошли МГУ" . 7 April 2021.
- ↑ "Ural Federal University – UrFU" .
- ↑ Case study: Ural Federal University as a basic university of industry in the region Archived 1 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine . – Ekaterinburg: Ural Federal University, 2016. – p. 2, 9–10.
- ↑ "Гильдия издателей периодической печати" . 18 September 2011. Archived from the original on 18 September 2011 . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Welcome media-atlas.ru - BlueHost.com" . www.media-atlas.ru . Archived from the original on 15 June 2018 . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ Официальный сайт "Вести Урал" – Официальный сайт "Вести Урал" . Официальный сайт "Вести Урал" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 16 July 2012 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ Вальханская, Наталья (24 March 2018). Взрыв и обрушение: снос телебашни в Екатеринбурге на видео очевидцев . Телеканал "Звезда" (in Russian) . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Тёмная башня" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Uralnets" . uralnets.ru . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ Fletcher, Martin. "Yekaterinburg signs cooperative agreement with Vimpelcom under Beeline brand" Archived 22 July 2013 at archive.today , Yekateringburg News , 19 July 2013. (Retrieved 22 July 2013).
- ↑ "WiseCms – troubles..." culture.ekburg.ru . Archived from the original on 11 July 2012 . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ "WiseCms – troubles..." Culture.ekburg.ru . Archived from the original on 19 January 2011 . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Триумф России на Всемирной выставке в Париже 1900 года – Новости РуАН" . новости-россии.ru-an.info . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ Lykova TR Cultural and historical centres of the Sverdlovsk region Archived 11 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine // method. instructions for studying the course "Cultural and Historical Centres of the Urals" for full-time or part-time students, direction 100400 – Tourism. – Ekaterinburg: UGLTU, 2014. – P. 15-16 .
- ↑ "Главная страница - АПИ-Урал" . www.apiural.ru . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Архитектура и планировка социалистического Свердловска. Часть 2" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ Вейн, Инна (10 November 2020). "Уральские актеры и режиссеры привезли домой сразу четыре "Золотые маски" " . Ekb.dk.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ Fletcher, Martin. "Yekaterinburg to showcase city’s cultural achievements during Year of Culture" Archived 13 February 2014 at archive.today . Yekaterinburg News . 13 February 2014. (Retrieved 13 Feb 2014).
- ↑ Pozdnyakova, Julia (27 May 2016). "Sverdlovsk Oblast was in the picture" . Kommersant . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Интервью - АПИ-Урал" . www.apiural.ru . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Премией "Шаривари" отметили лучших деятелей циркового искусства – В МИРЕ ЦИРКА И ЭСТРАДЫ" . ruscircus.ru . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Ельцин Центр признали «лучшим европейским музеем 2017 года»" . The Village (in Russian) . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ Самые популярные достопримечательности Екатеринбурга соединит красная линия на тротуаре . Interfax-Russia.ru (in Russian). 17 June 2011 . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- 1 2 Yekaterinburg Encyclopedia (PDF) . Yekaterinburg: "Akademkniga". 2002. p. 30. ISBN 5-93472-068-6 – via PDF.
- ↑ Yekaterinburg Encyclopedia (PDF) . Yekaterinburg: "Akademkniga". 2002. pp. 30–31. ISBN 5-93472-068-6 – via PDF.
- ↑ Yekaterinburg Encyclopedia (PDF) . Yekaterinburg: "Akademkniga". 2002. p. 31. ISBN 5-93472-068-6 – via PDF.
- 1 2 3 Shvets, A. V. (2016). "Domestic architecture of the late XX – early XXI century" (PDF) . New Ideas of the New Century: Scientific. Compilation . 2 . Khabarovsk: Pacific State University: 355–362. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2016 . Retrieved 8 June 2018 – via PDF.
- ↑ GmbH, Emporis. "Yekaterinburg | Buildings | EMPORIS" . Emporis . Archived from the original on 8 April 2015 . Retrieved 8 June 2018 . {{ cite web }} : CS1 maint: unfit URL ( link )
- ↑ "Официальный портал Екатеринбурга" . Официальный портал Екатеринбурга . Archived from the original on 8 August 2010 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "The announcement ceremony of the host cities of the 2018 World Cup united the whole of Russia" . ru.fifa.com . Archived from the original on 3 September 2014 . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ "База данных показателей муниципальных образований" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 14 August 2009 . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ sport, Guardian (4 October 2017). "Outer space: the Russia World Cup stadium with a novel seating extension" . the Guardian . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Construction: Tsentralnyj Stadion Yekaterinburg – StadiumDB.com" . stadiumdb.com . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ FIFA.com. "2018 FIFA World Cup Russia - News - FIFA Fan Fest venues announced for 2018 FIFA World Cup Russia" . fifa.com . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ Azmukhanov, Alexander (3 May 2018). "The three most expensive projects of the region for the World Cup" . Oblastnaya Gazeta . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Official website of the U.S. Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Archived from the original on 8 April 2012 . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Official website of the British Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Archived from the original on 3 January 2012 . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Official website of the German Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Official website of the French Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Archived from the original on 29 April 2012 . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Chinese Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Retrieved 7 September 2013 .
- ↑ "First summit for emerging giants" . BBC News . 16 June 2009 . Retrieved 16 June 2009 .
- ↑ Hamilton, Louis (18 June 2013). "Yekaterinburg presents city's bid for 2020 World Expo" . Yekaterinburg News. Archived from the original on 27 November 2013 . Retrieved 20 June 2013 .
- ↑ "Глобальный саммит по производству и индустриализации (GMIS – 2019)" . Росконгресс . Retrieved 12 December 2021 .
- ↑ КИРЯГИН, Кирилл (22 July 2015). "ИННОПРОМ – в пятёрке крупнейших промышленных выставок мира" . ural.aif.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 12 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Побратимы и тезки Екатеринбурга" . ekb-room.ru (in Russian). The Ekb Room. 20 October 2014. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018 . Retrieved 22 December 2020 .
- ↑ "Museum Vladimir Mulyavin in Belarusian State Philharmonic" . Retrieved 22 April 2022 .
- Екатеринбургская городская Дума. Решение №8/1 от 30 июня 2005 г. «О принятии Устава муниципального образования "Город Екатеринбург"», в ред. Решения №1/27 от 27 января 2015 г. «О внесении изменений в Устав муниципального образования "Город Екатеринбург"». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Вестник Екатеринбургской городской Думы", №95, 15 июля 2005 г. (Yekaterinburg City Duma. Decision # 8/1 of June 30, 2005 On the Adoption of the Charter of the Municipal Formation of the "City of Yekaterinburg" , as amended by the Decision # 1/27 of January 27, 2015 On Amending the Charter of the Municipal Formation of the "City of Yekaterinburg" . Effective as of the day of the official publication.).
- Областная Дума Законодательного Собрания Свердловской области. Областной закон №30-ОЗ от 20 мая 1997 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Свердловской области», в ред. Закона №32-ОЗ от 25 апреля 2012 г. «О внесении изменений в Областной закон "Об административно-территориальном устройстве Свердловской области"». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования за исключением отдельных положений, вступающих в силу в иные сроки. Опубликован: "Областная газета", №81, 3 июня 1997 г. (Oblast Duma of the Legislative Assembly of Sverdlovsk Oblast. Oblast Law # 30-OZ of May 20, 1997 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Sverdlovsk Oblast , as amended by the Law # 32-OZ of April 25, 2012 On Amending the Oblast Law "On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Sverdlovsk Oblast" . Effective as of the day of the official publication with the exception of several clauses which take effect on a different date.).
- Областная Дума Законодательного Собрания Свердловской области. Закон №85-ОЗ от 12 июля 2007 г. «О границах муниципальных образований, расположенных на территории Свердловской области», в ред. Закона №107-ОЗ от 29 октября 2013 г. «Об упразднении отдельных населённых пунктов, расположенных на территории города Ивделя, и о внесении изменений в Приложение 39 к Закону Свердловской области "О границах муниципальных образований, расположенных на территории Свердловской области"». Вступил в силу через 10 дней после официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Областная газета", №232–249, 17 июля 2007 г. (Oblast Duma of the Legislative Assembly of Sverdlovsk Oblast. Law # 85-OZ of July 12, 2007 On the Borders of the Municipal Formations on the Territory of Sverdlovsk Oblast , as amended by the Law # 107-OZ of October 29, 2013 On Abolishing Several Inhabited Localities on the Territory of the Town of Ivdul and on Amending the Law of Sverdlovsk Oblast "On the Borders of the Municipal Formations on the Territory of Sverdlovsk Oblast" . Effective as of the day which is 10 days after the official publication.).
- Official website of Yekaterinburg (in Russian)
| : • | |
| Administrative districts | |
| Cities and towns | |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Whether it's a luxury superyacht or a more modest vessel, yacht designs tend to be all about the exterior, while the interior can feel like something of an afterthought. However, UK-based studio ...
ISA Yachts are leading the way in the drastic re-conception of modern superyachts. Where ISA Yachts feel that outdoor space has been neglected in recent years for the benefit of improved indoor spaces, the Italian yacht builders have designed superyachts Route 66 and Yara 44 to curb the trend. Indeed their vision was shared by many at the 2014 ...
Cetera 60. The Cetera 60 is a fresh take on a liveaboard cruising yacht with an innovative 'multispace' layout that prioritises space and comfort over performance. A joint venture between Guida Design & Engineering and the Fiart shipyard, it is claimed to have 30m² more living space than a conventional 60ft flybridge.
The Code X Yacht. The Code X Yacht. This one is real as well and it has an in-built solar panel which can provide for energy to power the motor to up to 9 knots. Sleek, smart and sexy, it has something of a Bond charm to it. Her full capabilities will impress any Bond girl 1420 horse power that provide up to 80 knots.
Suite au succès rencontré lors du Cannes Yachting Festival 2023, Abys Yachting vous dévoile les toutes dernières photos de ce yacht futuriste, sous toutes les coutures. Un bateau explorer et familial, qui fascine, tant par son pont avant entièrement couvert, que par son design des plus futuristes...
The 75 feet long yacht has a total living space of 4,350 sqft! It is truly floating architecture and modern interior goals at its finest. Arkup is a game-changer for the hospitality market when it comes to self-sustainable, blue developments. floating and overwater eco-resorts a reality with the versatility to scale, configure, even relocate ...
To that end, here are 10 futuristic yacht concepts to ponder. Happy dreaming. 1. Jazz Yacht. Designed by:Zaha Hadid. From the mind of one of the world's most renowned and well-known architects ...
New lighter battery banks and intelligent monitoring systems, such as those on the Sea Ray SLX-R 400e "Smart Boat" crossover yacht, are becoming increasingly more prevalent, perhaps even expected on the top-of-the-line 2021 and 2022 models from major builders. See boats.com's walkthrough video of the SLX-R 400e below for a deeper look ...
Pure. Unveiled by Feadship at the 2021 Monaco Yacht Show, the 81.75 metre superyacht concept Pure was designed following "massive client feedback" to the Dutch yard. The result is a yacht boasting a "sculptural exterior profile and open plan interior". The yacht also emphasises that the project could be "built tomorrow with adventurous clients".
the yacht with a futuristic nature For Dutch design studio Vripack , inspiration is all around; from a three-jointed bird's wing to the powerful thrust of a shark's tail. When the studio set about designing its latest concept, the 66m fossil-free Futura, the focus was to capture wildlife's innate ability to freely propel through air and ...
Le WallyWhy150 présente une évolution majeure. Ce yacht de luxe futuriste développe des idées pionnières dans la gamme, tout en embellissant les caractéristiques principales qui font la renommée de la marque. Avec un volume total de 150GT, il offre l'expérience unique d'être comme sur un yacht plus grand.
Futureyachts. With new technologies and cutting-edge materials, the yachting industry is evolving rapidly to meet the needs of modern yacht owners, but what does the future hold for superyacht design? Discover the latest trends and read our in-depth interviews with yachting's key influencers and disruptors.
Le Yacht Solaire Autonome : Ce concept mise sur l'énergie solaire pour une navigation plus écologique, tout en offrant des espaces de vie luxueux et modernes. ... Les yachts conceptuels et futuristes représentent l'essence même de l'innovation dans l'industrie nautique. En combinant design avant-gardiste, technologies de pointe et un ...
Azimut says the Seadeck 6 and its larger cousin, the 71-foot Seadeck 7, achieve an operational carbon output 60 percent that of comparable vessels. Alessandro Grassani for The New York Times ...
GRIS GRIS is a 2018 Bertram 35 C7.1 500HP for sale in Fort Lauderdale Florida. GRIS GRIS is a contemporary interpretation of a timeless Bertram design. ... • Molded, yacht-finish, sand-texture non-skid gelcoat on deck surfaces • Teak Sole • Deck and FRP components molded vinylester blend construction • Hatches and doors with FRP liners
Over the next decade, Ballin sees serial hybrid power as the optimum solution for yachts, systems that involve a large battery bank with a mix of solar and hydro power generation. This reduces the ...
Motor yacht for sale GRIS GRIS (11M/35') is a contemporary interpretation of a timeless Bertram design. With a wider and longer hull, this Bertram 35 pays homage to the iconic Bertram 31 by maintaining the brand's unwavering commitment to quality. Drawing inspiration from tradition and propelled by a commitment to excellence, Bertram Yachts ...
2019 Sunseeker motor yacht, 131′ (40.2 m), (US$22,650,789). View the listing. One of the largest UK yacht builders, Sunseeker mainly manufactures its vessels in Poole, Dorset. Four superyacht models (ranging from 116-161 ft.) secure Sunseeker's place in the niche of large and extravagant vessels.
Buy a Neel 47 - sailing trimaran? Navigation equipment: Radar Antenna, Interface (marinisé avec ecran), Sonar (TRITON). Staging and technical...
Yekaterinburg [a] is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia.The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia, with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, [14] up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in the Ural ...
SVERDLOVSK OBLAST. Sverdlovsk Oblast is the largest region in the Urals; it lies in the foothills of mountains and contains a monument indicating the border between Europe and Asia.
14. Visit the Old Water Tower. Source: Photo by Wikimedia Commons user Dom kobb used under CC BY-SA 3.0. The old water tower is one of Yekaterinburg's oldest structures dating back to the 1800s and stands as a monument of industrial architecture. It is one of the city's endearing symbols.
Yekaterinburg [lower-alpha 1] is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia.The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia, with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, [14] up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in ...